Jobs
Biology Questions and Answers Form 1
Published
7 years agoon
[ad_1]
Click Here – Free KCSE Past Papers » KNEC Past Exams » Free Downloads » KCSE Papers & Marking Schemes
Biology Questions and Answers Form 1
KCSE Revision Questions and Answers
K.C.S.E Online Revision
Biology Notes Form 1 – Biology Form 1 Notes – Form 1 Biology Notes
Introduction to Biology
Biology is a branch of science that deals with the study of living things. There are diverse forms of life
on earth ranging from the invisible microscopic living things to the gigantic life forms. It aims at
explaining the living world in terms of scientific principles.
It is important to note, however, that living
things interact with the non living things in the environment as Well. Biology, therefore also entails the
study of non living things as well.
The role of human beings in shaping the environment is also
investigated in biology.
In summary, biology deals with the study of origins, types, nature,
growth, development, interactions and maintenance of all life forms on earth.
Branches of Biology
Biology is such a broad field of knowledge. It is divided into two broad branches
1. Zoology– This is a branch of biology that deals with the study of animal life.
2. Botany– This is a branch of biology that deals with the study of plant life.
Within the two branches, there exist even smaller branches because the branches (botany and
Zoology) are very wide and complex.
The smaller branches of biology include:
a) Ecology– This is the study of the interrelationships between organisms and their
environment. Ecology aims at establishing how organisms are related to each other
and their environment.
Ecology is further subdivided into smaller branches. These
can be forest ecology, marine ecology, rangeland ecology etc.
b) Genetics– This sub-branch of biology deals with the study of inheritance and variation.
It deals with the study of how variations (differences) occur between parents and their
offspring. It is also concerned with how various characteristics are passed on from
parents to offspring.
c) Entomology– This is the study of insects.
d) Parasitology– This is the study of parasites.
e) Physiology– This deals with the study of the functions of various structures of an
organism. It deals with the processes that take place in the body of organisms.
f) Anatomy– The study of the internal structure of organisms
g) Microbiology– This is the study of microorganisms
h) Bacteriology– The study of bacteria
i) Ornithology– This is the study of birds
j) Itchthology-This is the study of fishes
This list is in-exhaustive as there are very many other branches of biology.
Importance of biology
benefit an individual in myriad ways. The study of biology is important in that:
environmental problems such as food shortage, poor health services, pollution and
environmental degradation.
veterinary medicine, animal husbandry, horticulture and dentistry.
life. These include skills of observing, identifying, recording, classifying, measuring,
analyzing and evaluating. These skills can enable one learn how to make right choices
and lead an improved life.
and how best these diseases can be prevented and cured.
international cooperation. Some biology related international conventions include:
> Joint development of HIV/AIDS vaccine by Kenyan and British scientists.
> The coordinated fight against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome involving scientist
all over the world.
> The fight to save the ozone layer from depletion through various international
agreements such as the Kyoto protocol.
> Management of resources through international treaties such as the CITES
(Convention against International Trade on Endangered Species).
Characteristics Of Living Things
Living things share a lot of characteristics in common. These characteristics are discussed below.
a) Nutrition
Nutrition is the process by which living things obtain and assimilate (utilize) nutrients.
Living things require nutrients for various purposes; growth, repair of worn out tissues and for
provision of energy. Plants manufacture their own food using light energy, carbon (IV) oxide,
water and mineral salts through the process of photosynthesis. Conversely, animals feed on
already manufactured foods from plants and other animals.
b) Respiration
Respiration is the process by which food substances are chemically broken down to release
energy. During respiration, oxygen is used while energy, carbon (IV) oxide and water are
released. Respiration occurs in all living cells.
The energy produced in living things is very
useful as it enables the living things carry out some of their physiological processes.
The energy
is also required for growth and development, movement and repair of worn out tissues.
c) Gaseous Exchange
Gaseous exchange refers to the process by which living things exchange oxygen and carbon
(IV) oxide across the respiratory surfaces. Animals always take in air rich in oxygen and give
out air rich in carbon (IV) oxide.
Carbon (IV) oxide is a waste product of chemical reactions in
the body. Animals require oxygen for respiration. Gaseous exchange, therefore, enables animals
obtain oxygen for respiration and get rid of carbon (IV) oxide, a waste product.
Plants, however, require carbon (IV) oxide for photosynthesis during the day. They give away
oxygen as a by-product. The plants equally require oxygen for respiration and give away carbon
(IV) oxide.
d) Excretion
This is the process by which living things separate and eliminate the waste or harmful
materials resulting from chemical reactions Within the cells. These harmful waste products of
metabolism maybe toxic to the body if they are left to accumulate in the cells of the living things
e) Growth and Development
Growth refers to an irreversible increase in size and mass while development refers to the
irreversible change in complexity of the structure of living things. Growth and development
of living things is essential as it enables the living things to attain maximum size that can enable
them to perform their functions and roles.
f) Reproduction
This is the process by which living things give rise to new individuals of the same kind. All
living things reproduce. Reproduction is essential as it leads to perpetuation of species and it
avoids extinction of certain animals and plants.
g) Irritability
This is the ability of living things to perceive (detect) changes in their environment and
respond to them appropriately. Living things respond to changes in temperature, humidity,
light, presence or absence of certain chemicals.
Response of organisms to these changes is
crucial as it enables them to escape from harmful stimuli. Ability to detect changes in the
environment also enables organisms to obtain resources in their environment.
h) Movement
Movement refers to change is position (displacement) of a part or parts of an organism.
Movement in plants includes folding of leaves, closing of flowers and growing of shoots towards
light. The change of position of an entire organism from one position to another is locomotion.
Study questions
a) Motor vehicles move, use energy and produce carbon dioxide and water. Similar
characteristics occur in living organisms yet motor vehicles are not classified as living.
List the other characteristics of living things that do NOT occur in motor vehicles.
b) Give the name to the study of:
Collection of Specimen
We have defined biology as the study of living things. For effective study, a biologist
may have to collect some living things or some parts of living things for observation and
analysis. The living things or parts of living things that are used for biological study are called
specimens.
Biological studies always take place in laboratories. A laboratory is a building or a
room that is designed and equipped for scientific studies.
Collections of living things especially animals may not be very easy. Some of the animals
are not easy to catch while some are quite dangerous. Knowledge on proper specimen collection and handling of is very important. We will discuss some of the apparatus used in specimen
collection.
a) Sweep net– This is used for catching flying insects.

b) Fish net– This is used for trapping small fish and other small Water animals.

c) Pooter– This is used for sucking small animals from rock surfaces or barks of trees.
d) Bait trap– This is used for attracting and trapping small animals including rats.
e) Pit fall trap– This is used for catching crawling animals.
f) Pair of forceps– This is an apparatus used for picking up small crawling animals e.g.
stinging insects.
g) Specimen bottles– These are bottles used for keeping collected specimen. They are of
different sizes depending on the size of the specimen being studied.
h) Magnifying lens– This is used to enlarge small objects. A hand lens is a common
magnifying lens used in the laboratory. The magnifying power of the hand lenses is
always indicated on the lens e. g. X10, X5, X8. The magnifying power of a lens shows
how many times the image will be enlarged compared to the object.

How to use a magnifying lens
To use a magnifying lens, place the object to be enlarged on the bench. Hold the magnifying lens
on one hand and while closing one eye, move the lens towards the object until the image comes
into clear focus.
If a magnifying lens is used to make a drawing of a specimen, the magnification of the drawing
will have no relation with the size of the drawing.
The magnification of the drawing can be calculated using the formula shown below.
Drawing magnification: Length of drawing divided by Length of the actual object
The sign of “times” must come before the magnification value e. g. X10, X5, X15 etc.
Precautions During Collection and Observation of Specimen
While collecting specimen for observation, a biologist should play close attention to the
following:
stinging plants or insects. Forceps and hand gloves should be used in such cases.
Comparison Between Plants and Animals
Plants
Animals
Chapter Two: Classification 1
Introduction
living things share similar characteristics discussed in the introductory chapter, the living
things exhibit a lot of differences.
In particular, animals and plants are all living things
yet they differ in many aspects. Amongst animals and plants also there exist a lot of
differences.
There are millions of different plant and animal types exhibiting a range of
differences. This created a need for a classification system of living things to make study
of the living organisms easier.
referred to as a taxon (plural: taxa).
evolutionary relationships (phylogeny) of the organisms. It is believed that all organisms
once had a common ancestor (theory of evolution). During classification, organisms that
are believed to have evolved along the same line of evolution are placed in one taxon.
taxonomy is a taxonomist.
observable features of organisms.
External features of plants used in classification
External features of animals used in classification
Importance of Classification
arranges the information on organisms in an orderly manner.
separate those with different features.
organisms
etc.
biology depend on classification of pests, disease vectors, pathogens and components of
an ecosystem.
Historical background of Classification
heavily relied on very few observable features. There was no standard classification
system as each and every scientist would classify organisms in a way that would suit his
intentions.
were also classified as herbs, trees, shrubs. Animals were also grouped into herbivores,
carnivores and omnivores.
a) Edible or non edible
b) Flowering or non-flowering
between living organisms. It has overcome the many weaknesses of the artificial
(traditional) classification systems.
changes that enabled them to live in different habitats. The structural changes account for
the great diversity of living organisms observed today.
contribution to the development of the modern classification system.
Taxonomic Units of Classification
placed as a matter of convenience.
are common in that group.
classification scheme.
first largest and highest group, the kingdom to the smallest and lowest unit, the species.
1. Kingdom
2. Phylum (animals)/division (plants)
3. Class
4. Order
5. Family
6. Genus
7. Species
All living organisms are classified into five major kingdoms:
a) Kingdom Monera– This is composed of microscopic unicellular organisms
mainly bacteria e.g amoeba.
b) Kingdom Protoctista– This kingdom is comprised of members who are
microscopic. Though, some are large enough to be seen with the naked eyes.
Members of this kingdom include algae and protozoa.
c) Kingdom Fungi– Members of this kingdom comprises the mushrooms, toadstools,
moulds and yeast.
d) Kingdom Plantae– This kingdom comprises the moss plant, ferns, maize plants,
hibiscus, meru oak tree etc.
e) Kingdom Animalia — Members of this kingdom include the tapeworms, hydra,
fishes, human beings, lizards, earthworms etc.
In hierarchy of classification, a kingdom is further divided into several phyla (plural of
phylum) or divisions (in plants). Within the phyla or divisions, organisms are further sorted out
into groups known as classes based on their similarities and mode of life.
Each class is further
subdivided into small groups called orders based on structural similarities. Orders subdivide into
families which subdivide into genera (plural for genus).
Genera are then subdivided into smaller
units of classification called the species.
Species is the smallest unit of classification whose members share many similarities and
can freely interbreed to give rise to fertile or viable offspring.
Members of a particular species can, however, exhibit various differences e. g. differences in skin
colour or body forms. Within the species, organisms can further be classified based on the
differences in colour or forms.
In humans, this gives the races, in animals the term used is breed
while in plants, variety is preferred. In bacteria, the term strain is used to describe the variant
forms.
Members of different but very closely related species can breed but the resulting
offspring will be sterile (infertile). In particular, a mule is a sterile offspring between a horse and
a donkey.
Moving from kingdom to species, it is important to note that the number of organisms
in each taxon decreases. The similarities, however, increase as one moves from kingdom to
species.
Scientific Naming of Living Organisms
naming system was developed by Carolus Linnaeus in the 18th century.
names by which the organisms are known in the vernacular languages. In particular, a cat
is an English name, mbura is a luo name, paka is a Swahili name etc. these names differ
across cultures and cannot be used by scientists to communicate across the world. This
makes sharing scientific knowledge on organisms very difficult. There was need for a
common language and this led to development of scientific language in latin.
widely spoken at that time. Similarly, latin language is a dead language hence not
subjected to a lot of changes. The scientific names are, therefore, static.
name adopts two names. This implies that the specific scientific name of an organism has
two names. This double naming system is known as binomial nomenclature.
which are internationally recognized and referred to as binomial nomenclature which
literally means the rule of double naming system.
Rules of Binomial Nomenclature
Binomial nomenclature requires that:
a) The first part of the scientific name is that of the genus name which should begin with a
capital letter. The second name is that of species. The species name should be written in
small letters e. g.
a) Maize- Zea mays
b) Lion- Panthera leo
c) Leopard- Panthera pardus
d) Domestic dog- Canisfamiliaris
e) Human being- Homo sapiens
b) When printed in books and other printed works, the scientific names should be printed in
italics. However, in handwritten manuscripts and typed works, the genus and species
names should be lined separately.
Printed work- Homo sapiens
c) The specific name is frequently written with the name of the scientist who first
adequately described and named the organism e. g. Balanus balanoides Linneaus.
d) Scientists must give a latinised name for a newly described animal or plant species where
a Latin name is missing e,g.
Aloe kilzfiensis– A type of aloe found in kilifi
Meladogyne kikuyuensis– A nematode found in kikuyu.
Origin of scientific names
Scientific names assigned to organisms can be:
Chapter Three: The Cell
Introduction
cells make up the structures of the living organisms and are responsible for carrying out
various biological processes in the bodies of the living organisms.
kingdom monera. These organisms are known as unicellular organisms.
and animals are multicellular.
instrument is required. The microscope is used to view the cells.
lenses for greater magnification.
lenses which provided a greater magnification. He used the microscope to view nuclei
and unicellular organisms including bacteria.
studies. Through this microscope, it was possible to study very finer details of structures.
The Light Microscope
on very fine details of the internal structures of cells.
is imperative to understand the parts and functions of various parts of a microscope.
magnification of the specimen.
by:
power is X8, then the total magnification of the specimen would be:
Magnification=Eyepiece magnification X Objective lens magnification
= 10 X 8
=X80.
Figure 1. The light microscope

