Jobs
KCSE Biology Questions and Answers – KCSE Biology Revision
Published
7 years agoon
[ad_1]
Biology is a branch of science that deals with the study of living things. There are diverse forms of life
on earth ranging from the invisible microscopic living things to the gigantic life forms. It aims at
explaining the living world in terms of scientific principles.
It is important to note, however, that living
things interact with the non living things in the environment as Well. Biology, therefore also entails the
study of non living things as well.
The role of human beings in shaping the environment is also
investigated in biology.
In summary, biology deals with the study of origins, types, nature,
growth, development, interactions and maintenance of all life forms on earth.
Biology is such a broad field of knowledge. It is divided into two broad branches
1. Zoology– This is a branch of biology that deals with the study of animal life.
2. Botany– This is a branch of biology that deals with the study of plant life.
Within the two branches, there exist even smaller branches because the branches (botany and
Zoology) are very wide and complex.
a) Ecology– This is the study of the interrelationships between organisms and their
environment. Ecology aims at establishing how organisms are related to each other
and their environment.
Ecology is further subdivided into smaller branches. These
can be forest ecology, marine ecology, rangeland ecology etc.
b) Genetics– This sub-branch of biology deals with the study of inheritance and variation.
It deals with the study of how variations (differences) occur between parents and their
offspring. It is also concerned with how various characteristics are passed on from
parents to offspring.
c) Entomology– This is the study of insects.
d) Parasitology– This is the study of parasites.
e) Physiology– This deals with the study of the functions of various structures of an
organism. It deals with the processes that take place in the body of organisms.
This list is in-exhaustive as there are very many other branches of biology.
> Mitochondria are self replicative that is they can divide to form new ones.
Figure 5. The Mitochondrion (Animal)
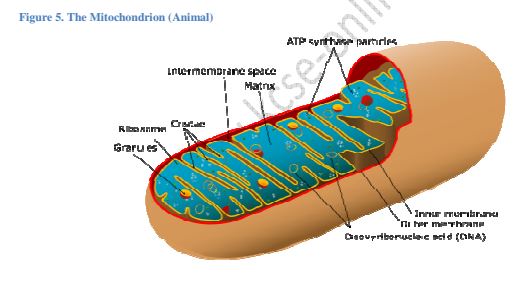
Figure 6, (generalize(lmage23 mitochondrion Structure)
throughout the cytoplasm.
referred to as rough or granular endoplasmic reticula. Endoplasmic reticula that are
not associated with ribosomes are called smooth endoplasmic reticula.
as enzymes. They also contribute to mechanical support.
e) Ribosomes
ribosomes are scattered within the cytoplasm (free ribosomes). Their largest dimension is
25 nanometres.
f) Lysosomes
enzvmes which break down large molecules. destroy Worn out oraanelles or even the
entire cells.
that might have been ingested in food. This explains their high relative abundance in
injured or infected cells.
out, they may destroy the whole cell.
g)Golgi bodies/Golgi apparatus
membrane.
1) They package and transport glycoproteins.
2) They are involved in secretion of synthesized proteins and carbohydrates.
3) They manufacture lysosomes.
Note: Golgi bodies are abundant in cells that are active in secretion. For instance pancreatic cells
which secrete enzymes and the nerve cells which secrete neurotransmitter substances.
h)Centrioles
organisms.
i) Chloroplasts
like stroma through which runs a system of membranes that are stacked together to form
grana.
photosynthesis.
j) Vacuoles
contain one large centrally placed vacuole.
the cell. This influences how materials move in and out of the cell.
the contractile vacuole excretes unwanted materials from the cell.
k) Cell wall
1. It gives plant cells their definite shape
2. It provides mechanical support and protection against mechanical injury.
3. The cell wall allows gases, water and other substances to pass through it.
i) Nucleus
nucleoplasm in which nucleolus and chromatin materials are suspended. The nuclear
membrane has minute pores, nuclear pores which allow materials to move in and out of
the nucleus.
hereditary materials.
Comparison between Plant Cells and Animal Cells
While there exist many similarities between plant and animal cells, there are a number of
differences.