Handling and Care of the Microscope
Part of the microscope: Limb
function: supports the body tube and stage
Base:
function: provides firm and steady support to the microscope
Body tube:
function: holds the eyepiece and the revolving nose piece
Coarse adjustment knob:
function: raises or lowers the body tube through longer distances to bring the image into sharper focus
Fine adjustment knob:
function: raises or lowers the body tube through smaller distances to bring the image into sharper focus. it is mostly used with the high power objective lens
Diaphragm:
function: an aperture that regulates the amount of light passing through the condenser to illuminate the specimen
Eye-piece:
function: contains a lens which contributes to the magnification of the specimen under review
Objective lens:
function: bring image into focus and magnifies it.
Mirror:
function: reflects light through the condenser to the object on the stage
Revolving nose piece:
function: holds the objective lenses in place and enables the change from one objective lens to the other
Condenser:
function: concentrates light on the object on stage
Stage:
function: flat platform where specimen on the slide is placed.it has two clips to hold the slide into position
The following rules should be observed when handling the microscope:
> Always use both hands when carrying the microscope. One hand should hold the base to
provide support while the other hand holds the limb.
> Never place the microscope too close to the edge of the working bench or table.
> Do not touch the mirror or the lenses with your fingers.
> Dirty lenses should be cleaned using a special soft lens tissue paper or tissue paper
moistened with ethanol. The other parts of the microscope may be cleaned using a
microscope.
> Do not wet any part of the microscope.
> Make sure the low power objective lens clicks into position in line with the eye piece
before and after use.
> After use, always clean and store the microscope in a safe place, free from moisture and
dust.
How to use the Microscope
ensure that maximum light can pass through. The circular area seen is referred to as the
field of view.
sufficient light is passing through the specimen.
comes into focus.
what you observe.
the focus using the coarse adjustment knob. For sharper images, use the fine adjustment
knob.
the fine adjustment knob to bring the details into sharper focus.
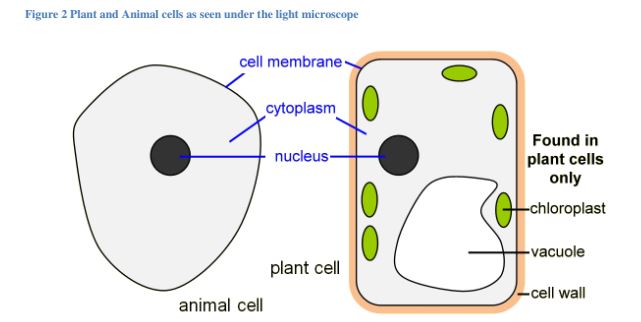
Cell Structures as seen under the Light Microscope
that can be observed under the light microscope include the cell wall, cell membrane,
cytoplasm, nucleus, vacuole and chloroplasts.
Figure 2 Plant and animal cells as seen under the light microscope
The cell as seen under the Electron Microscope
electrons to illuminate the specimen instead of light as in the case of light microscope.
between separate things which are close to each other.
in microbiology.
Figure 4. The plant cell
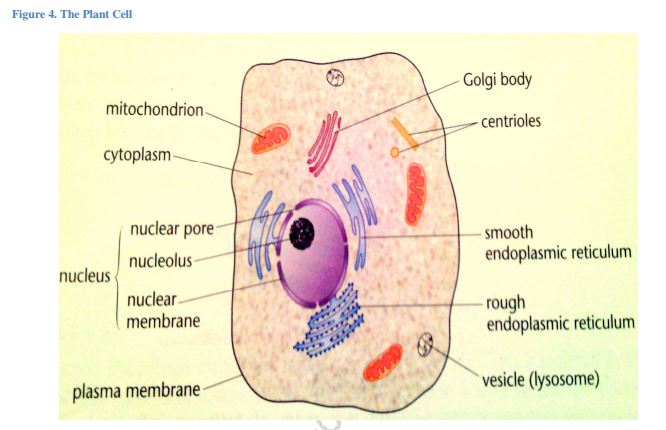
Structure and Functions of the Cell Organelles
Cell membrane
The three layers are composed of one layer of phospholipid sandwiched between two protein layers.
Cytoplasm
dissolved substances.
c) Mitochondrion
reactions that yield energy for the cell. Mitochondria is thus, referred to as the
powerhouse of the cell.
increase surface area for respiration.
requirements. Cells that require large amounts of energy contain high amount of
mitochondria.
> Mitochondria are self replicative that is they can divide to form new ones.
Figure 5. The Mitochondrion (Animal)
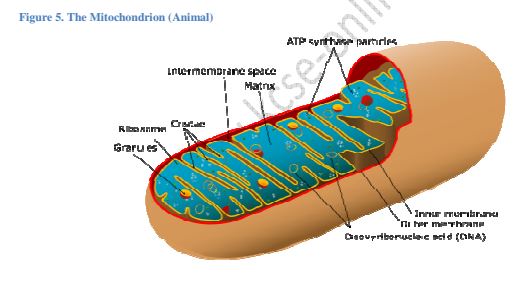
Figure 6, (generalize(lmage23 mitochondrion Structure)
throughout the cytoplasm.
referred to as rough or granular endoplasmic reticula. Endoplasmic reticula that are
not associated with ribosomes are called smooth endoplasmic reticula.
as enzymes. They also contribute to mechanical support.
e) Ribosomes
ribosomes are scattered within the cytoplasm (free ribosomes). Their largest dimension is
25 nanometres.
f) Lysosomes
enzvmes which break down large molecules. destroy Worn out oraanelles or even the
entire cells.
that might have been ingested in food. This explains their high relative abundance in
injured or infected cells.
out, they may destroy the whole cell.
g)Golgi bodies/Golgi apparatus
membrane.
1) They package and transport glycoproteins.
2) They are involved in secretion of synthesized proteins and carbohydrates.
3) They manufacture lysosomes.
Note: Golgi bodies are abundant in cells that are active in secretion. For instance pancreatic cells
which secrete enzymes and the nerve cells which secrete neurotransmitter substances.
h)Centrioles
organisms.
i) Chloroplasts
like stroma through which runs a system of membranes that are stacked together to form
grana.
photosynthesis.
j) Vacuoles
contain one large centrally placed vacuole.
the cell. This influences how materials move in and out of the cell.
the contractile vacuole excretes unwanted materials from the cell.
k) Cell wall
1. It gives plant cells their definite shape
2. It provides mechanical support and protection against mechanical injury.
3. The cell wall allows gases, water and other substances to pass through it.
i) Nucleus
nucleoplasm in which nucleolus and chromatin materials are suspended. The nuclear
membrane has minute pores, nuclear pores which allow materials to move in and out of
the nucleus.
hereditary materials.
Comparison between Plant Cells and Animal Cells
While there exist many similarities between plant and animal cells, there are a number of
differences.
Plant cells
Animal cells
Estimation of Cell Size
The light microscope can be used to estimate the size of a cell. Most cells have diameters
smaller than a millimeter. Due to this, cell sizes are always measures in smaller units.
These are micrometres and nanometers. These units of measurements are related as
shown below.
1 millimeter (mm) = 1000 micrometres (pm).
1 micrometer (pm) = 1000 nanometres (nm).
Procedure in cell size estimation
of cells.
microscope.
the first mark and the last one across the field of view. Count only the spaces between
two thick dark lines.
cell diameter = diameter of the field of view in micrometers divided by number of cells.
Cell Specialization. Tissues. Organs and Organ Systems
Cell Specialization/Cell Differentiation
specific functions
has a tail-like extension for swimming towards the ovum.
Tissues
same function.
a) Tissue types in animals
1. Epithelial tissue– This is a thin continuous layer of cells for lining and protection of
internal and external surfaces.
2. Skeletal muscle– This is a bundle or sheets of elongated cells with fibres that can
contract. Its contraction and relaxation brings about movement.
4. Blood tissue– This is a fluid containing red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets.
The main functions of blood tissue are transportation of nutrients and gases as well as
protection of the body against infections.
5. Connective tissue– This tissue consists of strong fibres that connects other tissues and
organs thereby holding them in position.
b)Tissue types in plants
1. Epidermal tissue– This is a single thin layer of cells covering the outer surfaces. It
protects inner tissues of plants from mechanical damage and infection.
2. Palisade tissue– This is a group of cells rich in chloroplasts containing chlorophyll. It has
a site for the absorption of light energy and manufacture of food by photosynthesis.
3. Parenchyma tissue– This tissue consists of special thin walled irregularly shaped cells.
They form packaging and storage cells.
4.Conducting tissue/Vascular bundle– This tissue consists of xylem and phloem. Xylem
conducts water and dissolved mineral salts in a plant while phloem conducts food
substances in solution.
Organs
function.
a) Heart– composed of connective, muscle, epithelial and blood tissues.
b) Kidney– Composed of connective, epithelial and muscle tissues
c) Brain– Composed of epithelial, connective tissues
d) Lungs– Composed of epithelial, connective tissues.
a) Roots– composed of epidermal, conducting and parenchyma tissues.
b) Flowers– This is composed of epidermal, conducting tissues.
c) Stem– Composed of conducting, parenchyma, and epidermal tissues and palisade
tissues in some cases
d) Leaves– Composed of palisade, conducting and epidermal tissues.
Organ system
This is a group of organs Whose functions are coordinated and synchronized to perform
the same function.
Organ systems are more pronounced in animals than in plants
Organ systems in animals include
a) Digestive system composed of organs such as oesophagus, stomach, intestines and
their associated glands.
b) Circulatory system composed of the heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries).
c) Excretory this is composed of kidney, liver, and blood vessels.
d) Respiratory system composed of trachea, bronchus, and lungs.
e) Reproductive system composed of the reproductive organs and associated glands.
f) Nervous systems composed of the brain, spinal cord, eye, ear organs.
Chapter Four: Cell Physiology
Introduction
activities of life or of living matter such as organs, tissues or cells. It aims at
understanding the mechanism of living.
the body cells of organisms.
perform various functions of life. In particular:
a) Chloroplasts play a vital role in carbohydrate synthesis.
b) Mitochondrion produces energy required to carry out life processes.
c) Ribosomes manufacture of proteins.
into the chloroplasts.
oxygen have to be taken into the mitochondrion. Energy, carbon (IV) oxide, water and
alcohol (in plants) are some of the end products of respiration.
harmful when allowed to accumulate in the cells. They, thus, have to be eliminated from
the cells.
organelles where these physiological processes are taking place. There is a constant
movement of materials across the cell membrane in the cells.
which materials move in and out of the cells.
Structure of the membrane
membrane and chloroplast membrane.
materials in and out of the cells.
(it is a lipoprotein layer) the overall thickness of the cell membrane is about 7.5 nm thick.
out of the cells.
Properties of the cell membrane
a) The cell membrane is semi permeable– The pores that occur on the cell membrane
allows the passage of the small size molecules but does not allow the passage of the large
sized molecules.
Such a membrane is said to be selectively permeable or semi-permeable.
In particular, when a cell is surrounded by a dilute sugar solution, the small sized water
molecules will enter the cell but the larger sugar molecules will not pass through the cell
membrane.
In contrast, the cell wall is permeable as it allows both sugar and water
molecules to pass through it; it has larger pores. This property of selectively permeability
enables the cell membrane to select what enters and leaves the cell.
b)The cell membrane is sensitive to changes in temperature and pH– Cell membranes
are made up of protein. Proteins are adversely affected by extreme changes in
temperature and pH.
Changes in temperature and pH will alter the structure of the cell
membrane thereby hindering the normal functioning of the cell membrane. High
temperature denatures (destroys) the proteins thereby impairing the functions of the cell
membrane.
c)The cell membrane possesses electric charges– The cell membrane has both positive
and negative charges. These charges affect the manner in which substances move in and
out of the ells. The charges also enable the cell to detect changes in the environment.
Physiological Processes of the Cell membrane
move in and out of the cells across the cell membrane.
a) Diffusion
b) Osmosis
c) Active transport
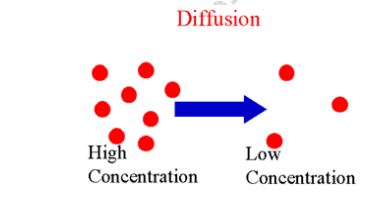
Diffusion
to another randomly. This movement of gas or liquid particles is observed to be from
regions of high concentration to a region of low concentration. The process by which
particles move from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration
is known as diffusion.
of the flower scent particles or perfume particles move from a region of high
concentration.
particles.
region of low concentration is known as the diffusion gradient/concentration gradient.
Demonstration of the process of diffusion using_potassium manganate (VII)
Requirements: potassium manganate (VII) crystals, glass tubing, 100 cm3 beaker and water.
Procedure
a) Hold the glass tubing vertically in a beaker so that one end of the tubing rests on the
bottom of the beaker.
b) Cautiously and quickly drop a crystal of potassium manganate (VII) through the upper
opening of the glass tubing.
c) Close the upper hand of the glass tubing with the thumb.
d) Half fill the beaker with water.
e) Carefully withdraw vertically the glass tubing so that the crystal is left undisturbed at the
bottom of the beaker.
f) Record your observations for the first 15 minutes.
g) Explain your observations.
Expected observations
the water and eventually all the water turned purple.
Explanation
manganate (VII) particles. The potassium manganate (VII) particles break away from the
crystals, dissolve in water and then diffuse through the water until they are evenly
distributed.
The Role of Diffusion in Living Organisms
a) In Plants
Diffusion plays an important role in plants in that:
water. For those salts whose concentration in soil water is higher that their concentration
in the cell sap of root hair cells, they move into the root hair cells through diffusion.
Plants require mineral salts for numerous life processes.
carbon (IV) oxide) diffuse across the stomata and lenticels of plants.
leaves to other parts of the plant.
b) In Animals
In animals diffusion plays the following important roles
of digestion such as amino acids and glucose diffuse across the wall of the ileum into the
blood for transport to other parts of the animal body.
gaseous exchange occurs at certain structures known as respiratory surfaces.
These
include the skin, gills, lungs, tracheal system and the cell membrane (in unicellular
organisms). Gaseous exchange at these surfaces occurs through the process of diffusion.
animals.
Factors affecting the rate of Diffusion
a) Diffusion gradient
the concentration of diffusing molecules also increases diffusion gradient with
corresponding regions hence increases the rate of diffusion.
b) Surface area to volume ratio
surface area to volume ratio, the greater the rate of diffusion will be. Conversely, low
surface area to volume ratio results in a low diffusion rate.
This is because the small organisms have a large surface area to volume ratio. As a result,
most of their body parts are closer to the external surrounding leading to faster diffusion.
foods, respiratory gases and waste products.
excretion. They have an additional transport system.
animals lose a lot of heat to the surrounding compared to the large animals.
c) Thickness of membranes and tissues
distance covered by the diffusing molecules is greater through the thicker membranes.
d) Size of molecules
e)Temperature
causing them to move faster, this implies that the rate of diffusion increases with increase
in temperature.
Osmosis
concentration (dilute solution) to a region of low concentration (concentrated solution)
through a semi permeable membrane.
solvent (Water) particles from a region of high concentration to a region of low
concentration.

Demonstration of Osmosis Using a Visking Tubing
Requirements
5OOcm3 beaker, visking tubing, a piece of thread, glass rod, concentrated sugar solution, 500 cm3
distilled Water.
Procedure
1. Into the beaker, put 350 cm3 of the distilled water.
2. Dip the visking tubing in water to moisten it. Open the visking tubing and tie one end
with the thread provided.
3. Half fill the visking tubing with the sugar solution provided and then tie the open end of
the tubing. Ensure no sugar solution spills out of the tubing.
4. Immerse the visking tubing into the distilled water in the beaker and suspend it using the
glass rod provided.
5. Leave the set up for about 30 minutes.
6. Record your observations.
7.Explain the observations made.
Observations
amount of water in the beaker decreased. This implies that water moved from the beaker
into the visking tubing.
Explanation
higher concentration of water molecules than the visking tubing. The water molecules
diffused from the beaker (where they are highly concentrated) into the visking tubing
(where they are lowly concentrated).
Even though there is a higher concentration of sugar
molecules in the visking tubing, they were not able to diffuse out of the visking tubing
due to their large molecular sizes. The visking tubing is semi permeable.
membranes that can be used in this experiment.
Osmosis explained
movement of water molecules from their region of high concentration (dilute solution) to
a region of low concentration (the highly concentrated solution) across the semi
permeable membrane. The semi permeable membrane does not allow movement of solute
particles across it.
same concentrations.
are said to be isotonic to each other.
hypotonic solution has less of the solute molecules but more of the solvent molecules.
particles is referred to as a hypertonic solution.
net movement of solvent molecules to any of the solutions since they have the same
concentration of solvent molecules.
Osmotic pressure
membrane, the concentrated solution will develop a force with which it draws water
through the semi permeable membrane from the distilled water.
itself.
Osmotic potential
from pure water when separated by a semi permeable membrane.
Water Relations in Animals
happen if an animal cell say red blood cell is placed in solutions of varying
concentrations
a) Red blood cell in hypotonic solution e. g. distilled water
cell cytoplasm.
When a red blood cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, water will move
into the cell through osmosis. The cell will swell and burst. Swelling of red blood cell
when placed in a hypotonic solution is referred to as haemolysis. The cell is said to be haemolysed.
b) Red blood cell in hypertonic solution
blood cell cytoplasm.
Water will, therefore, be drawn out of the cell into the hypertonic
solution. The cell will shrink and become small. The cell is said to be crenated.
The
process by which animal cells shrink and become smaller when placed in hypertonic
solutions is referred to as crenation.
c) Red blood cell in isotonic solution
When placed in an isotonic solution, the cell remains unchanged. This is because there
will be no net inflow or outflow of water between the cell and the solution.
Note:
that the body fluids and blood plasma surrounding the cells must be kept at the same
concentration as the animal cells.
This will prevent bursting or shrinking of the cells that
would otherwise impair their physiology.
same concentration.
Water Relations in Plants
contains vacuole with sap. The sap is a solution of salts and sugars and is bound by a
membrane, the tonoplast.
permeable.
a) Plant cell in hvpotonic solution e. g. distilled water
hypotonic solution through osmosis causing the cell to distend.
animal cells.
pressure on the cell wall called turgor pressure.
stretch until the cell cannot stretch any more. The cell becomes firm and is said to be
turgid.
it gains more water through osmosis.
pressure to stretching that is equal and opposite to turgor pressure called wall pressure.
b) A glam cell in a hygertonic solution
through osmosis. As the water moves out of the cell, the cell starts to shrink, becomes
less rigid or flabby and is said to be flaccid.
away from the cell wall towards the centre. The process through which plant cells lose
water, shrink and become flaccid is called plasmolysis.
called deplasmolysis.

Wilting
from the soil making the plant cells to lose their turgor pressure and droop.
through evapotranspiration is significantly reduced.
wilting and instead undergo permanent wilting.
Role of Osmosis in Organisms
soil through osmosis. Osmosis also helps in distribution and movement of water from the
roots to other parts of the plant.
When the cells of these plants take in water through osmosis, the cells become firm or
rigid and thus gain support.
surrounding the stomata synthesize glucose through photosynthesis in the presence of
light.
As glucose accumulates in the guard cells, the osmotic pressure of the guard cells
increase making them to draw water from adjacent cells through osmosis. When the
guard cells become turgid, they bulge outwards leading to opening of the stomata.
Opening of the stomata is crucial as it allows for gaseous exchange in plants. At night,
there is no glucose synthesis.
The glucose available in the guard cells is respired on
leading to reduction of glucose and consequently reduction in osmotic pressure. The
guard cells lose turgidity and close the stomata.
nitrogen deficient soils and trap insects from whence they obtain the nutrients. These
plants possess special structures that suddenly change their turgor pressure when
disturbed.
The change in turgor pressure enables the special structures to rapidly close
thereby trapping the insects.
through osmosis through the tubular walls. This enables animals to maintain the osmotic
pressure of the body fluids.
Factors Affecting the Rate of Osmosis
separated solutions have a greater difference in osmotic pressure. In summary, the greater
the concentration gradient, the greater the rate of osmosis and vice versa.
increases the energy content of the molecules.
while the rate of osmosis is greater through thinner membranes.
Active Transport
membrane and against a concentration gradient.
cells. In particular, there are some mineral salts that occur at low concentrations in the
soil water than in the cell sap.
Some of these mineral salts cannot be absorbed by the
plants through diffusion. A mechanism that would move them into the cells against the
concentration gradient will be useful.
on concentration gradient for them to take place.
the moving these substances across the membrane. These carrier molecules combine with
the substances being transported across the membrane and then move them from one side
of the membrane to the other side.
Role of active transport in living organisms
and saline environments
Factors affecting the rate of Active Transport
production process in living cells.
a) Oxygen concentration
Oxygen is required in respiration process that yields energy for active transport. Under low
oxygen concentration, the rate of respiration will be low hence there will be production of little
energy leading to low rate of active transport. Increase in oxygen concentration translates into a
higher energy production leading to high rate of active transport.
b) Change in pH
Change in pH affects the respiratory process which is enzyme controlled. Respiratory enzymes
require optimum pH for their efficient activity. Extreme pH conditions will increase lower the
rate of active transport since the enzymes controlling respiration Will be denatured.
c) Glucose concentration
Glucose is the chief respiratory substrate. At low glucose concentration, there will b less
production of energy leading to decreased rate of active transport. Rate of active transport
increases with increase in glucose concentration due to increase in the rate of energy production.
d ) Temperature
Temperature affects the enzyme controlled respiration process. At low temperatures, the
enzymes are inactive hence the rate of respiration will be low resulting into low rate of active
transport since there will be less production of energy. An increase in temperature increases the
rate of respiration since the enzymes become more activated. At temperatures beyond 40 degrees
celcius, the enzymes become denatured, respiration stops and so does active transport.
e) Presence of metabolic inhibitors e. g. cyanide.
These are substances which act as metabolic poisons. They stop the rate of respiration leading to
production of no energy. Active transport is, thus, stopped.
Nutrition Plants And Animals
Introduction
nutrients. It is one of the fundamental characteristics of living things.
The nutrients obtained are useful to the living organisms in many ways:
a) The nutrients are required for growth and development of the living organisms.
b) The nutrients are required for energy provision as they are broken down to release
energy.
c) They nutrients are also required for repair of worn out tissues
d) Nutrients are required for synthesis of very vital macromolecules in the body such as
hormones and enzymes.
Modes of nutrition
There are two main nutrition modes:
a) Autotrophism mode of nutrition through which living organisms manufacture their own
food from simple inorganic substances in the environment such as carbon (IV) oxide,
water and mineral ions. Organisms that make their own food through this mode are
autotrophs.
b) Heterotrophism mode of nutrition in which living organisms depend on already
manufactured food materials from other living organisms. Heterotrophs are the organisms
that feed on already manufactured food materials.
Autotrophism
In this mode of nutrition, organisms manufacture their own food from readily available
materials in the environment. These organisms use energy to combine carbon (IV) oxide,
water and mineral salts in complex reactions to manufacture food substances. Depending
on the source of energy used to manufacture the food, there are two types of
autotrophism:
a)Chemosynthesis
This is the process whereby some organisms utilize energy derived from chemical
reactions in their bodies to manufacture food from simple substances in the environment.
This nutrition mode is common in non green plants and some bacteria which lack the sun
trapping chlorophyll molecule.
b) Photosynthesis
the environment such as carbon (IV) oxide and water using sunlight energy.
and bacteria are also photosynthetic.
Importance of Photosynthesis
1. Photosynthesis helps in regulation of carbon (IV) oxide and oxygen gases in the
environment.
2. Photosynthesis enables autotrophs make their own food, thus, meet their nutritional
requirements.
3. Photosynthesis converts sunlight energy into a form (chemical energy) that can be
utilized by other organisms that are unable to manufacture their own food.
is important to understand the leaf structure.
External leaf structure
lamina- the broad flat surface, margin- the outline and the leaf apex.
leaves with some leaves reduced to needle like shape.
This helps reduce the rate of water
loss in such plants. However, the plants in areas of water abundance have broad leaves to
enable them lose the excess Water.