Plant cells
Animal cells
Estimation of Cell Size
The light microscope can be used to estimate the size of a cell. Most cells have diameters
smaller than a millimeter. Due to this, cell sizes are always measures in smaller units.
These are micrometres and nanometers. These units of measurements are related as
shown below.
1 millimeter (mm) = 1000 micrometres (pm).
1 micrometer (pm) = 1000 nanometres (nm).
Procedure in cell size estimation
of cells.
microscope.
the first mark and the last one across the field of view. Count only the spaces between
two thick dark lines.
cell diameter = diameter of the field of view in micrometers divided by number of cells.
Cell Specialization. Tissues. Organs and Organ Systems
Cell Specialization/Cell Differentiation
specific functions
has a tail-like extension for swimming towards the ovum.
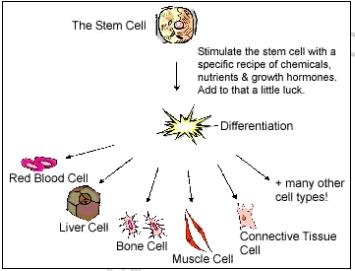
Tissues
same function.
a) Tissue types in animals
1. Epithelial tissue– This is a thin continuous layer of cells for lining and protection of
internal and external surfaces.
2. Skeletal muscle– This is a bundle or sheets of elongated cells with fibres that can
contract. Its contraction and relaxation brings about movement.
4. Blood tissue– This is a fluid containing red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets.
The main functions of blood tissue are transportation of nutrients and gases as well as
protection of the body against infections.
5. Connective tissue– This tissue consists of strong fibres that connects other tissues and
organs thereby holding them in position.
b)Tissue types in plants
1. Epidermal tissue– This is a single thin layer of cells covering the outer surfaces. It
protects inner tissues of plants from mechanical damage and infection.
2. Palisade tissue– This is a group of cells rich in chloroplasts containing chlorophyll. It has
a site for the absorption of light energy and manufacture of food by photosynthesis.
3. Parenchyma tissue– This tissue consists of special thin walled irregularly shaped cells.
They form packaging and storage cells.
4.Conducting tissue/Vascular bundle– This tissue consists of xylem and phloem. Xylem
conducts water and dissolved mineral salts in a plant while phloem conducts food
substances in solution.
Organs
function.
a) Heart– composed of connective, muscle, epithelial and blood tissues.
b) Kidney– Composed of connective, epithelial and muscle tissues
c) Brain– Composed of epithelial, connective tissues
d) Lungs– Composed of epithelial, connective tissues.
a) Roots– composed of epidermal, conducting and parenchyma tissues.
b) Flowers– This is composed of epidermal, conducting tissues.
c) Stem– Composed of conducting, parenchyma, and epidermal tissues and palisade
tissues in some cases
d) Leaves– Composed of palisade, conducting and epidermal tissues.
Organ system
This is a group of organs Whose functions are coordinated and synchronized to perform
the same function.
Organ systems are more pronounced in animals than in plants
Organ systems in animals include
a) Digestive system composed of organs such as oesophagus, stomach, intestines and
their associated glands.
b) Circulatory system composed of the heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries).
c) Excretory this is composed of kidney, liver, and blood vessels.
d) Respiratory system composed of trachea, bronchus, and lungs.
e) Reproductive system composed of the reproductive organs and associated glands.
f) Nervous systems composed of the brain, spinal cord, eye, ear organs.
Chapter Four: Cell Physiology
Introduction
activities of life or of living matter such as organs, tissues or cells. It aims at
understanding the mechanism of living.
the body cells of organisms.
perform various functions of life. In particular:
a) Chloroplasts play a vital role in carbohydrate synthesis.
b) Mitochondrion produces energy required to carry out life processes.
c) Ribosomes manufacture of proteins.
into the chloroplasts.
oxygen have to be taken into the mitochondrion. Energy, carbon (IV) oxide, water and
alcohol (in plants) are some of the end products of respiration.
harmful when allowed to accumulate in the cells. They, thus, have to be eliminated from
the cells.
organelles where these physiological processes are taking place. There is a constant
movement of materials across the cell membrane in the cells.
which materials move in and out of the cells.