a) Cuticle
lower leaf surfaces.
Functions of the cuticle
a) Being waterproof, it minimizes water loss from the leaf cells to the environment through
transpiration and evaporation.
b) It protects the inner leaf tissues from mechanical damage.
c) It prevents entry of pathogenic microorganisms into the leaf.
b) Epidermis
are flattened and lack chloroplasts.
Functions of the epidermis:
a) It protects the leaf from mechanical damage.
b) It also protects the leaf from entry of disease-causing microorganisms.
c) It secretes the cuticle.
which exchange of materials occur. The opening and closing of the stomata is controlled
by the guard cells. Each stoma is controlled by two guard cells.
and thinner outer cell wall.
Adaptations of the guard cells
osmosis from the neighboring cells making them to open the stomata.
guard cells. As they draw water through osmosis, they bulge making the stomata to open.
c) Palisade mesophyll
sunlight for photosynthesis.
greener than the lower surfaces.
d) Spongy mesophyll layer
the cells which permits free circulation of gases carbon (IV) oxide and oxygen into the
photosynthetic cells. Spongy mesophyll cells contain fewer chloroplasts compared to
palisade cells.
e) Vascular bundle/tissue
tissues. Xylem tissues conduct Water and some dissolved mineral salts from the roots to
other plant parts while phloem translocates manufactured food materials from
photosynthetic areas to other plant parts.
Chloroplast
membrane bound organelle.
called stroma.
are contained in the grana.
place.
Adaptations of the leaf to photosynthesis
and for gaseous exchange.
molecules which trap sunlight energy for photosynthesis.
absorption of sunlight energy.
the photosynthetic cells and phloem to translocate manufactured food materials to other
plant parts.
Raw materials for photosynthesis
Conditions for photosynthesis
Photosynthesis Process
summarized into two main reactions.
a)Light reaction/Light stage
cannot take place.
i) Photolysis of water
and oxygen gas.
energy for photolysis.
plant for respiration.
Water– Hydrogen atoms + Oxygen gas
ii) Formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
plant tissues with a phosphate molecule to form Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP). ATP is
an energy rich molecule that stores energy for use in the dark stage when sunlight energy
could be unavailable.
ADP + P = ATP
b) Dark reaction/Dark stage
from the ATP formed during light stage.
(IV) oxide molecule with hydrogen ions to form a simple carbohydrate and a water
molecule.
synthesis reactions.
inactive. When a lot of simple sugars accumulate in the chloroplasts, osmotic pressure of
the guard cells would increase causing the guard cells to draw a lot of water through
osmosis. This makes the guard cells to bulge and open the stomata. This can result into
excessive water loss.
photosynthesis has taken place in a leaf, therefore, a test for presence of starch and not
simple sugars is carried out.

Testing for starch in a leaf
Requirements
Procedure
that the leaf has photosynthesized.
enzymes and stops any chemical reactions in the leaf.
boil in a water bath. Methylated spirit is highly flammable hence should be boiled
indirectly. Boiling with methylated spirit or alcohol decolourises the leaf (removes the
chlorophyll). This ensures that the leaf becomes white so that colour changes can be
observed easily when iodine is added.
leaf.
Observations
Factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis
a) Carbon (IV) oxide concentration
0.03%, an increase in carbon (IV) oxide concentration translates into an increase in the
rate of photosynthesis up to a certain point when the rate of photosynthesis becomes
constant.
At this point, other factors such as light intensity, water and temperature
become limiting factors.

b)Light intensity
level. Beyond the optimum light intensity the rate of photosynthesis becomes constant.
To this effect, plants photosynthesize faster on bright and sunny days than on dull cloudy
days.
and blue wavelengths of light for photosynthesis. Light duration also affects
photosynthesis rate.

c)Temperature
photosynthesis is slow because the enzymes are inactive. As temperature increases, the
rate of photosynthesis increases because the enzymes become more active.
Rate of
photosynthesis is optimum at (35-40) °C. Beyond 40°C the rate of photosynthesis
decreases and eventually stops since the enzymes become denatured.

d) Water
photosynthesis will be severely affected.
Experiment to investigate the gas produced during photosynthesis
Requirements
wooden blocks, test tubes, wooden splints and sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Procedure
a) Set up the apparatus as shown in the figure below
b) Place the set up in the sunlight to allow photosynthesis to take place.
c) Leave the set up in the sun until sufficient gas has collected in the test tube.
d) Test the gas collected with a glowing splint.
e) Record your observations.
Note:
of carbon (IV) oxide in the water since water has a low concentration of carbon (IV)
oxide.
the low light intensity in water where terrestrial plants cannot easily photosynthesize.
photosynthesis:
1) Carbon (IV) oxide concentration: Carry out the experiment using different
amounts of dissolved sodium hydrogen carbonate e. g 5 g, 10g, 15g, 20g and
examine the rate at which the gas collects.
2) Light intensity: An artificial light source can be used. Illuminate the plant and
vary the distance between the set up and the light source While recording the time
it takes for the gas jar to fill or counting the number of bubbles peer unit time.
3) Temperature: carry out the experiment at varying temperatures and record the
rate at which the gas collects.
Experiments on factors necessary for photosynthesis
Light
Requirements
boiling tube, light proof material e.g. aluminium foil, potted plant and clips.
Procedure
to ensure that all the starch in it is used up. This makes the leaves ideal for investigating
whether starch would form in the experimental period. This is called destarching).
leaves and one that was not covered.
Carbon (IV) oxide
Requirements
Procedure
Chlorophyll
lack chlorophyll.
place in them.
Procedure
Chemicals Of Life
and their reactions.
Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides
Properties of Monosaccharides
Benedict’s solution to red brown copper (I) oxide when heated.
Note:
a process known as condensation. Water molecules are produced in the process.
Functions
body.
Disaccharides
condensation.
is called glycosidic bond.
transported in plants
Properties of Disaccharides
as a complex reducing sugar.
Hydrolysis is the process through which complex molecules are broken down in the
presence of water molecules.
hydrolysis can be carried out by boiling the disaccharide in dilute aid such as
hydrochloric acid.
Functions
and inert nature.
Polysaccharides
condensation.
Properties of polysaccharides
Examples of polysaccharides
a) Starch– Made by linking numerous glucose molecules. It is a form in which
carbohydrates are stored in plants.
b) Glycogen– Is a storage carbohydrate in liver and muscles of animals. It is broken down to
glucose in animals when blood glucose falls.
c) Cellulose– This is a structural polysaccharide in plants. It is a component of the cell wall
d) Chitin– A structural carbohydrate found in cell wall of fungi and arthropod exoskeletons
Functions of polysaccharides
storing carbohydrates.
Lipids
oxygen but higher hydrogen compared to carbohydrates.
three fatty acids and a glycerol molecule are linked through a condensation reaction.
type of fatty acids that link up with the glycerol.
also form through condensation.
Properties of lipids
form emulsions
Functions
carbohydrates when oxidized per unit weight. However, they are less preferred as source
of energy because they require a lot of oxygen to oxidize. In addition, they are insoluble
hence not easy to transport to respiratory sites.
This explains why some desert animals such as camels store large quantities of fat in their
bodies.
shock absorbers.
conductors of heat hence do not conduct heat away from the body. Organisms in cold
areas tend to be short and plump as they have fatter fat adipose.
Proteins
nitrogen and sometimes phosphorous or sulphur or both.
Some proteins molecules contain other elements. In particular, haemoglobin contains
iron.
acids are of two kinds:
a) Essential– These are those amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the body
systems hence have to be supplied in the diet.
b) Non essential– These are amino acids that can be synthesized by the body
mechanisms hence do not need to be supplied in the diet.
group. Amino acids differ from each other by the alkyl group.
a) First class proteins– Contain all essential amino acids
b) Second class proteins– Proteins lack one or more essential amino acids
Protein synthesis
Several amino acids link up to form a polypeptide chain. Proteins are made up of long
chain polypeptides.
sequence in which the amino acids link up in the polypeptide chain.
Properties of Proteins
suspended in water.
organic solvents also denature proteins.
conjugated proteins such as:
Functions of proteins
a) They are structural compounds of the body. Cell membrane is protein in nature. Hair,
nails and hooves are made up of protein keratin.
b) Proteins are broken down to release energy during starvation when all carbohydrate and
lipid reserves are depleted.
c) Functional proteins play vital roles in metabolic regulation. Hormones are chemical
messengers while enzymes regulate the speed of metabolic reactions.
d) Proteins such as antibodies provide protection to the body against infections
e) Some protein molecules are transport molecules. Haemoglobin molecule plays a crucial
role in transportation of respiratory gases.
f) Proteins play a vital role in blood clotting e. g. fibrinogen.
g) Contractile proteins such as actin and myosin bring about movement.
Enzymes
What are enzymes?
Types of enzymes
a) Extracellular: Are produced within the cells but used outside the cells e. g. digestive
enzymes.
b) Intracellular: Are enzymes produced and used within the cells e. g. respiratory enzymes.
Importance of Enzymes
life.
DNA.
utilized by the cells.
poisonous substances less harmful.
Enzyme nomenclature
a).Trivial naming
Examples
b). Use of suffix -ase
or by adding the suffix to the reaction being catalyzed by the enzyme.
Substrates
Processes/Reactions
Hydrolysis ……………….. ..hydrolase
Reduction ………………… ..reductase
Oxidation …………………. ..oxidase
Mechanism of action of Enzymes
which the substrate molecules bind to the enzymes. The reaction is then catalyzed and the
end products released. The enzyme is free to bind with another substrate molecule. The
enzymes can be used again and again.

Properties of Enzymes
Factors affecting enzyme activity
a)Temperature
collisions leading to low enzyme activity.
increases leading to increased collisions hence increase in enzyme activity.
enzymes get denatured and their active sites get destroyed.
b)pH
under acidic conditions e. g. pepsin. However, most intracellular enzymes work better
under neutral conditions.
c)Enzyme Specificity
particular reaction.
d)Substrate Concentration
activity is low.
sites of the enzymes will be occupied and there will also be an increase in enzyme-
substrate collisions leading to increased reaction.
sites are utilized. The enzymes become the limiting factor of reaction. Increasing enzyme
concentration would increase the rate of enzyme activity.
e) Enzyme Concentration
beyond which the rate of reaction becomes constant.
and also fewer enzyme-substrate collisions that would lead to reactions.
increase in number of active sites and enzyme-substrate collisions.
Increasing substrate concentration increases the rate of reaction.
f) Enzyme co-factors
as vitamins.
reactions.
g) Co-enzymes
functioning. Some enzymes will not function without them.
Examples
NAD- Nicotine Adenine Dinucleotide.
FAD- Flavine Adenine Dinucleotide.
NADP- Nicotine Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate.
h) Enzyme inhibitors
1. Competitive
2. Non- competitive
Competitive inhibitors
up the shape of the substrates and compete for the active sites of the enzymes.
site for a long time) thereby slowing down the rate of enzyme activity.
Non competitive inhibitors
the enzyme at any site other the active site and alter the structure of the active site of the
enzyme. The normal substrate, therefore, fails to bind to the active site leading to
decreased rate of reaction.
Examples of non competitive inhibitors
Heavy metals (such as lead, mercury, silver), Cyanide, organophosphates such as malathion.
Heterotrophism
food substances such as carbohydrates, proteins and lipids.
food substances that can be absorbed and be utilized by the cells.
Modes of Heterotrophism
substances.
decomposition.
nutrients on another organism, the host.
mutually benefit from each other.
a) Parasitism
hosts and damage their tissues thereby weakening them.
b) Symbiosis
> Rhizobium and leguminous plants: rhizobium fixes nitrogen for the legume while
the bacteria obtains manufactured food from the legumes.
> Lichen: association of fungi (absorbing water and nutrients) and algae
(manufacturing food for the association.
> Catalase digesting bacteria and ruminants.
Dentition
utilized by the cells. The breakdown is both physical and chemical.
substances.
Types of Dentition
the same size and shape. Fishes and birds have homodont dentition.

incisors, canines, premolars and molars. Heterodont dentition is common with mammals
and reptiles.
a) Incisors

a. Canines
carnivores.
b. Premolar and molar

Classes of Holozoic Heterotrophs
a) Herbivores: heterotrophs that exclusively feed on vegetation.
b) Carnivores: heterotrophs exclusively feed on flesh.
c) Omnivores: heterotrophs that feed on both flesh and vegetation.
Dental Formula
a) i-incisors.
b) c-canines.
c) pm-premolars.
d) m-molars.
premolars and four molars on the upper jaw. On the lower jaw, it had eight incisors, no
canines, six premolars and six molars.
a) Write down its dental formula.
b) State its mode of feeding.
c) Give a reason.
Herbivores
pressed and cut by the lower incisors.
which allows the tongue to manipulate food.
out surfaces due to grinding.
grinding of grass.

Carnivores
carnassial teeth which have smooth sides and sharp edges to slice through flesh and crush
bones

Dental Diseases
a) Dental Carries
of vitamin D, lack of cleaning teeth and general ill-health. The bacteria in the mouth
break down the sugars to form energy and organic acids. The acids corrode the enamel.
b) Periodontal Diseases
of gums.
than children.
Are of two types:
a) Gingivitis– Characterized by reddening of gums, bleeding and pus in the gums.
b) Pyorrhea– The teeth become loose due to infection of the fibres holding the teeth in
the sockets.
Dental Hygiene
Digestion
chemically into simpler food substances that can be absorbed by body cells.
absorbed into the bloodstream without undergoing digestion.
bladder, salivary glands.


Digestion in the mouth
process is called mastication.
action.
from the salivary glands. The salivary glands are:
a) Sublingual salivary gland; beneath the tongue
b) Sub mandibular gland: under the jaw
c) Parotid gland: Found in the cheeks in front of the ears.
then pushed to the back of the mouth to initiate the swallowing process. The boluses are
then moved to the stomach via oesophagus. Movement is facilitated by a wave of
muscular contractions of longitudinal and circular muscles of the oesophagus known as
peristalsis.
swallowing.
Digestion in the stomach
the stomach via the cardiac sphincter (a muscular valve).
produce movements that mix the contents of the stomach. The mixing process is known
as churning and results in formation of a fluid called chyme
stimulates the gastric glands in the stomach walls to secrete gastric juice which contains:
a) Pepsinogen-This is activated to pepsin which breaks down proteins to peptides.
b) Rennin– Digests caseinogens protein in milk to casein (curd).
e) Hydrochloric acid– This:
d) Mucus– Forms a protective barrier to the stomach wall against corrosion by the
HC1. Mucus is secreted by goblet cells in the epithelial membrane of the
alimentary canal.

Duodenum
chyme is let down into the duodenum in small quantities.
a) Gall bladder in the liver- Secretes bile.
b) Pancreas- Secrete hormones and digestive enzymes.
i. Secretin hormone from the pancreas: Secretin stimulates secretion of pancreatic
juice into the duodenum
ii. Cholecystokinin from the duodenal wall: This stimulates secretion of bile from
the gall bladder.
a) Pancreatic amylase– This facilitates breakdown of the remaining starch into maltose
b) Trypsin– Digests proteins into peptides.
c) Pancreatic juice-Digests lipids into fatty acids and glycerol
d) Sodium hydrogen carbonate– This:
Provides alkaline medium for activity of the duodenum enzymes.
taurocholate. These salts:
i. Aid in emulsification (breakdown of fat molecules into tiny fat droplets to
increase surface area for digestion).
ii. The salts also provide a suitable alkaline medium for action of the duodenal
enzymes.
iii. In addition they neutralize the acidic chyme.

Digestion in the ileum
an alkaline fluid known as succus entericus (intestinal juice). The arrival of chyme in
ileum stimulates secretion of intestinal juice which contains:
a) Maltase: speeds up breakdown of maltose to glucose
b) Sucrase: speeds breakdown of sucrose to glucose and fructose
c) Peptidase: speeds breakdown of peptides to amino acids
d) Lipase: speeds breakdown of lipids to fatty acids and glycerol.
e) Lactase: speeds breakdown of lactose to glucose and galactose.
f) Polypeptidase: speeds breakdown of plypeptides into amino acids
Note:
The mucus secreted by the goblet cells lubricates food along the alimentary canal and
also protect the canal from being digested by enzymes.
At the end of digestion in the ileum, the resulting watery emulsion is called chyle; it
contains soluble end products of digestion ready to be absorbed.
Absorption
cellular lining of the villi.
are absorbed at the stomach. Alcohol is equally absorbed here without undergoing
digestion.
walls into the blood system by active transport.
transported to the liver before they are circulated to other body parts.
vessels. The lymphatic vessels later join the blood circulatory system which transports
them to other body parts.
a) It is long to provide a large surface area for absorption
b) It has a narrow lumen so as to bring the digested food into close contact with the
walls of the ileum for easier absorption
c) It is highly coiled to slow down movement of food thus allowing more time for
digestion and absorption of food.
d) The inner surfaces have numerous villi and microvilli to increase surface area for
absorption of end products of digestion.
e) The epithelial lining is one cell thick to reduce the distance through which
digested food diffuses.
f) Has a dense network of blood capillaries into which digested food materials
diffuse to increase transport and thus maintain a steep concentration gradient.
g) Have lacteal vessels in the villi for absorption of fatty acids and glycerol.