Structure of the membrane
membrane and chloroplast membrane.
materials in and out of the cells.
(it is a lipoprotein layer) the overall thickness of the cell membrane is about 7.5 nm thick.
out of the cells.
Properties of the cell membrane
a) The cell membrane is semi permeable– The pores that occur on the cell membrane
allows the passage of the small size molecules but does not allow the passage of the large
sized molecules.
Such a membrane is said to be selectively permeable or semi-permeable.
In particular, when a cell is surrounded by a dilute sugar solution, the small sized water
molecules will enter the cell but the larger sugar molecules will not pass through the cell
membrane.
In contrast, the cell wall is permeable as it allows both sugar and water
molecules to pass through it; it has larger pores. This property of selectively permeability
enables the cell membrane to select what enters and leaves the cell.
b)The cell membrane is sensitive to changes in temperature and pH– Cell membranes
are made up of protein. Proteins are adversely affected by extreme changes in
temperature and pH.
Changes in temperature and pH will alter the structure of the cell
membrane thereby hindering the normal functioning of the cell membrane. High
temperature denatures (destroys) the proteins thereby impairing the functions of the cell
membrane.
c)The cell membrane possesses electric charges– The cell membrane has both positive
and negative charges. These charges affect the manner in which substances move in and
out of the ells. The charges also enable the cell to detect changes in the environment.
Physiological Processes of the Cell membrane
move in and out of the cells across the cell membrane.
a) Diffusion
b) Osmosis
c) Active transport
Diffusion
to another randomly. This movement of gas or liquid particles is observed to be from
regions of high concentration to a region of low concentration. The process by which
particles move from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration
is known as diffusion.
of the flower scent particles or perfume particles move from a region of high
concentration.
particles.
region of low concentration is known as the diffusion gradient/concentration gradient.
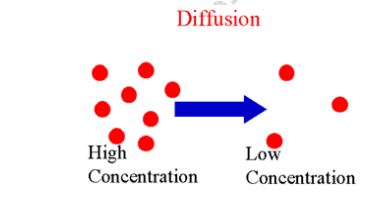
Demonstration of the process of diffusion using_potassium manganate (VII)
Requirements: potassium manganate (VII) crystals, glass tubing, 100 cm3 beaker and water.
Procedure
a) Hold the glass tubing vertically in a beaker so that one end of the tubing rests on the
bottom of the beaker.
b) Cautiously and quickly drop a crystal of potassium manganate (VII) through the upper
opening of the glass tubing.
c) Close the upper hand of the glass tubing with the thumb.
d) Half fill the beaker with water.
e) Carefully withdraw vertically the glass tubing so that the crystal is left undisturbed at the
bottom of the beaker.
f) Record your observations for the first 15 minutes.
g) Explain your observations.
Expected observations
the water and eventually all the water turned purple.
Explanation
manganate (VII) particles. The potassium manganate (VII) particles break away from the
crystals, dissolve in water and then diffuse through the water until they are evenly
distributed.
The Role of Diffusion in Living Organisms
a) In Plants
Diffusion plays an important role in plants in that:
water. For those salts whose concentration in soil water is higher that their concentration
in the cell sap of root hair cells, they move into the root hair cells through diffusion.
Plants require mineral salts for numerous life processes.
carbon (IV) oxide) diffuse across the stomata and lenticels of plants.
leaves to other parts of the plant.
b) In Animals
In animals diffusion plays the following important roles
of digestion such as amino acids and glucose diffuse across the wall of the ileum into the
blood for transport to other parts of the animal body.
gaseous exchange occurs at certain structures known as respiratory surfaces.
These
include the skin, gills, lungs, tracheal system and the cell membrane (in unicellular
organisms). Gaseous exchange at these surfaces occurs through the process of diffusion.
animals.