Egestion
> This is the process through which the undigested and indigestible food substances are
eliminated from the body.
Caecum and Appendix
herbivores.
digest cellulose since most digestive systems cannot secrete cellulose digesting enzyme.
The bacteria and the herbivores are in a symbiotic relationship.
Assimilation
a) Glucose
important structural compound in plants.
b) Fatty acids and glycerol
c) Amino acids
Vitamins
are also obtained in fresh fruits and vegetables.
quantities.
influence the intake of certain substances. In particular, vitamin C influences uptake of
iron while vitamin D influences absorption of calcium ions in the gut.
deficiency diseases. These deficiency diseases can be corrected by inclusion of the
deficient vitamins in the diet or taking the vitamin supplements.
a) Fat soluble vitamins– They dissolve in fats and are often stored in the liver.
Include Vitamins A, D, E, K.
b) Water soluble vitamins– Dissolve in water. Include vitamins B1, B2, B5, B12 and
C.
Vitamin A (retinol)
main food source
uses in the body
deficiency disease symptoms
Vitamin B1 (thiamine)
main food source
uses in the body
deficiency disease symptoms
Vitamine B2 (riboflavine and nicotinic acid)
main food source
uses in the body
deficiency disease symptoms
Vitamin B5 (pentathonic acid)
main food source
uses in the body
deficiency disease symptoms
Vitamin B12 (cobalamine)
main food source
uses in the body
deficiency disease symptoms
Vitamin C (absorbic acid)
main food source
uses in the body
deficiency disease symptoms
Vitamin D (calciferol)
main food source
uses in the body
deficiency disease symptoms
Vitamin E (tosopherol)
main food source
uses in the body
deficiency disease symptoms
Vitamin K (quinone)
main food source
uses in the body
deficiency disease symptoms
Mineral salts
body functioning. Depending on body requirements, mineral salts are of two classes:
a) Macro-nutrients: Nutrients required in large quantities. These include nitrogen,
sulphur, phosphorous, calcium, sodium, iron and magnesium.
b) Micro-nutrients: Nutrients required in small quantities. Include copper,
manganese, boron, iodine and cobalt.
Element: Nitrogen
source
function in the body
deficiency symptoms
–
Element: Phosphorous
source
function in the body
deficiency symptoms
Element: Calcium
source
function in the body
deficiency symptoms
Element: Iodine
source
function in the body
deficiency symptoms
Element: Potassium
source
function in the body
deficiency symptoms
Element: Iron
source
function in the body
deficiency symptoms
Element: Sodium
source
function in the body
Element: Chlorine
source
function in the body
Element: Sulphur
source
function in the body
Element: Magnesium
source
function in the body
deficiency symptoms
Roughage
walls.
vegetables.
Importance of roughage
a) It rubs against the walls of the alimentary canal stimulating secretion of digestive
enzymes and mucus to lubricate the epithelial lining.
b) Roughage enhance peristalsis since as they rub against the walls of the alimentary canal,
they stimulate contraction and relaxation of the muscles.
c) Roughage is an absorbent; it extracts water from the alimentary canal making the fecal
matter bulky and moist hence can be easily propelled by peristaltic movements. This
prevents constipation.
Factors affecting energy requirements in humans
Discuss how the following factors affect energy requirements in humans:
Biology Notes FAQ Form
Please insert your question in the form below. Check and ensure that your question has not been asked and answered in the enquiries appearing beneath the form.
KCSE Results » KCSE Results Top 100 Schools – Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education – KCSE » KCSE Top 100 Candidates » Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education – KCSE » KNEC – Kenya National Examinations Council » Secondary Schools in Kenya » KNEC – Kenya National Examinations Council » Free KNEC KCSE Past Papers
Kenya Scholarships for Undergraduate Students » Kenya Scholarships for Postgraduate Students » Undergraduate Scholarships for Kenyan Students » Kenya Undergraduate Scholarships » Full Undergraduate Scholarships for Kenyans » Kenya Postgraduate Scholarships » Scholarships & Grants » Undergraduate Scholarships » Universities in Kenya » Kenya Universities and Colleges Central Placement Service (KUCCPS) » Colleges in Kenya » KASNEB Registration & Results » Secondary Schools Scholarships in Kenya » Undergraduate & Graduate Scholarships for Kenyans
Scholarships for African Students » Undergraduate Scholarships » African Women Scholarships & Grants » Developing Countries Scholarships » Erasmus Mundus Scholarships for Developing Countries » Fellowship Programs » Funding Grants for NGOs » Government Scholarships » LLM Scholarships » MBA Scholarships » PhD and Masters by Research Scholarships » Public Health Scholarships – MPH Scholarships » Refugees Scholarships » Research Grants » Scholarships and Grants
Scholarships in Australia » Scholarships in Belgium » Scholarships in Canada » Scholarships in Germany » Scholarships in Italy » Scholarships in Japan » Scholarships in Korea » Scholarships in Netherlands » Scholarships in UK » Scholarships in USA
KCSE Revision Notes Form 1 – Form 4 All Subjects
aa Biology Questions and Answers
10th Grade Biology Questions and Answers
10th Grade Biology Test
11th Ncert Biology
12th Class Biology Book Free Download
2017 Biology Hsc Answers
9th Grade Biology Study Guide
A Level Biology Biological Molecules Questions
A Level Biology Exam Questions by Topic
A Level Biology Notes Edexcel
A Level Biology Notes Xtremepapers
A Level Biology Questions and Answers
A Level Biology Questions and Answers (Pdf)
A Level Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
A Level Biology Questions by Topic – Kidney Questions With Markschemes
A Level Biology Revision
A Level Biology Revision Edexcel
A Level Biology Revision Guide
A Level Biology Revision Notes
A Level Biology Revision Notes Pdf
A Level Biology Textbook Pdf
A Level Biology Year 1 / as Aqa Exam Questions by Topic
A Level Edexcel Notes – a* Biology
Aerobic Respiration in Plants
All Biology Essays
All Biology Essays Form 1
All Biology Essays Form 2
All Biology Essays Form 3
All Biology Essays Form 4
Anaerobic Respiration Equation
Animal Cell Organelles Quiz Answers
Animal Cell Questions and Answers
Animal Cell Quiz
Animal Cell Quiz Labeling
Ap Bio Quizzes
Ap Biology Essay Questions and Answers
As Level Biology Notes
Bbc Bitesize Biology Ks3
Biology 101
Biology 12th
Biology 12th Class Notes Pdf
Biology 2019 Syllabus
Biology Book 3 Klb
Biology Book 3 Notes
Biology Book for Class 11
Biology Book Pdf Free Download
Biology Cell Structure Test
Biology Class 12 Ncert Solutions
Biology Class 12 Pdf
Biology Communication Syllabus
Biology Diagrams for Class 12 – Biology Diagram Software – Biology Diagrams for Class-10 – Biology Diagrams for Class 11 – Biology Diagrams for Class 9 – Biology Diagrams to Label – Biology Diagram of Female Reproductive System – Biology Diagrams Pdf – Biology Diagrams in Form 1 – Biology Diagrams in Form 2 – Biology Diagrams in Form 3 – Biology Diagrams in Form 4 – Kcse Biology Diagrams -biology Revision Tips
Biology Essay Questions and Answers
Biology Essay Questions and Answers 2018
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 1
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 2
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 3
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 4
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 4 Pdf
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf Form 1
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf Form 2
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf Form 3
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf Form 4
Biology Essays and Answers
Biology Essays and Answers Form 1
Biology Essays and Answers Form 2
Biology Essays and Answers Form 3
Biology Essays and Answers Form 4
Biology Essays Kcse
Biology Essays Kcse Form 1
Biology Essays Kcse Form 2
Biology Essays Kcse Form 3
Biology Essays Kcse Form 4
Biology Essays Pdf
Biology Exam 2 Test
Biology Exam Form Four
Biology Exam Form One
Biology Exam Form Three
Biology Exam Form Two
Biology Exam Practice Test
Biology Exam Questions and Answers
Biology Exam Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Exam Study Guide
Biology Excretion Notes
Biology Exercise Form 4 With Answers
Biology Final Exam Answer Key
Biology Final Exam Answer Key 2016
Biology Final Exam Answer Key 2017
Biology Final Exam Answers 2018
Biology Final Exam Answers 2019
Biology Final Exam Questions and Answers
Biology Form 1 & 2 and Answers
Biology Form 1 Chapter 1
Biology Form 1 Diagrams
Biology Form 1 Notes
Biology Form 1 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 1 Past Papers
Biology Form 1 Questions
Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf Form 1
Biology Form 1 Revision Questions
Biology Form 1 Syllabus
Biology Form 2 Chapter 1
Biology Form 2 Chapter 2
Biology Form 2 Diagrams
Biology Form 2 Notes
Biology Form 2 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 2 Past Papers
Biology Form 2 Pdf
Biology Form 2 Questions
Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf Form 2
Biology Form 2 Revision Notes
Biology Form 2 Syllabus
Biology Form 3 Chapter 3
Biology Form 3 Classification
Biology Form 3 Diagrams
Biology Form 3 Ecology
Biology Form 3 Notes
Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 3 Past Papers
Biology Form 3 Questions
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf Form 3
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Term 3
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers+pdf
Biology Form 3 Revision Notes
Biology Form 3 Syllabus
Biology Form 3 Topics
Biology Form 4 All Chapter
Biology Form 4 Chapter 4
Biology Form 4 Diagrams
Biology Form 4 Notes
Biology Form 4 Notes All Chapter Pdf
Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 1
Biology Form 4 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 4 Past Papers
Biology Form 4 Questions
Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers Pdf Form 4
Biology Form 4 Syllabus
Biology Form 4 Textbook Pdf
Biology Form Four Notes Pdf
Biology Form Four Questions and Answers
Biology Form Four Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form One
Biology Form One Exam
Biology Form One Notes Pdf
Biology Form One Questions
Biology Form One Questions and Answers
Biology Form One Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form One Term Three Test
Biology Form Three Questions and Answers
Biology Form Three Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Three Reproduction
Biology Form Three Reproduction.
Biology Form Three-questions and Answers
Biology Form Two Diagrams
Biology Form Two Notes Pdf
Biology Form Two Questions and Answers
Biology Form Two Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form2
Biology Form2 Textbook
Biology Grade 10 Exam Papers
Biology Hsc Pdf
Biology Human Reproduction Video
Biology Kcse 2017
Biology Kcse 2017 Paper 1
Biology Kcse Questions
Biology Made Familiar
Biology Mcq for Class 11
Biology Mcq for Class 12
Biology Mcq for Competitive Exams
Biology Mcq for Competitive Exams Pdf
Biology Mcq for Neet Pdf
Biology Mcq With Answers Pdf
Biology Mcqs for Class 12 Pdf
Biology Mid Familia Form One
Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Cxc
Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Multiple Choice Questions With Answers Pdf
Biology Notes
Biology Notes for High School Students
Biology Notes for Igcse 2014
Biology Notes Form 1
Biology Notes Form 1 Pdf
Biology Notes Form 2
Biology Notes Form 2 Pdf
Biology Notes Form 3
Biology Notes Form 3 Pdf
Biology Notes Form 4
Biology Notes Form 4 Chapter 2
Biology Notes Form 4 Pdf
Biology Notes Form One Pdf
Biology Notes Form Three
Biology Notes Form Two
Biology Objective Answer
Biology Objective Questions for Competitive Exams Pdf
Biology Paper 1
Biology Paper 1 Notes
Biology Paper 1 Questions
Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers
Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers Form 1
Biology Paper 1 Topics
Biology Paper 2 2017
Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers
Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers Form 2
Biology Paper 2 Revision
Biology Paper 2018
Biology Paper 3 Questions and Answers Form 3
Biology Paper 4 Questions and Answers Form 4
Biology Paper One Questions and Answers
Biology Past Papers 2017
Biology Past Papers Form 3
Biology Practical Book Class 12 Pdf
Biology Practical Exam
Biology Practicals Questions and Answers
Biology Practice Test 9th Grade
Biology Practice Test Answers
Biology Practice Test Questions and Answers
Biology Question and Answers Note
Biology Questions
Biology Questions and Answers
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Form 1
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Form 2
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Form 3
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf Form 4
Biology Questions and Answers Form 1
Biology Questions and Answers Form 2
Biology Questions and Answers Form 3
Biology Questions and Answers Form 4
Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice
Biology Questions and Answers on Cells
Biology Questions and Answers Online
Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Questions for High School
Biology Questions for High School Students With Answers
Biology Questions Multiple Choice
Biology Questions Quizlet
Biology Questions to Ask Your Teacher
Biology Quiz for Class 9
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 12
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 9
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for High School
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Quiz Questions for Class 12
Biology Quiz Questions for College Students
Biology Quiz With Answers
Biology Quiz With Answers Pdf
Biology Revision
Biology Revision a Level
Biology Revision Notes Form 1
Biology Revision Notes Form 2
Biology Revision Notes Form 3
Biology Revision Notes Form 4
Biology Revision Notes Igcse
Biology Revision Questions
Biology Study Guide
Biology Study Guide – Biology Questions and Answers
Biology Study Guide Answer Key
Biology Study Guide Answers
Biology Study Guide Ib
Biology Study Guide Pdf
Biology Study Notes
Biology Syllabus in Kenya
Biology Test Questions and Answers
Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Topics Form One
Biology Unit 1 Quiz
Biology | Revision Science
Cell Biology Exam Questions and Answers
Cell Biology Exam Questions Pdf
Cell Biology Mcq With Answers
Cell Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf
Cell Biology Multiple Choice Questions Pdf
Cell Biology Previous Question Papers
Cell Biology Question Bank
Cell Biology Question Bank Pdf
Cell Biology Question Paper Pdf
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice Pdf
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Pdf in Hindi
Cell Biology Short Answer Questions
Cell Biology Test Bank Questions
Cell Biology Test Questions and Answers
Cell Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf
Cell Mcq Pdf
Cell Organelles Labeling Quiz
Cell Organelles Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Cell Questions and Answers
Cell Questions and Answers Pdf
Cell Questions Quizlet
Cell Structure and Function Pdf
Cell Structure and Function Pdf Class 11
Cell Structure and Function Quiz Answers
Cell Structure and Function Test Answer Key
Cell Structure and Function Test Pdf
Cells
Cells Questions
Cellular Organization Pdf
Chemical Equation for Aerobic Respiration
Chemistry Form 1 Questions and Answers
Chemistry Form 2 Exams
Chemistry Form 2 Questions and Answers
Chemistry Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf
Chemistry Form 3 Questions and Answers
Chemistry Form 3 Revision Questions
Chemistry Form 4 Questions and Answers
Chemistry Form One Questions and Answers Pdf
Chemistry Kcse Questions and Answer
Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers
Chemistry Paper 3 Question and Answer
Cie a Level Biology Notes 2016
Cie a Level Biology Notes Pdf
Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 Mcqs
College Biology Practice Test
College Biology Quiz
College Biology Quiz Chapter 1
College Biology Quizlet
College Biology Study Guide
College Biology Study Guide Pdf
College Biology Test Questions and Answers
Complete Biology for Cambridge Igcse Revision Guide Pdf
Cytology Mcqs With Answers Pdf
Difficult Questions on Gaseous Exchange in Animals
Download Form Three Biology Notes
Download Klb Biology Book 2
Easy Biology Questions
Easy Cell Questions
Edexcel a Level Biology B
Edexcel a Level Biology Notes Pdf
Edexcel a Level Biology Salters Nuffield
Edexcel A2 Biology Notes
Edexcel as Biology Revision Guide Pdf
Edexcel Biology A2 Revision Notes Pdf
Edexcel Biology Unit 2 Revision Notes
Edexcel Gcse Science Revision Guide Pdf
Energy Questions Science Bowl
Essential Cell Biology Test Bank Answers
Essential Cell Biology Test Bank Download Free
Exam Notes for Biology 101
Excretion Question and Answer Form 4 Work
Excretion Questions and Answers
Excretory System Questions and Answers Pdf
Excretory System Structure
F3 Biology Test Paper
Form 1 Biology Exam
Form 1 Biology Notes
Form 1 Biology Questions and Answers
Form 1 Biology Syllabus
Form 1 Mathematics Questions and Answers
Form 1 Mathematics Test Paper Pdf
Form 1 Revision Papers
Form 2 Biology Exam
Form 2 Biology Notes Pdf
Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers
Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers >
Form 2 Biology Syllabus
Form 2 Mathematics Questions and Answers
Form 3 Biology Book
Form 3 Biology Exam
Form 3 Biology Questions and Answers
Form 3 Chemistry Exam Paper
Form 3 Chemistry Questions and Answers Pdf
Form 3 English Exam Paper
Form 3 History Exam Paper
Form 3 Maths Exam Paper
Form 4 Biology Exam
Form 4 Biology Questions and Answers
Form Four Biology Book
Form Four Biology Revision Questions
Form Four Biology Syllabus
Form Four Biology Topics
Form One Biology Book
Form One Biology Questions
Form One Biology Revision Questions
Form One Biology Syllabus
Form One Biology Topics
Form One Geography Questions and Answers
Form One Notes of Biology
Form One Past Papers
Form Three Biology Book
Form Three Biology Notes
Form Three Biology Revision Questions
Form Three Biology Syllabus
Form Three Biology Topics
Form Three Cre Notes Pdf
Form Two Biology Book
Form Two Biology Examination
Form Two Biology Notes
Form Two Biology Revision Questions
Form Two Biology Syllabus
Form Two Biology Topics
Form Two Chemistry Cat
Form Two Chemistry Past Papers
Form Two Chemistry Questions and Answers
Form Two Chemistry Questions and Answers Pdf
Form Two Notes
Free a-level Biology Revision App | Pass Your Biology Exams
Free Biology Form 1 Notes
Free Biology Form 2 Notes
Free Biology Form 3 Notes
Free Biology Form 4 Notes
Free College Biology Practice Test
Free Kcse Revision Notes
Fun Biology Questions
Funny Biology Questions and Answers
Funny Biology Quotes
Funny Science Questions
Funny Science Questions to Ask
Gas Exchange Exam Questions
Gas Exchange Practice Test
Gas Exchange Quiz
Gcse Biology Exam Questions and Answers
Gcse Biology Past Papers
Gcse Biology Revision
Gcse Biology Revision Notes
Gcse Biology Revision Notes Pdf
Gcse Biology Revision Notes Pdf 9-1
Gcse Biology Revision Questions and Answers
Gcse Biology Textbook Pdf
Gcse Biology Topics – Pass My Exams: Easy Exam Revision Notes
General Biology Practice Test With Answers
General Biology Quiz
General Biology Test Questions and Answers
General Knowledge in Biology Human Body
General Science Mcq for Ssc
General Science Mcqs With Answers Pdf
General Science Notes Pdf
Geography Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf
Geography Form 1 Revision Questions
Geography Form 3 Questions
Good Biology Questions to Ask
Gre Biology Practice Test
Gre Biology Subject Test Pdf
Hard Biology Quiz Questions
Hard Science Questions and Answers
Hard Science Questions to Ask Your Teacher
High School Biology Final Exam Doc
High School Biology Final Exam Pdf
High School Biology Final Exam Questions
High School Biology Final Exam Questions and Answers
High School Biology Practice Test
High School Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf
How Does the Excretory System Work
How Many Chromosomes Do Gametes Have
How Many Copies of Each Gene Do Gametes Have
How Much Genetic Information Is Found in a Gamete
How to Study Biology: 5 Study Techniques to Master Biology
Hsc Biology 2018
Hsc Biology 2019
Ial Biology Notes
Ib Biology Question Bank by Topic
Igcse Biology Alternative to Practical Revision
Igcse Biology Notes 2017 Pdf
Igcse Biology Notes Edexcel
Igcse Biology Paper 6 Notes
Igcse Biology Revision Guide
Igcse Biology Revision Notes Pdf
Igcse Biology Revision Worksheets
Igcse Biology Znotes
Igcse Notes Chemistry
Igcse Physics Revision Notes Pdf
Interesting Biology Questions
Interesting Questions to Ask About Biology
Interesting Science Questions and Answers
Intro to Biology Quiz
K.c.s.e Mathematics Paper 1 2017
Kcse 2015 Biology Paper 3
Kcse 2016 Biology Paper 1
Kcse 2016 Biology Paper 2
Kcse 2017 Biology Paper 2
Kcse 2017 Papers
Kcse Biology Essay Questions and Answers
Kcse Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf
Kcse Biology Essays
Kcse Biology Essays Pdf
Kcse Biology Essays Pdf Form 1
Kcse Biology Essays Pdf Form 2
Kcse Biology Essays Pdf Form 3
Kcse Biology Essays Pdf Form 4
Kcse Biology Notes
Kcse Biology Notes Pdf
Kcse Biology Paper 1
Kcse Biology Paper 1 2017
Kcse Biology Paper 1 2017 Pdf
Kcse Biology Paper 2
Kcse Biology Paper 2 2013
Kcse Biology Paper 2 2015
Kcse Biology Paper 2 2017
Kcse Biology Paper 3 2016
Kcse Biology Paper 3 Past Papers
Kcse Biology Past Papers and Answers
Kcse Biology Practical Past Papers
Kcse Biology Practicals
Kcse Biology Questions and Answers
Kcse Chemistry Notes
Kcse Chemistry Paper 1 2013
Kcse Chemistry Paper 1 2016
Kcse Chemistry Paper 2 2014
Kcse Chemistry Paper 2 2016
Kcse Chemistry Past Papers
Kcse Chemistry Past Papers and Answers
Kcse Chemistry Practical
Kcse Cre Past Papers and Answers
Kcse English Paper 3 2016
Kcse Essays
Kcse Made Familiar Chemistry
Kcse Made Familiar Geography
Kcse Made Familiar Kiswahili
Kcse Made Familiar Mathematics Pdf
Kcse Mathematics Paper 1 2016
Kcse Mathematics Past Papers Pdf
Kcse Mock Papers Pdf
Kcse Past Papers
Kcse Past Papers 2012
Kcse Past Papers 2013
Kcse Past Papers 2014 Pdf
Kcse Past Papers 2017
Kcse Past Papers Biology
Kcse Past Papers Chemistry
Kcse Revision Question
Kcse Revision Question for Biology
Kcse Syllabus Pdf
Kenya Secondary School Chemistry Syllabus
Kenya Secondary School Syllabus Pdf
Klb Biology Book 2
Klb Biology Book 2 Notes
Klb Biology Book 2 Pdf
Klb Biology Book 3 Pdf
Klb Biology Form 1
Klb Biology Form 1 Notes
Klb Biology Form 1 Notes Pdf
Klb Biology Form 1 Pdf
Klb Biology Form 2 Book
Klb Biology Form 2 Notes
Klb Biology Form 2 Pdf
Klb Biology Form 3 Notes
Klb Biology Form 3 Pdf
Klb Biology Form 4 Notes
Klb Biology Form 4 Pdf
Klb Biology Form One
Klb Geography Form 3
Knec Biology Syllabus
Kusoma Biology Notes
Kusoma Biology Notes Pdf
Kusoma.com Past Papers
Made Familiar Biology Pdf
Made Familiar Mathematics
Mathematics Form 3 Questions and Answers
Mathematics Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf
Mcq on Cell Biology Class 9
Mcqs About Gaseous Exchange
Middle School Science Bowl Biology Questions
More Than 1800 Biology Questions and Answers to Help You Study
Most Tested Questions in Form 1 Biology and Their Answers
Most Tested Questions in Form 2 Biology and Their Answers
Most Tested Questions in Form 3 Biology and Their Answers
Most Tested Questions in Form 4 Biology and Their Answers
Most Tested Questions in Form Four Biology and Their Answers
Most Tested Questions in Form One Biology and Their Answers
Most Tested Questions in Form Three Biology and Their Answers
Most Tested Questions in Form Two Biology and Their Answers
Multiple Choice Questions on Biology
Multiple Choice Questions on Cell Structure and Function
O Level Biology Practical Experiments
Orm Three Biology Notes
Page Navigation
Past Paper Questions by Topic Biology
Pdf Biology Form 3
Physics Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf
Physics Form One Questions and Answers
Physics Questions and Answers Pdf for Competitive Exams
Plant and Animal Cell Organelles Quiz
Plant and Animal Cell Organelles Quiz Answers
Plant and Animal Cell Quiz for 5th Grade
Plant and Animal Cell Quiz Grade 8
Plant and Animal Cell Quiz Pdf
Plant Cell
Plant Cell Pdf Download
Plant Cell Questions and Answers
Plant Cell Test Questions
Practical Biology Experiments Pdf
Practical Biology Question and Answer Pdf
Preliminary Biology
Questions About Cells Biology
Questions and Answers on Gaseous Exchange
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 1
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 2
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 3
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 4
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Four
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form One
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Three
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Two
Questions Based to Introduction to Biology
Questions on Cell Structure and Function
Questions on Gaseous Exchange in Humans
Questions to Ask in Biology Class
Questions to Confuse Your Science Teacher
Respiration and Gas Exchange Worksheet
Respiration Notes My Elim Form Two
Revision Papers
Revision Quiz for Biology for Form Three
Science Bowl Biology Study Guide
Science Bowl Questions Biology
Science Bowl Questions Chemistry
Science Bowl Questions Earth Science
Science Bowl Questions Math
Science Bowl Questions Middle School
Science Bowl Questions Physics
Science Quiz for Class 9 Biology
Science Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10
Science Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10 Pdf
Science Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 9 Pdf
Simple Scientific Questions
Smart Questions to Ask a Physics Teacher
Smart Questions to Ask a Science Teacher
Snab Biology Revision Notes
The Animal Cell Quiz Answers
The Excretory System Answer Key
The Excretory System Worksheet Answers
The Plant Cell Quiz Answer Key
Tricky Biology Questions and Answers
Tricky Science Questions for Adults
Tricky Science Quiz Questions
Two Biology Revision Questions
Types of Respiration
What Are Gametes
What Are Gametes in Biology
What Are Gametes in Plants
What Are Gametes in Punnett Squares
What Are Gametes Quizlet
What Are the Types of Gametes
Working of Excretory System
Year 11 Biology
Znotes as Biology
Biology Questions and Answers Form 1
“Pdf” Revision Questions Biology Form 2
“Pdf” Revision Questions Biology Form 3
“Pdf” Revision Questions Biology Form 4
“Pdf” Revision Questions Biology Form Four
“Pdf” Revision Questions Biology Form One
“Pdf” Revision Questions Biology Form Three
“Pdf” Revision Questions Biology Form Two
1 a a KCSE Past Papers
10th Grade Biology Questions and Answers
10th Grade Biology Test
11th Ncert Biology
12th Class Biology Book Free Download
2014 KCSE Marking Schemes
2014 Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2015
2015 Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 4
2016 KCSE Papers
2016 KCSE Prediction Questions
2017 Biology Hsc Answers
2017 KCSE Prediction Questions
2018 Biology KCSE Leakage
2018 Biology KCSE Questions
2018 KCSE Busineness Studies
2018 KCSE Exam
2018 KCSE Leakage
2018 KCSE Prediction Questions
2018 KCSE Questions
2019 Biology KCSE Leakage
2019 Biology KCSE Questions
2019 KCSE Leakage
2019 KCSE Questions
9th Grade Biology Study Guide
A a a Biology Notes
a a a Biology Notes!
a a a BiologyNotes!
A a KCSE Past Papers
A Biblical View of Social Justice
A Level Biology Biological Molecules Questions
A Level Biology Exam Questions by Topic
A Level Biology Notes Edexcel
A Level Biology Notes Xtremepapers
A Level Biology Past Papers
A Level Biology Questions and Answers
a Level Biology Questions and Answers
A Level Biology Questions and Answers (Pdf)
A Level Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
A Level Biology Questions by Topic Kidney Questions With Markschemes
A Level Biology Revision
A Level Biology Revision Edexcel
A Level Biology Revision Guide
A Level Biology Revision Notes
A Level Biology Revision Notes Pdf
A Level Biology Textbook Pdf
A Level Biology Year 1 / as Aqa Exam Questions by Topic
A Level Edexcel Notes a* Biology
aa Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers
Advance KCSE Past Papers
Advance-africa.com KCSE Rev Quiz
Advantages and Disadvantages.
Aerobic Respiration in Plants
All Biology Essays
All Biology Notes for Senior Two
All KCSE Past Papers Biology With Making Schemes
All Marking Schemes Questions and Answers
All Past K.c.s.e Questions With Answers
Alliance Mocks 2017
Anaerobic Respiration Equation
Animal Cell Organelles Quiz Answers
Animal Cell Questions and Answers
Animal Cell Quiz
Animal Cell Quiz Labeling
Ap Bio Quizzes
Ap Biology 1 Textbook Pdf
Ap Biology Essay Questions and Answers
Are Sourced From KNEC.
As Level Biology Notes
Atika Biology Notes
Atika School Biology Notes
B/s Book 2 Notes
Basic Biology Books Pdf
basic Biology Interview Questions and Answers Pdf
Basic Biology Interview Questions and Answers Pdf
Basic Biology Pdf
Basic Biology Questions and Answers
Basic Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Bbc Bitesize Biology Ks3
Bihar Board Biology Objective Answer 2017
Bihar Board Biology Objective Answer 2018
Bio Answers
Bio Quesions
Biology 0478
Biology 101
Biology 12th
Biology 12th Class Notes Pdf
Biology 2019 Syllabus
Biology All KCSE Short Notes
Biology Answers
Biology Answers Online Free
Biology Answers Quizlet
Biology Bk 2 Notes
Biology Book 1
Biology Book 1 Notes
Biology Book 2
Biology Book 2 Notes
Biology Book 3
Biology Book 3 KLB
Biology Book 3 Notes
Biology Book 4
Biology Book 4 Notes
Biology Book 4 Pdf
Biology Book for Class 11
Biology Book Four
Biology Book Four Notes
Biology Book One
Biology Book One Notes
Biology Book Pdf Free Download
Biology Book Three
Biology Book Three Notes
Biology Book Three Pdf
Biology Book Two
Biology Book Two Notes
Biology Books Form Three
Biology Bowl Biology Study Guide
Biology Bowl Questions Biology
Biology Bowl Questions Earth Biology
Biology Bowl Questions Math
Biology Bowl Questions Middle School
Biology Brekthrough Form Two Notes
Biology Cell Structure Test
Biology Class 12 Ncert Solutions
Biology Class 12 Pdf
Biology Communication Syllabus
Biology Diagram of Female Reproductive System
Biology Diagram Software
Biology Diagrams for Class 11
Biology Diagrams for Class 12
Biology Diagrams for Class 9
Biology Diagrams for Class-10
Biology Diagrams in Form 1
Biology Diagrams in Form 2
Biology Diagrams in Form 3
Biology Diagrams in Form 4
Biology Diagrams Pdf
Biology Diagrams to Label
Biology Essay Questions and Answers
Biology Essay Questions and Answers 2018
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 1
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 2
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 3
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 4
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 4 Pdf
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Essay Revision Q
Biology Essays and Answers
Biology Essays Form One to Form Four
Biology Essays Form One to Form Three
Biology Essays KCSE
Biology Essays Pdf
Biology Exam 1 Multiple Choice
Biology Exam 2 Advance
Biology Exam 2 Test
Biology Exam 2016
Biology Exam Form Four
Biology Exam Form One
Biology Exam Form Three
Biology Exam Form Two
Biology Exam Practice Test
Biology Exam Questions
Biology Exam Questions and Answers
Biology Exam Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Exam Study Guide
Biology Exams
Biology Excretion Notes
Biology Exercise Form 4 With Answers
Biology Final Exam Answer Key
Biology Final Exam Answer Key 2016
Biology Final Exam Answer Key 2017
Biology Final Exam Answers 2018
Biology Final Exam Answers 2019
Biology Final Exam Questions and Answers
Biology Fom 1 Notes
Biology Fom 2 Notes
Biology Fom 3 Notes
Biology Fom 4 Notes
Biology Form 1
Biology Form 1 & 2 and Answers
Biology Form 1 and 2 Essays
Biology Form 1 and 2 Essays Questions and Answers
Biology Form 1 Chapter 1
Biology Form 1 Diagrams
Biology Form 1 Exams
Biology Form 1 Mid Year Exam
Biology Form 1 Notes
Biology Form 1 Notes and Questions
Biology Form 1 Notes Download
Biology Form 1 Notes Free Download
Biology Form 1 Notes GCSE
Biology Form 1 Notes KCSE-kcse
Biology Form 1 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 1 Notes Pdf Download
Biology Form 1 Past Papers
Biology Form 1 Pdf
Biology Form 1 Pressure
Biology Form 1 Question Papers
Biology Form 1 Questions
Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 1 Quiz
Biology Form 1 Revision Questions
Biology Form 1 Summary Notes
Biology Form 1 Syllabus
Biology Form 1 Work
Biology Form 1-4 Notes
Biology Form 2
Biology Form 2 Chapter 1
Biology Form 2 Chapter 2
Biology Form 2 Diagrams
Biology Form 2 Exam Paper 2014
Biology Form 2 Exams
Biology Form 2 Notes
Biology Form 2 Notes and Questions
Biology Form 2 Notes GCSE
Biology Form 2 Notes KCSE-kcse
Biology Form 2 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 2 Notes Pdf Download
Biology Form 2 Past Papers
Biology Form 2 Pdf
Biology Form 2 Question Papers
Biology Form 2 Questions
Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 2 Quiz
Biology Form 2 Revision Notes
Biology Form 2 Salts
Biology Form 2 Structure and Bonding
Biology Form 2 Summary Notes
Biology Form 2 Syllabus
Biology Form 2 Work
Biology Form 3
Biology Form 3 and 4 Essays
Biology Form 3 and 4 Essays Questions and Answers
Biology Form 3 Chapter 3
Biology Form 3 Classification
Biology Form 3 Diagrams
Biology Form 3 Ecology
Biology Form 3 Exams
Biology Form 3 Notes
Biology Form 3 Notes and Questions
Biology Form 3 Notes GCSE
Biology Form 3 Notes KCSE-kcse
Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf Download
Biology Form 3 Notes Topic 1
Biology Form 3 Past Papers
Biology Form 3 Pdf
Biology Form 3 Question Papers
Biology Form 3 Questions
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Term 3
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers+pdf
Biology Form 3 Quiz
Biology Form 3 Revision Notes
Biology Form 3 Revision Questions
Biology Form 3 Summary Notes
Biology Form 3 Syllabus
Biology Form 3 Syllabus Pdf
Biology Form 3 Topics
Biology Form 3 Work
Biology Form 4
Biology Form 4 All Chapter
Biology Form 4 Chapter 1 Conversion of Units
Biology Form 4 Chapter 1 Exercise
Biology Form 4 Chapter 1 Exercise and Answers
Biology Form 4 Chapter 1 Exercise Pdf
Biology Form 4 Chapter 1 Mind Map
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Exercise and Answers
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Exercise Pdf
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Experiment
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Formula
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Mind Map
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Momentum
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Objective Questions and Answers
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Paper 2
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Slideshare
Biology Form 4 Chapter 3
Biology Form 4 Chapter 3 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 4 Chapter 4
Biology Form 4 Chapter 4 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 4 Chapter 5 Light Questions and Answers
Biology Form 4 Chapter 5 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 4 Diagrams
Biology Form 4 Exam Paper 1
Biology Form 4 Exams
Biology Form 4 Exercise
Biology Form 4 Exercise Pdf
Biology Form 4 Module With Answer
Biology Form 4 Note
Biology Form 4 Notes
Biology Form 4 Notes (Pdf)
Biology Form 4 Notes All Chapter Pdf
Biology Form 4 Notes and Questions
Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 1
Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 2
Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 3
Biology Form 4 Notes Download
Biology Form 4 Notes Free Download
Biology Form 4 Notes GCSE
Biology Form 4 Notes KCSE-kcse
Biology Form 4 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 4 Notes Pdf Download
Biology Form 4 Paper 2 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 4 Past Papers
Biology Form 4 Question Papers
Biology Form 4 Questions
Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 4 Quiz
Biology Form 4 Revision Notes
Biology Form 4 Schemes of Work
Biology Form 4 Summary Notes
Biology Form 4 Syllabus
Biology Form 4 Textbook Pdf
Biology Form 4 Work
Biology Form 5 Chapter 1 Exercise and Answers
Biology Form 5 Chapter 1 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 5 Chapter 2 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 5 Chapter 2 Slideshare
Biology Form 5 Chapter 3 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 5 Notes Pdf
Biology Form Four Book
Biology Form Four Notes
Biology Form Four Notes and Questions
Biology Form Four Notes GCSE
Biology Form Four Notes Pdf
Biology Form Four Past Papers
Biology Form Four Questions
Biology Form Four Questions and Answers
Biology Form Four Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Four Quiz
Biology Form Four Study Notes
Biology Form Four Syllabus
Biology Form Four Topic 2
Biology Form Four Topic 4
Biology Form Four Topics
Biology Form Four Work
Biology Form One
Biology Form One Book
Biology Form One Book Pdf
Biology Form One Download Topic 1 Upto 3
Biology Form One Exam
Biology Form One Notes
Biology Form One Notes and Questions
Biology Form One Notes GCSE
Biology Form One Notes Pdf
Biology Form One Pdf
Biology Form One Questions
Biology Form One Questions and Answers
Biology Form One Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form One Questions and Their Answers
Biology Form One Quiz
Biology Form One Revision Question
Biology Form One Schemes of Work
Biology Form One Study Notes
Biology Form One Syllabus
Biology Form One Term Three Test
Biology Form One to Three Notes
Biology Form One Work
Biology Form Three
Biology Form Three Book
Biology Form Three Notes
Biology Form Three Notes and Questions
Biology Form Three Notes GCSE
Biology Form Three Questions and Answers
Biology Form Three Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Three Quiz
Biology Form Three Reproduction
Biology Form Three Reproduction.
Biology Form Three Study Notes
Biology Form Three Work
Biology Form Three-questions and Answers
Biology Form Two
Biology Form Two Book
Biology Form Two Diagrams
Biology Form Two Notes
Biology Form Two Notes and Questions
Biology Form Two Notes GCSE
Biology Form Two Notes Pdf
Biology Form Two Notes-pdf
Biology Form Two Pdf
Biology Form Two Questions
Biology Form Two Questions and Answers
Biology Form Two Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Two Quiz
Biology Form Two Study Notes
Biology Form Two Topics
Biology Form Two Work
Biology Form Two,schemes of Work
Biology Form2
Biology Form2 Textbook
Biology Game Form Four Question End Answers
Biology Grade 10 Exam Papers
Biology Hsc Pdf
Biology Human Reproduction Video
Biology IGCSE Past Papers Xtremepapers
Biology K.c.s.e 2017
Biology KCSE
Biology KCSE 2016
Biology KCSE 2017
Biology KCSE 2017 Paper 1
Biology KCSE Past Papers
Biology KCSE Questions
Biology KCSE Questions and Answer
Biology KCSE Quizzes & Answers
Biology KCSE Revision
Biology KCSE Revision Notes
Biology KCSE Setting Questions Form One and Two
Biology Ksce 2015
Biology Last Year K.c.s.e Questions
Biology Lesson Plan Form Two
Biology Made Familiar
Biology Mcq for Class 11
Biology Mcq for Class 12
Biology Mcq for Competitive Exams
Biology Mcq for Competitive Exams Pdf
Biology Mcq for Neet Pdf
Biology Mcq for Ssc
Biology Mcq Questions With Answers
Biology Mcq With Answers Pdf
Biology Mcqs for Class 12 Pdf
Biology Mcqs With Answers Pdf
Biology Mid Familia Form One
Biology Mock Papers
Biology Module Form 5
Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Cxc
Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Multiple Choice Questions With Answers Pdf
Biology Note
Biology Note Form Two All Chapters
Biology Notes
Biology Notes and Guestion and Answear
Biology Notes and Syllabus
Biology Notes Class 10
Biology Notes for Class 11 Pdf
Biology Notes for Class 12 Pdf
Biology Notes for High School Students
Biology Notes for IGCSE 2014
Biology Notes Form 1
Biology Notes Form 1 4
Biology Notes Form 1 Free Download
Biology Notes Form 1 KLB
Biology Notes Form 1 Pdf
Biology Notes Form 1-4
Biology Notes Form 1-4(1) Biology
Biology Notes Form 14
Biology Notes Form 2
Biology Notes Form 2 KLB
Biology Notes Form 2 Pdf
Biology Notes Form 2; Biology Notes
Biology Notes Form 3
Biology Notes Form 3 KLB
Biology Notes Form 3 Pdf
Biology Notes Form 4
Biology Notes Form 4 Chapter 2
Biology Notes Form 4 KLB
Biology Notes Form 4 Pdf
Biology Notes Form 4-pdf
Biology Notes Form Four
Biology Notes Form Four KLB
Biology Notes Form Four Pdf
Biology Notes Form One
Biology Notes Form One KLB
Biology Notes Form One Pdf
Biology Notes Form One to Form Four
Biology Notes Form Three
Biology Notes Form Three KLB
Biology Notes Form Three Pdf
Biology Notes Form Two
Biology Notes Form Two KLB
Biology Notes Form Two Pdf
Biology Notes Form2
Biology Notes IGCSE
Biology Notes Kenya
Biology Notes on Agroforestry
Biology Notes Pdf
Biology Notes:
Biology Objective Answer
Biology Objective Answer 2018
Biology Objective Questions for Competitive Exams
Biology Objective Questions for Competitive Exams Pdf
Biology Oral Exam Questions
Biology Paper 1
Biology Paper 1 2018 Marking Rules
Biology Paper 1 Notes
Biology Paper 1 Questions
Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers
Biology Paper 1 Topics
Biology Paper 1 With Answers
Biology Paper 2
Biology Paper 2 2017
Biology Paper 2 2018 Marking Rules
Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers
Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Paper 2 Revision
Biology Paper 2 Topics
Biology Paper 2018
Biology Paper 3 2018 Marking Rules
Biology Paper 3 Question and Answer
Biology Paper 3 Question Paper 2014 KCSE
Biology Paper 3 Question Paper 2015 KCSE
Biology Paper 3 Question Paper 2016 KCSE
Biology Paper 3 Question Paper 2017 KCSE
Biology Paper 3 Question Paper 2018 KCSE
Biology Paper 3 Questions and Answers
Biology Paper One Questions and Answers
Biology Paper One Topics
Biology Paper Two Qestions With Answers
Biology Paper1
Biology Paper2
Biology Paper3
Biology Paper4
Biology Past Papers
Biology Past Papers 2017
Biology Past Papers a Level
Biology Past Papers Form 1
Biology Past Papers Form 2
Biology Past Papers Form 3
Biology Past Papers O Level
Biology Pdf Download
Biology Pp1 KCSE 2016
Biology Practical Book Class 12 Pdf
Biology Practical Exam
Biology Practicals Form One
Biology Practicals Questions and Answers
Biology Practice Test 9th Grade
Biology Practice Test Answers
Biology Practice Test Questions and Answers
Biology Practice Test Quizlet
Biology Predicted Questions This Year KCSE
Biology Preparation Notes
Biology Pretest High School Pdf
Biology Question and Answer With Explanation
Biology Question and Answers 2019
Biology Question and Answers 2020
Biology Question and Answers 2021
Biology Question and Answers 2022
Biology Question and Answers Note
Biology Questions
Biology Questions and Answers
Biology Questions and Answers for High School
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf
Biology Questions and Answers for Secondary Schools
Biology Questions and Answers Form 1
Biology Questions and Answers Form 2
Biology Questions and Answers Form 3
Biology Questions and Answers Form 4
Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice
Biology Questions and Answers Notes
Biology Questions and Answers O
Biology Questions and Answers on Cells
Biology Questions and Answers Online
Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Questions and Answers Pdf for Class 12
Biology Questions and Answers Pdf for Competitive Exams
Biology Questions and Answers-form 2
Biology Questions for High School
Biology Questions for High School Students With Answers
Biology Questions for Senior 1
Biology Questions for Senior 2
Biology Questions for Senior 3
Biology Questions for Senior 4
Biology Questions for Senior 5
Biology Questions for Senior 6
Biology Questions for Senior Five
Biology Questions for Senior Four
Biology Questions for Senior One
Biology Questions for Senior Six
Biology Questions for Senior Three
Biology Questions for Senior Two
Biology Questions Form One
Biology Questions Multiple Choice
Biology Questions Quizlet
Biology Questions to Ask Your Teacher
Biology Quetion and Answer Form Four
Biology Quetion and Answer Form One
Biology Quetion and Answer Form Three
Biology Quetion and Answer Form Two
Biology Quiz for Class 9
Biology Quiz for Class 9 Biology
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10 Pdf
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 12
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 9
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 9 Pdf
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for High School
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers Multiple Choice
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Quiz Questions for Class 12
Biology Quiz Questions for College Students
Biology Quiz With Answers
Biology Quiz With Answers Pdf
Biology Quizlet
Biology Revision
Biology Revision a Level
Biology Revision Biology Notes Biology
Biology Revision Exam
Biology Revision Examination
Biology Revision Form One
Biology Revision Notes
Biology Revision Notes Biology
Biology Revision Notes Form 1
Biology Revision Notes Form 2
Biology Revision Notes Form 3
Biology Revision Notes Form 4
Biology Revision Notes IGCSE
Biology Revision Paper One
Biology Revision Questions
Biology Revision Questions and Answers
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form 1
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form 2
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form 3
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form 4
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form Four
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form One
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form Three
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form Two
Biology Revision Questions Form 1
Biology Revision Questions Form 2
Biology Revision Questions Form 3
Biology Revision Questions Form 4
Biology Revision Questions Form Four
Biology Revision Questions Form One
Biology Revision Questions Form Three
Biology Revision Questions Form Two
Biology Revision Quiz
Biology Revision Test
Biology Secondary School Revision
Biology Simple Notes
Biology Spm Notes Download
Biology Spm Notes Pdf
Biology Spm Questions
Biology Study Form 2
Biology Study Guide
Biology Study Guide Answer Key
Biology Study Guide Answers
Biology Study Guide Biology Questions and Answers
Biology Study Guide Ib
Biology Study Guide Pdf
Biology Study Guides
Biology Study Notes
Biology Study Notes Materials Form 1 Pdf
Biology Study Notes Materials Form 2 3 Pdf
Biology Study Notes Materials Form 2 Pdf
Biology Study Notes Materials Form 3 Pdf
Biology Study Notes Materials Form 4 Pdf
Biology Syllabus in Kenya
Biology Syllabus Pdf
Biology Test 1 Quizlet
Biology Test Questions
Biology Test Questions and Answers
Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Topic One Form Four
Biology Topics Form One
Biology Unit 1 Quiz
Biology Vol 3
Biology | Revision Biology
Biology,form 4
Biology.form Four.topic Three
BiologyExam Form Three
BiologyModule Form 5
BiologyNotes
BiologyNotes for Class 11 Pdf
BiologyNotes for Class 12 Pdf
BiologyNotes Form 1
BiologyNotes Form 1 Free Download
BiologyNotes Form 2
BiologyNotes Form 3
BiologyNotes Form 3 Pdf
BiologyNotes IGCSE
BiologyNotes Pdf
BiologyPast Papers
BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf
BiologySimple Notes
BiologySpm Notes Download
BiologySpm Notes Pdf
BiologySpm Questions
BiologyStudy Guide Answers
BiologyStudy Guide Pdf
BiologyStudy Guides
Blologytextpapers
Bridge Biology
Business Past KCSE Past Papers
Business Studies Form 3 Notes Pdf
Business Studies Form 4 Notes Pdf
C R E Form One KLB
C R E Form One Oli Topic
C.r.e Form 1 Notes Kenya
C.r.e Form 2 Notes Kenya
C.r.e Form 3 Notes
C.r.e Form 3 Notes Kenya
C.r.e Form 3 Pdf
C.r.e Form 4 Notes Kenya
C.r.e Form One Notes Pdf
C.r.e Notes Form 1
C.r.e Revision Notes
C.r.e Short Notes
Cambridge IGCSE Biology
Cambridge IGCSE Biology 3rd Edition
Cambridge IGCSE Biology 3rd Edition Plus Cd South Asia Edition
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Answers
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Coursebook Pdf Download
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Practical Workbook
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Pdf
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Study and Revision Guide 2nd Edition Pdf
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Study and Revision Guide Pdf
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Workbook Free Download
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Workbook Pdf
Cambridge IGCSE® Biology Coursebook
Caucasian Chalk Circle Essay Questions
Cell Biology Exam Questions and Answers
Cell Biology Exam Questions Pdf
Cell Biology Mcq With Answers
Cell Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf
Cell Biology Multiple Choice Questions Pdf
Cell Biology Previous Question Papers
Cell Biology Question Bank
Cell Biology Question Bank Pdf
Cell Biology Question Paper Pdf
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice Pdf
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Pdf in Hindi
Cell Biology Short Answer Questions
Cell Biology Test Bank Questions
Cell Biology Test Questions and Answers
Cell Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf
Cell Mcq Pdf
Cell Organelles Labeling Quiz
Cell Organelles Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Cell Questions and Answers
Cell Questions and Answers Pdf
Cell Questions Quizlet
Cell Structure and Function Pdf
Cell Structure and Function Pdf Class 11
Cell Structure and Function Quiz Answers
Cell Structure and Function Test Answer Key
Cell Structure and Function Test Pdf
Cells
Cells Questions
Cellular Organization Pdf
Chapter 1 Introduction to Biology
Chapter 1 Introduction to Biology Studies
Chemical Equation for Aerobic Respiration
Cie a Level Biology Notes 2016
Cie a Level Biology Notes Pdf
Cie Past Papers
Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 Mcqs
Class 8 Biology Notes KCSE-kcse
College Biology Notes
College Biology Practice Test
College Biology Quiz
College Biology Quiz Chapter 1
College Biology Quizlet
College Biology Study Guide
College Biology Study Guide Pdf
College Biology Test Questions and Answers
College Biology Volume 3 Pdf
College BiologyNotes
Complete Biology for Cambridge IGCSE
Complete Biology for Cambridge IGCSE Revision Guide Pdf
County Mocks 2017
Cse Past Papers Biology 2017
Cytology Mcqs With Answers Pdf
Difficult Questions on Gaseous Exchange in Animals
Dl Biology Form 3 Pdf Kusoma
Download Biology Form 1
Download Biology Form 2
Download Biology Form 2 Notes
Download Biology Form 3
Download Biology Form 3 Notes
Download Biology Form 4
Download Biology Form Four
Download Biology Form One
Download Biology Form Three
Download Biology Form Two
Download Biology Notes Form 3
Download Biology Notes Form One
Download BiologyNotes Form 3
Download Form Three Biology Notes
Download Free KCSE Past Papers Biology
Download Free KCSE Past Papers From KNEC.
Download KCSE Past Papers With Answers
Download KCSE Revision Notes
Download KLB Biology Book 2
Download KLB Biology Book 3
Download KLB Biology Book 4
Download Notes of Biology
Downloads | Biology | Form Four Exams | Exams
Downloads | Biology | Form One Exams | Exams
Downloads | Biology | Form Three Exams | Exams
Downloads | Biology | Form Two Exams | Exams
Downloads | KCSE Papers and Marking Schemes |
Dvance KCSE Past Papers
Easy Biology Questions
Easy Cell Questions
Edexcel a Level Biology B
Edexcel a Level Biology Notes Pdf
Edexcel a Level Biology Salters Nuffield
Edexcel A2 Biology Notes
Edexcel as Biology Revision Guide Pdf
Edexcel Biology A2 Revision Notes Pdf
Edexcel Biology Unit 2 Revision Notes
Edexcel GCSE Biology Revision Guide Pdf
Edexcel IGCSE Biology Past Papers
Edexcel IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Free Pdf Download
Edexcel IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Pdf
Edexcel IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Pdf Download
Electronics Form Four Notes
Energy Questions Biology Bowl
Essay Questions and Answers KCSE Biology Notes
Essay Questions and Answers on Betrayal in the City
Essay Questions Based on Betrayal in the City
Essential Cell Biology Test Bank Answers
Essential Cell Biology Test Bank Download Free
Evolving World Biology Book 1 Pdf
Evolving World Biology Book 4 Notes
Evolving World Biology Book Form 1
Evolving World-history Book 3
Exam Notes for Biology 101
Exams KCSE Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers
Excretion Question and Answer Form 4 Work
Excretion Questions and Answers
Excretory System Questions and Answers Pdf
Excretory System Structure
F3 Biology Test Paper
Find Download KCSE Past Papers With Answers
Find KCSE Biology Essay Questions and Answers
Form 1 Biology Exam
Form 1 Biology Notes
Form 1 Biology Questions and Answers
Form 1 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form 1 Biology Revision Notes
Form 1 Biology Summurized Revision Pdf
Form 1 Biology Syllabus
Form 1 Biology Test Paper Pdf
Form 1 Biology Topics
Form 1 BiologyNotes
Form 1 BiologyQuestions and Answers
Form 1 BiologyRevision Notes
Form 1 BiologySyllabus
Form 1 BiologyTest Paper Pdf
Form 1 Past Papers
Form 1 Past Papers With Answers
Form 1 Revision Papers
Form 1 Subjects in Kenya
Form 2 Biology Exam
Form 2 Biology Exam Paper
Form 2 Biology Exam Paper 2016
Form 2 Biology Exam Paper Free Download
Form 2 Biology Exam Paper With Answer
Form 2 Biology Final Year Exam Paper 2
Form 2 Biology Notes
Form 2 Biology Notes and Revision Questions
Form 2 Biology Notes Pdf
Form 2 Biology Past Papers
Form 2 Biology Questions
Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers
Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers >
Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form 2 Biology Revision Notes
Form 2 Biology Short Notes
Form 2 Biology Syllabus
Form 2 BiologyExam Paper
Form 2 BiologyExam Paper Free Download
Form 2 BiologyExam Paper With Answer
Form 2 BiologyFinal Year Exam Paper 2
Form 2 BiologyPast Papers
Form 2 BiologyRevision Notes
Form 2 BiologyShort Notes
Form 2 BiologySyllabus
Form 2 Revision Papers
Form 2 Subjects in Kenya
Form 3 Biology Book
Form 3 Biology Exam
Form 3 Biology Exam Paper
Form 3 Biology Notes
Form 3 Biology Past Papers
Form 3 Biology Questions
Form 3 Biology Questions and Answers
Form 3 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form 3 Biology Revision Notes
Form 3 Biology Syllabus
Form 3 BiologyExam Paper
Form 3 BiologyNotes
Form 3 BiologyPast Papers
Form 3 BiologyQuestions