Factors affecting the rate of Diffusion
a) Diffusion gradient
the concentration of diffusing molecules also increases diffusion gradient with
corresponding regions hence increases the rate of diffusion.
b) Surface area to volume ratio
surface area to volume ratio, the greater the rate of diffusion will be. Conversely, low
surface area to volume ratio results in a low diffusion rate.
This is because the small organisms have a large surface area to volume ratio. As a result,
most of their body parts are closer to the external surrounding leading to faster diffusion.
foods, respiratory gases and waste products.
excretion. They have an additional transport system.
animals lose a lot of heat to the surrounding compared to the large animals.
c) Thickness of membranes and tissues
distance covered by the diffusing molecules is greater through the thicker membranes.
d) Size of molecules
e)Temperature
causing them to move faster, this implies that the rate of diffusion increases with increase
in temperature.
Osmosis
concentration (dilute solution) to a region of low concentration (concentrated solution)
through a semi permeable membrane.
solvent (Water) particles from a region of high concentration to a region of low
concentration.

Demonstration of Osmosis Using a Visking Tubing
Requirements
5OOcm3 beaker, visking tubing, a piece of thread, glass rod, concentrated sugar solution, 500 cm3
distilled Water.
Procedure
1. Into the beaker, put 350 cm3 of the distilled water.
2. Dip the visking tubing in water to moisten it. Open the visking tubing and tie one end
with the thread provided.
3. Half fill the visking tubing with the sugar solution provided and then tie the open end of
the tubing. Ensure no sugar solution spills out of the tubing.
4. Immerse the visking tubing into the distilled water in the beaker and suspend it using the
glass rod provided.
5. Leave the set up for about 30 minutes.
6. Record your observations.
7.Explain the observations made.
Observations
amount of water in the beaker decreased. This implies that water moved from the beaker
into the visking tubing.
Explanation
higher concentration of water molecules than the visking tubing. The water molecules
diffused from the beaker (where they are highly concentrated) into the visking tubing
(where they are lowly concentrated).
Even though there is a higher concentration of sugar
molecules in the visking tubing, they were not able to diffuse out of the visking tubing
due to their large molecular sizes. The visking tubing is semi permeable.
membranes that can be used in this experiment.
Osmosis explained
movement of water molecules from their region of high concentration (dilute solution) to
a region of low concentration (the highly concentrated solution) across the semi
permeable membrane. The semi permeable membrane does not allow movement of solute
particles across it.
same concentrations.
are said to be isotonic to each other.
hypotonic solution has less of the solute molecules but more of the solvent molecules.
particles is referred to as a hypertonic solution.
net movement of solvent molecules to any of the solutions since they have the same
concentration of solvent molecules.
Osmotic pressure
membrane, the concentrated solution will develop a force with which it draws water
through the semi permeable membrane from the distilled water.
itself.
Osmotic potential
from pure water when separated by a semi permeable membrane.
Water Relations in Animals
happen if an animal cell say red blood cell is placed in solutions of varying
concentrations
a) Red blood cell in hypotonic solution e. g. distilled water
cell cytoplasm.
When a red blood cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, water will move
into the cell through osmosis. The cell will swell and burst. Swelling of red blood cell
when placed in a hypotonic solution is referred to as haemolysis. The cell is said to be haemolysed.
b) Red blood cell in hypertonic solution
blood cell cytoplasm.
Water will, therefore, be drawn out of the cell into the hypertonic
solution. The cell will shrink and become small. The cell is said to be crenated.
The
process by which animal cells shrink and become smaller when placed in hypertonic
solutions is referred to as crenation.
c) Red blood cell in isotonic solution
When placed in an isotonic solution, the cell remains unchanged. This is because there
will be no net inflow or outflow of water between the cell and the solution.
Note:
that the body fluids and blood plasma surrounding the cells must be kept at the same
concentration as the animal cells.
This will prevent bursting or shrinking of the cells that
would otherwise impair their physiology.
same concentration.