Form 3 BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf
Form 3 BiologyRevision Notes
Form 3 BiologySyllabus
Form 3 C.r.e
Form 3 Notes of Biology Topic on Fish
Form 3 Past Papers
Form 3 Revision Papers
Form 3 Subjects in Kenya
Form 4 Biology Exam
Form 4 Biology Notes
Form 4 Biology Notes Pdf
Form 4 Biology Questions and Answers
Form 4 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form 4 Biology Revision Notes
Form 4 Biology Syllabus
Form 4 Biology Topics
Form 4 BiologyNotes
Form 4 BiologyRevision Notes
Form 4 BiologySyllabus
Form 4 BiologyTopics
Form 4 Exam Papers
Form 4 Revision Papers
Form 4 Subjects in Kenya
Form 5 Biology Topics
Form 5 BiologyTopics
Form Five Biology Notes
Form Five BiologyNotes
Form Four Biology Book
Form Four Biology Notes
Form Four Biology Notes Pdf
Form Four Biology Questions and Answers
Form Four Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form Four Biology Revision Questions
Form Four Biology Syllabus
Form Four Biology Topics
Form Four BiologyNotes
Form Four BiologyQuestions and Answers
Form Four BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf
Form Four BiologyTopics
Form Four Notes
Form Four Revision Papers
Form Four Subjects in Kenya
Form One Biology Book
Form One Biology Examination
Form One Biology First Topic
Form One Biology Lesson Plan
Form One Biology Notes Pdf
Form One Biology Past Papers Pdf
Form One Biology Questions
Form One Biology Questions and Answers
Form One Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form One Biology Revision Questions
Form One Biology Short Notes
Form One Biology Syllabus
Form One Biology Topics
Form One BiologyExamination
Form One BiologyPast Papers Pdf
Form One BiologyQuestions and Answers
Form One BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf
Form One BiologyTopics
Form One Exams
Form One Notes of Biology
Form One Past Papers
Form One Subjects in Kenya
Form One Term One Biology Exam
Form One Term One BiologyExam
Form Three Biology Book
Form Three Biology Book Pdf
Form Three Biology Notes
Form Three Biology Notes Pdf
Form Three Biology Questions and Answers
Form Three Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form Three Biology Revision Questions
Form Three Biology Syllabus
Form Three Biology Topics
Form Three BiologyNotes
Form Three BiologyNotes Pdf
Form Three BiologyQuestions and Answers
Form Three BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf
Form Three BiologyTopics
Form Three Subjects in Kenya
Form Two Biology Book
Form Two Biology Cat
Form Two Biology Examination
Form Two Biology Notes
Form Two Biology Notes Pdf
Form Two Biology Past Papers
Form Two Biology Questions and Answers
Form Two Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form Two Biology Revision Questions
Form Two Biology Syllabus
Form Two Biology Topics
Form Two BiologyNotes
Form Two BiologyNotes Pdf
Form Two BiologyQuestions and Answers
Form Two BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf
Form Two BiologySyllabus
Form Two BiologyTopics
Form Two Notes
Form Two Subjects in Kenya
Free a-level Biology Revision App | Pass Your Biology Exams
Free Biology Form 1 Notes
Free Biology Notes Form 1
Free Biology Notes Pdf
Free BiologyNotes Pdf
Free College Biology Practice Test
Free Form1,form2,form3 Past Papers Free KCSE Past Papers
Free KCSE Mocks 2015
Free KCSE Past Papers 2014
Free KCSE Past Papers KCSE Past
Free KCSE Past Papers Kenya,
Free KCSE Past Papers With Answers
Free KCSE Questions and Answers on Biology
Free KCSE Revision Notes
Free Marking Schemes
Free Mocks Online KCSE Answers Past Exams Question Papers
Free Revision Papers
From Three Notes Topic One KLB
Fun Biology Questions
Funny Biology Questions
Funny Biology Questions and Answers
Funny Biology Questions to Ask
Funny Biology Quotes
Gas Exchange Exam Questions
Gas Exchange Practice Test
Gas Exchange Quiz
GCSE Biology Exam Questions and Answers
GCSE Biology Past Papers
GCSE Biology Revision
GCSE Biology Revision Notes
GCSE Biology Revision Notes Pdf
GCSE Biology Revision Notes Pdf 9-1
GCSE Biology Revision Questions and Answers
GCSE Biology Textbook Pdf
GCSE Biology Topics Pass My Exams: Easy Exam Revision Notes
General Biology Notes Pdf
General Biology Practice Test With Answers
General Biology Quiz
General Biology Quiz Pdf
General Biology Test Questions and Answers
General Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf
General Knowledge in Biology Human Body
Good Biology Questions to Ask
GRE Biology Practice Test
GRE Biology Subject Test Pdf
Handbook of Biology Pdf Free Download
Hard Biology Questions
Hard Biology Questions and Answers
Hard Biology Questions to Ask Your Teacher
Hard Biology Quiz Questions
Hard Form 3 Biology Question
High School Biology Final Exam Doc
High School Biology Final Exam Pdf
High School Biology Final Exam Questions
High School Biology Final Exam Questions and Answers
High School Biology Notes
High School Biology Practice Test
High School Biology Pretest With Answers
High School Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
High School Biology Study Guide
High School Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf
High School BiologyNotes
High School BiologyStudy Guide
How Does the Excretory System Work
How Many Chromosomes Do Gametes Have
How Many Copies of Each Gene Do Gametes Have
How Much Genetic Information Is Found in a Gamete
How to Answer KCSE Biology Question
How to Motivate a Form 4 Student
How to Motivate a KCSE Candidate
How to Motivate a KCSE Student
How to Pass Biology Questions & Answers Form 1&2 | Text Book
How to Revise Biology
How to Revise Effectively for KCSE
How to Study Biology: 5 Study Techniques to Master Biology
Hsc Biology 2018
Hsc Biology 2019
Https://www.knec.ac.ke/ Www.knec-portal.ac.ke/ KNEC Portal:
Ial Biology Notes
Ib Biology Cold War Notes
Ib Biology Notes
Ib Biology Notes Pdf
Ib Biology of the Americas Notes
Ib Biology of the Americas Study Guide
Ib Biology Paper 2 Study Guide
Ib Biology Question Bank by Topic
Ib Biology Study Guide Pdf
Ict Notes Form 1
IGCSE Biology Alternative to Practical Revision
IGCSE Biology Alternative to Practical Revision Notes
IGCSE Biology Book
IGCSE Biology Book Pdf Download
IGCSE Biology Notes
IGCSE Biology Notes 2017 Pdf
IGCSE Biology Notes Edexcel
IGCSE Biology Paper 2 Notes
IGCSE Biology Paper 6 Notes
IGCSE Biology Past Papers
IGCSE Biology Past Papers 2014
IGCSE Biology Past Papers 2017
IGCSE Biology Pdf
IGCSE Biology Pre Release Material 2018
IGCSE Biology Resources
IGCSE Biology Revision Guide
IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Free Download
IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Pdf Download
IGCSE Biology Revision Notes Pdf
IGCSE Biology Revision Worksheets
IGCSE Biology Workbook Pdf
IGCSE Biology Znotes
IGCSE BiologyPast Papers
IGCSE Notes Biology
Importance of Agroforestry
Inorganic Biology Multiple Choice Questions With Answers Pdf
Inorganic Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Interesting Biology Questions
Interesting Biology Questions and Answers
Interesting Questions to Ask About Biology
Intro to Biology Quiz
Introduction of Biology Form One
Introduction to Biology
Introduction to Biology Notes
Introduction to Biology Pdf
Introduction to BiologyNotes
Is Agroforestry Sustainable?
K.c.s.e Answers Biology Paper One 2018
K.c.s.e Biology 2017
K.c.s.e Biology 2018
K.c.s.e Biology Paper 1 2017
K.c.s.e Mocks 2018
K.c.s.e Papers 2015
K.c.s.e Papers 2016
K.c.s.e Past Papers 2014
K.c.s.e.Biology Paper 2 Year 2018
K.c.s.e.results 2018 for Busia County
K.l.b Biology Form 3
K.l.b Biology Notes
K.l.b BiologyNotes
Kasneb Past Papers for Colleges Biology Past Papers
KCSE 2010 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2010 Past Papers
KCSE 2011 Biology Paper 1
KCSE 2011 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2012 Biology Paper 2 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2012 Marking Schemes
KCSE 2013 Biology Paper 1
KCSE 2013 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2013 Marking Scheme Pdf
KCSE 2014
KCSE 2015 Biology Paper 2
KCSE 2015 Biology Paper 3
KCSE 2015 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2015 Past Papers
KCSE 2016 Biology Paper 1
KCSE 2016 Biology Paper 2
KCSE 2017 Biology Paper 1
KCSE 2017 Biology Paper 2
KCSE 2017 Hostory Papers With Answers.com
KCSE 2017 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2017 Papers
KCSE 2017 Papers and Marking Scheme
KCSE 2017 Papers Pdf
KCSE 2017 Past Papers
KCSE 2017 Prediction Pdf
KCSE 2018 Biology and Answers
KCSE 2018 Biology Prediction
KCSE 2018 Leakage
KCSE 2018 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2018 Papers
KCSE 2018 Prediction Pdf
KCSE 2018 Predictions
KCSE 2018 Questions
KCSE 2018 Questions and Answers
KCSE 2019 Leakage Biology
KCSE 2019 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2019 Questions
KCSE 2019 Questions and Answers
KCSE 2020 Questions
KCSE 2020 Questions and Answers
KCSE Answers
KCSE Answers Past Exams Question Papers Downloads |
KCSE Biology 2011
KCSE Biology 2016
KCSE Biology Diagramsbiology Revision Tips
KCSE Biology Essay Questions and Answers
KCSE Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf
KCSE Biology Essays
KCSE Biology Essays Pdf
KCSE Biology Marking Schemes
KCSE Biology Notes
KCSE Biology Notes Pdf
KCSE Biology Notes, Syllabus, Questions, Answers
KCSE Biology Paper 1
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2011
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2012
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2013
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2015
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2016
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2017
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2017 Pdf
KCSE Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers
KCSE Biology Paper 2
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2012
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2012 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2015
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2013
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2014
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2015
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2016
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2017
KCSE Biology Paper 3
KCSE Biology Paper 3 2012
KCSE Biology Paper 3 2016
KCSE Biology Paper 3 2017
KCSE Biology Paper 3 Past Papers
KCSE Biology Past Papers
KCSE Biology Past Papers and Answers
KCSE Biology Past Papers Pdf
KCSE Biology Practical
KCSE Biology Practical 2015
KCSE Biology Practical 2016
KCSE Biology Practical Past Papers
KCSE Biology Practicals
KCSE Biology Practicals KCSE Biology Paper 1
KCSE Biology Question and Answer
KCSE Biology Questions and Answers
KCSE Biology Questions and Answers Ap Biology
KCSE Biology Revision
KCSE Biology Revision Notes
KCSE Biology Revision Papers
KCSE Biology Revision Questions
KCSE Biology Revision Questions and Answers
KCSE Biology Syllabus
KCSE BiologyNotes
KCSE BiologyPaper 1
KCSE BiologyPaper 2
KCSE BiologyPaper 2 Pdf
KCSE BiologySyllabus
KCSE Business Paper 1 2016
KCSE Business Past Papers
KCSE Business Studies Past Papers
KCSE Essay Questions in Betrayal in the City
KCSE Essays
KCSE Exam Papers 2018
KCSE Exam Papers Answers
KCSE Form 1 Biology Revision
KCSE Form 2 Biology Revision
KCSE Form 3 Biology Revision
KCSE Form 4 Biology Revision
KCSE Form Four Biology Revision
KCSE Form One Biology Revision
KCSE Form Three Biology Revision
KCSE Form Two Biology Revision
KCSE KCSE Past Papers KNEC
KCSE Leakage
KCSE Leakage Biology
KCSE Made Familiar Biology
KCSE Made Familiar Biology Pdf
KCSE Marking Scheme 2016
KCSE Marking Schemes
KCSE Marking Schemes 2017
KCSE Marking Schemes Pdf
KCSE Mock Exams
KCSE Mock Papers 2015
KCSE Mock Papers 2017
KCSE Mock Papers 2018
KCSE Mock Papers Pdf
KCSE Mock Papers Pdf 2018
KCSE Mock Papers Pdf KCSE Past Papers
KCSE Mocks 2017
KCSE Mocks 2018
KCSE Notes
KCSE Online Notes
KCSE Online Past Papers
KCSE Online Registration
KCSE Papers 2015
KCSE Papers and Marking Schemes | Exams
KCSE Past Papers
KCSE Past Papers 2007
KCSE Past Papers 2009
KCSE Past Papers 2010
KCSE Past Papers 2011
KCSE Past Papers 2011 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2012
KCSE Past Papers 2013
KCSE Past Papers 2013knec
KCSE Past Papers 2014
KCSE Past Papers 2014 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2015
KCSE Past Papers 2015 Marking Schemes
KCSE Past Papers 2015 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2016
KCSE Past Papers 2016 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2017
KCSE Past Papers 2017 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2018
KCSE Past Papers Biology
KCSE Past Papers Biology and Answers
KCSE Past Papers Biology Pdf
KCSE Past Papers Biology With Answers
KCSE Past Papers Biologyand Answers
KCSE Past Papers Business Studies and Answers
KCSE Past Papers KCSE and Answers
KCSE Past Papers KCSE and Answers Free Mocks Online
KCSE Past Papers Marking Scheme
KCSE Past Papers Pdf Download
KCSE Past Papers Pdf Download KCSE 2013
KCSE Past Papers With Answers
KCSE Past Papers Woodwork and Answers
KCSE Prediction 2017
KCSE Prediction 2018
KCSE Prediction 2018 Pdf
KCSE Prediction Papers 2018
KCSE Prediction Questions
KCSE Prediction Questions 2018
KCSE Prediction Questions and Answers
KCSE Questions
KCSE Questions and Answers
KCSE Questions and Answers.
KCSE Questions on Biology
KCSE Results, Online Registration, KCSE Result Slip.
KCSE Revision
KCSE Revision Notes
KCSE Revision Notes Biology
KCSE Revision Notes Pdf
KCSE Revision Papers
KCSE Revision Papers 2014
KCSE Revision Papers With Answers
KCSE Revision Question for Biology
KCSE Revision Questions
KCSE Revision Questions and Answers
KCSE Revision | Secondary School | Text Books | Text Book Centre
KCSE Syllabus Pdf
KCSE Trial 2017
KCSE Trial Exams 2017
Kenya Secondary School Biology Syllabus
Kenya Secondary School Biology Syllabus Pdf
Kenya Secondary School BiologySyllabus Pdf
Kenya Secondary School Syllabus Pdf
Kenya-kcse-christian Religious Education Syllabus
Kenyaplex KCSE Past Papers
Kenyaplex Past Papers for Secondary
KLB Biology Book 1 Download
KLB Biology Book 1 Notes
KLB Biology Book 1 Pdf
KLB Biology Book 2
KLB Biology Book 2 Notes
KLB Biology Book 2 Notes Pdf
KLB Biology Book 2 Pdf
KLB Biology Book 3 Notes
KLB Biology Book 3 Pdf
KLB Biology Book 3 Pdf Download
KLB Biology Book 4 Notes
KLB Biology Book 4 Pdf
KLB Biology Book 4 Pdf Download
KLB Biology Book 4 Topics
KLB Biology Book One
KLB Biology Form 1
KLB Biology Form 1 Notes
KLB Biology Form 1 Pdf
KLB Biology Form 2
KLB Biology Form 2 Book
KLB Biology Form 2 Notes
KLB Biology Form 2 Pdf
KLB Biology Form 2 Pdf Download
KLB Biology Form 2 Schemes of Work
KLB Biology Form 3
KLB Biology Form 3 Notes
KLB Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf
KLB Biology Form 3 Pdf
KLB Biology Form 3 Pdf Download
KLB Biology Form 4
KLB Biology Form 4 Notes
KLB Biology Form 4 Pdf
KLB Biology Form Four
KLB Biology Form Four Notes
KLB Biology Form One
KLB Biology Form One Notes
KLB Biology Form Three
KLB Biology Form Three Notes
KLB Biology Form Two
KLB Biology Form Two Notes
KLB Biology Notes
KLB Biology Notes Form 4
KLB Biology Pdf
KLB BiologyNotes
KLB BiologyNotes Form 4
KLB BiologyPdf
KNEC Biology Syllabus
KNEC Examiners Portal KNEC Website
KNEC Ict Past Papers
KNEC Past Papers for Colleges
KNEC Past Papers Free Download
KNEC Past Papers Free Downloads
KNEC Past Papers Pdf
KNEC Portal Confirmation
KNEC Portal KCSE Results
KNEC Portal KNEC Past Papers for Colleges Kasneb Past Papers
KNEC Revision Papers
KNEC Technical Exams Past Papers
Kusoma Biology Notes
Kusoma Biology Notes Pdf
Kusoma Notes Biology
Kusoma.co.ke
Kusoma.com Past Papers
Learner Guide for Cambridge IGCSE Biology
Longhorn Biology Book 3 Pdf
Made Familiar Biology
Made Familiar Biology Pdf
Made Familiar Biology Questions
Maktaba Tetea Notes
Marking Scheme KCSE Biology Past Papers
Math Form2 Note
Mcq on Cell Biology Class 9
Mcqs About Gaseous Exchange
Middle School Biology Bowl Biology Questions
Mock Past Papers 2017
Mock Past Papers With Answers
Mokasa Mock 2017
More Than 1800 Biology Questions and Answers to Help You Study
Multiple Choice Questions on Biology
Multiple Choice Questions on Cell Structure and Function
Necta Biology Past Papers
Necta Biology Practicals
Necta BiologyPast Papers
Necta BiologyPracticals
Necta Form Four Past Papers
Necta Past Papers Form 4
Necta Past Papers Form 4 2016
Necta Past Papers Form Six
Necta Past Papers Form Two
Necta Questions and Answers
Necta Review Questions
Notes Biology Form 1
Notes Biology Form 2
Notes Biology Form 3
Notes Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf
Notes Biology Form 3 Syllabus
Notes Biology Form 4 Syllabus
Notes on Biology Studies
Notes Za Biology 4m 2
Notes Za Biology Form One
Notes Za Biology Form Three
O Level Biology Practical Experiments
O Level Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Orm Three Biology Notes
Page Navigation
Papacambridge Biology IGCSE
Papers KNEC KCSE Online Past
Papers KNEC KCSE Results Past Papers
Past KCSE Papers
Past Paper Questions by Topic Biology
Past Papers 2014
Past Papers in Kenya
Pdf Biology Form 3
Pdf Biology Notes
Pdf Biology Notes Form 1
Pdf Biology Notes Form 2
Pdf Biology Notes Form 3
Pdf Biology Notes Form 4
Pdf Biology Notes Form Four
Pdf Biology Notes Form One
Pdf Biology Notes Form Three
Pdf Biology Notes Form Two
Pdf Form 1 Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form 3 Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form 4 Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form Four Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form One Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form Three Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form Two Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Free KCSE Past Papers and Marking Schemes
Pdf” Revision Questions Biology Form 1
Plant and Animal Cell Organelles Quiz
Plant and Animal Cell Organelles Quiz Answers
Plant and Animal Cell Quiz for 5th Grade
Plant and Animal Cell Quiz Grade 8
Plant and Animal Cell Quiz Pdf
Plant Cell
Plant Cell Pdf Download
Plant Cell Questions and Answers
Plant Cell Test Questions
Practical Biology Experiments Pdf
Practical Biology Question and Answer Pdf
Pre Mocks 2018
Preliminary Biology
Primary and Secondary Tillage Implements Ppt
Pte KNEC Past Papers
Questions About Cells Biology
Questions and Answers on Gaseous Exchange
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 1
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 2
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 3
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 4
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Four
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form One
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Three
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Two
Questions Based to Introduction to Biology
Questions on Cell Structure and Function
Questions on Gaseous Exchange in Humans
Questions on Introduction to Biology
Questions to Ask in Biology Class
Questions to Confuse Your Biology Teacher
Quizlet Biology Cells
Quizlet Biology Test
Quizlet Test Questions
Qustions in Biology and Answers
Radioactivity Form Four
Respiration and Gas Exchange Worksheet
Respiration Notes My Elim Form Two
Revision
Revision Biology Notes and Questions?
Revision Quiz for Biology for Form Three
S.1 Biology Questions
S.2 Biology Questions
S.3 Biology Questions
S.4 Biology Questions
Sample Essays on Betrayal in the City
School Biology Notes
Secondary Biology Notes
Secondary Biology Notes Pdf
Secondary BiologyNotes Pdf
Senior 1 Biology Notes
Senior 2 Biology Notes
Senior 3 Biology Notes
Senior 4 Biology Notes
Senior 5 Biology Notes
Senior 6 Biology Notes
Senior Five Biology Notes
Senior Four Biology Notes
Senior One Biology Notes
Senior Six Biology Notes
Senior Three Biology Notes
Senior Two Biology Notes
Simple Scientific Questions
Smart Questions to Ask a Biology Teacher
Snab Biology Revision Notes
Southwest Mock Paper 2 2016 Biology Only
Spm Biology Revision Notes
Spm Notes
Success Biology Spm Pdf
Success BiologySpm Pdf
Summary of Biology Form 3
Tahossa Past Papers
The Animal Cell Quiz Answers
The Excretory System Answer Key
The Excretory System Worksheet Answers
The Plant Cell Quiz Answer Key
To Motivate a Form 4 KCSE Student
To Motivate a Form 4 Student
Topical Revision Material
Tricky Biology Questions and Answers
Tricky Biology Questions for Adults
Tricky Biology Questions With Answers
Tricky Biology Quiz Questions
Two Biology Revision Questions
Types of Respiration
University Biology Volume 3 Openstax
University Biology Volume 3 Pdf
University Biology Volume 4 Pdf
Ur Revision Guide IGCSE Biology
What Are Gametes
What Are Gametes in Biology
What Are Gametes in Plants
What Are Gametes in Punnett Squares
What Are Gametes Quizlet
What Are the Types of Gametes
Working of Excretory System
Www.Biology Form One Notes.com
Www.Biology From One KLB.com
Www.form 1 Biology.com
Www.form 2 Biology.com
Www.form 3 Biology.com
Www.form 4 Biology.com
Www.form Four Biology.com
Www.form One Biology.com
Www.form Three Biology.com
Www.form Two Biology.com
Www.kusoma Notes
Www.kusoma Revision Materials
Www.kusoma.co.ke Biology Notes
Xtremepapers IGCSE Biology
Year 11 Biology
Z Notes Biology IGCSE
Znotes as Biology
15 Common Biology Questions From Form 1
15 Common Biology Questions From Form 2
15 Common Biology Questions From Form 3
15 Common Biology Questions From Form 4
15 Common Biology Questions From Form Four
15 Common Biology Questions From Form One
15 Common Biology Questions From Form Three
15 Common Biology Questions From Form Two
150 Common Biology Questions From Form 1
150 Common Biology Questions From Form 2
150 Common Biology Questions From Form 3
150 Common Biology Questions From Form 4
150 Common Biology Questions From Form Four
150 Common Biology Questions From Form One
150 Common Biology Questions From Form Three
150 Common Biology Questions From Form Two
2019 KCSE Exams Biology Papers
2019 KCSE Exams Papers
2020 KCSE Exams Biology Papers
2021 KCSE Exams Biology Papers
Best Biology Books for KCSE Knec
Biology
Biology 2 Topic Form Two
Biology Diagrams
Biology Form 1 and 2 Notes
Biology Form 1 Download
Biology Form 1 Notes Online
Biology Form 1 Notes Revision
Biology Form 1 Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 1 Revision Notes
Biology Form 1 Text Book
Biology Form 1 Text Book Notes
Biology Form 2 Download
Biology Form 2 Notes
Biology Form 2 Notes Online
Biology Form 2 Notes Revision
Biology Form 2 Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form 2 Pdf
Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 2 Revision Notes
Biology Form 2 Text Book
Biology Form 2 Text Book Notes
Biology Form 3 Download
Biology Form 3 Notes Online
Biology Form 3 Notes Revision
Biology Form 3 Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 3 Revision Notes
Biology Form 3 Text Book
Biology Form 3 Text Book Notes
Biology Form 4 Download
Biology Form 4 Notes Online
Biology Form 4 Notes Revision
Biology Form 4 Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 4 Revision Notes
Biology Form 4 Text Book
Biology Form 4 Text Book Notes
Biology Form Four Download
Biology Form Four Notes Online
Biology Form Four Notes Revision
Biology Form Four Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form Four Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Four Revision Notes
Biology Form Four Text Book
Biology Form Four Text Book Notes
Biology Form One Download
Biology Form One Notes Online
Biology Form One Notes Revision
Biology Form One Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form One Questions and Answers
Biology Form One Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form One Revision Notes
Biology Form One Text Book
Biology Form One Text Book Notes
Biology Form Three Download
Biology Form Three Notes Online
Biology Form Three Notes Revision
Biology Form Three Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form Three Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Three Revision Notes
Biology Form Three Text Book
Biology Form Three Text Book Notes
Biology Form Two Download
Biology Form Two Notes Online
Biology Form Two Notes Revision
Biology Form Two Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form Two Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Two Revision Notes
Biology Form Two Text Book
Biology Form Two Text Book Notes
Biology Full Exam Papers
Biology K.C.S.E Revision Papers
Biology KCSE Revision
Biology Notes Book Four
Biology Notes Book One
Biology Notes Book Three
Biology Notes Book Two
Biology Notes Form 2
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf
Biology Questions and Answers Form 1
Biology Questions and Answers Form 2
Biology Questions and Answers Form 3
Biology Short Note for Revising Form 1
Biology Short Note for Revising Form 2
Biology Short Note for Revising Form 3
Biology Short Note for Revising Form 4
Biology Short Note for Revising Form Four
Biology Short Note for Revising Form One
Biology Short Note for Revising Form Three
Biology Short Note for Revising Form Two
Biology Short Notes Form 1
Biology Short Notes Form 2
Biology Short Notes Form 3
Biology Short Notes Form 4
Biology Short Notes Form Four
Biology Short Notes Form One
Biology Short Notes Form Three
Biology Short Notes Form Two
Biologyy Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf
Brief Notes Biology Form 1
Brief Notes Biology Form 2
Brief Notes Biology Form 3
Brief Notes Biology Form 4
Brief Notes Biology Form Four
Brief Notes Biology Form One
Brief Notes Biology Form Three
Brief Notes Biology Form Two
Brief Notes Biology Form3 Chapter1
Download Book 1 Biology Notes
Download Book 2 Biology Notes
Download Book 3 Biology Notes
Download Book 4 Biology Notes
Download Book Four Biology Notes
Download Book One Biology Notes
Download Book Three Biology Notes
Download Book Two Biology Notes
Download Book1 Biology Notes
Download Book2 Biology Notes
Download Book3 Biology Notes
Download Book4 Biology Notes
Download KCSE Biology Study Notes
Download Secondary Subjects
Download Secondary Subjects in Kenya
Download Secondary Subjects KCSE
Exams Revision Kenya
Exams Revision Kenya KCSE
Expected Questions and Answers in Biology Form One
Form 2 Biology Notes
Form 2 Biology Notes Pdf
Form 2 Biology Topics
Form 3 Biology Book Pdf
Form Iii Topics of Biology Revisios
How to Answer Biology Paper 1 Questions?
How to Answer Biology Paper 2 Questions?
How to Answer Biology Paper 3 Questions?
How to Answer KCSE Biology Paper 1 Questions?
How to Answer KCSE Biology Paper 2 Questions?
How to Answer KCSE Biology Paper 3 Questions?
How to Answer Paper 1 Biology Questions?
How to Answer Paper 2 Biology Questions?
How to Answer Paper 3 Biology Questions?
K.C.S.E Revision Papers
K.C.S.E Revision Papers Biology
KCSE Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf
KCSE Biology Revisions
KCSE Biology Study Notes
KCSE Free Biology Qussions
KCSE Free Qussions
KCSE Revision Kenya
KCSE Revisions
Biology Form Two Questions
Revision Kenya
Revision Kenya Kcsse
Sammary Note for Biology Form 1
Sammary Note for Biology Form 2
Sammary Note for Biology Form 3
Sammary Note for Biology Form 4
Sammary Note for Biology Form Four
Sammary Note for Biology Form One
Sammary Note for Biology Form Three
Sammary Note for Biology Form Two
Www.last Year KCSE Exams.com
Biology Past Papers and Marking Scheme
Igcse Biology Past Papers
Igcse Biology Past Papers 2015
Igcse Biology Past Papers by Topic
Edexcel Igcse Biology Past Papers
[ad_2]
Source link
Comments
The Kenyan Digest Team

You may like

EXPOSED: How Kenya’s Student Leaders Have Been Silenced as Lecturers’ Strike Enters Another Week
Paul Biya’s Re-Election: What Cameroon’s Political Longevity Reveals About Leadership and Governance in Africa

Influencers for Sale: Inside the Government’s Attempt to Control Public Opinion Through the Cyber Crimes Bill 2025

How Powerful Politicians Are Using Proxies to Privatize Kenya’s Public Assets

President Ruto Congratulates Harambee Starlets, Pledges Sh1 Million Each After Historic WAFCON Qualification

15 Proven Ways to Make Money Online in Kenya; No Scams!

15 Proven Ways to Make Money Online in Kenya; No Scams!

President Ruto Congratulates Harambee Starlets, Pledges Sh1 Million Each After Historic WAFCON Qualification

How Powerful Politicians Are Using Proxies to Privatize Kenya’s Public Assets

Influencers for Sale: Inside the Government’s Attempt to Control Public Opinion Through the Cyber Crimes Bill 2025

EXPOSED: How Kenya’s Student Leaders Have Been Silenced as Lecturers’ Strike Enters Another Week
Paul Biya’s Re-Election: What Cameroon’s Political Longevity Reveals About Leadership and Governance in Africa

Why Mutahi Kahiga’s Remarks Might Be Part of President Ruto’s Larger Political Game
From Power to Prison: The Fall of France’s Former President Nicolas Sarkozy

8 Laws, One Moment: How Ruto Quietly Changed Kenya While the Nation Grieved Raila Odinga

The War in Ukraine: A Comprehensive Analysis of the Conflict
Trending
-

 General News1 week ago
General News1 week agoEXPOSED: How Kenya’s Student Leaders Have Been Silenced as Lecturers’ Strike Enters Another Week
-
Politics1 week ago
Paul Biya’s Re-Election: What Cameroon’s Political Longevity Reveals About Leadership and Governance in Africa
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoInfluencers for Sale: Inside the Government’s Attempt to Control Public Opinion Through the Cyber Crimes Bill 2025
-

 Business News1 week ago
Business News1 week agoHow Powerful Politicians Are Using Proxies to Privatize Kenya’s Public Assets
-
 General News7 days ago
General News7 days agoPresident Ruto Congratulates Harambee Starlets, Pledges Sh1 Million Each After Historic WAFCON Qualification
-

 Business News23 hours ago
Business News23 hours ago15 Proven Ways to Make Money Online in Kenya; No Scams!