Water Relations in Plants
contains vacuole with sap. The sap is a solution of salts and sugars and is bound by a
membrane, the tonoplast.
permeable.
a) Plant cell in hvpotonic solution e. g. distilled water
hypotonic solution through osmosis causing the cell to distend.
animal cells.
pressure on the cell wall called turgor pressure.
stretch until the cell cannot stretch any more. The cell becomes firm and is said to be
turgid.
it gains more water through osmosis.
pressure to stretching that is equal and opposite to turgor pressure called wall pressure.
b) A glam cell in a hygertonic solution
through osmosis. As the water moves out of the cell, the cell starts to shrink, becomes
less rigid or flabby and is said to be flaccid.
away from the cell wall towards the centre. The process through which plant cells lose
water, shrink and become flaccid is called plasmolysis.
called deplasmolysis.

Wilting
from the soil making the plant cells to lose their turgor pressure and droop.
through evapotranspiration is significantly reduced.
wilting and instead undergo permanent wilting.
Role of Osmosis in Organisms
soil through osmosis. Osmosis also helps in distribution and movement of water from the
roots to other parts of the plant.
When the cells of these plants take in water through osmosis, the cells become firm or
rigid and thus gain support.
surrounding the stomata synthesize glucose through photosynthesis in the presence of
light.
As glucose accumulates in the guard cells, the osmotic pressure of the guard cells
increase making them to draw water from adjacent cells through osmosis. When the
guard cells become turgid, they bulge outwards leading to opening of the stomata.
Opening of the stomata is crucial as it allows for gaseous exchange in plants. At night,
there is no glucose synthesis.
The glucose available in the guard cells is respired on
leading to reduction of glucose and consequently reduction in osmotic pressure. The
guard cells lose turgidity and close the stomata.
nitrogen deficient soils and trap insects from whence they obtain the nutrients. These
plants possess special structures that suddenly change their turgor pressure when
disturbed.
The change in turgor pressure enables the special structures to rapidly close
thereby trapping the insects.
through osmosis through the tubular walls. This enables animals to maintain the osmotic
pressure of the body fluids.
Factors Affecting the Rate of Osmosis
separated solutions have a greater difference in osmotic pressure. In summary, the greater
the concentration gradient, the greater the rate of osmosis and vice versa.
increases the energy content of the molecules.
while the rate of osmosis is greater through thinner membranes.
Active Transport
membrane and against a concentration gradient.
cells. In particular, there are some mineral salts that occur at low concentrations in the
soil water than in the cell sap.
Some of these mineral salts cannot be absorbed by the
plants through diffusion. A mechanism that would move them into the cells against the
concentration gradient will be useful.
on concentration gradient for them to take place.
the moving these substances across the membrane. These carrier molecules combine with
the substances being transported across the membrane and then move them from one side
of the membrane to the other side.
Role of active transport in living organisms
and saline environments
Factors affecting the rate of Active Transport
production process in living cells.
a) Oxygen concentration
Oxygen is required in respiration process that yields energy for active transport. Under low
oxygen concentration, the rate of respiration will be low hence there will be production of little
energy leading to low rate of active transport. Increase in oxygen concentration translates into a
higher energy production leading to high rate of active transport.
b) Change in pH
Change in pH affects the respiratory process which is enzyme controlled. Respiratory enzymes
require optimum pH for their efficient activity. Extreme pH conditions will increase lower the
rate of active transport since the enzymes controlling respiration Will be denatured.
c) Glucose concentration
Glucose is the chief respiratory substrate. At low glucose concentration, there will b less
production of energy leading to decreased rate of active transport. Rate of active transport
increases with increase in glucose concentration due to increase in the rate of energy production.
d ) Temperature
Temperature affects the enzyme controlled respiration process. At low temperatures, the
enzymes are inactive hence the rate of respiration will be low resulting into low rate of active
transport since there will be less production of energy. An increase in temperature increases the
rate of respiration since the enzymes become more activated. At temperatures beyond 40 degrees
celcius, the enzymes become denatured, respiration stops and so does active transport.
e) Presence of metabolic inhibitors e. g. cyanide.
These are substances which act as metabolic poisons. They stop the rate of respiration leading to
production of no energy. Active transport is, thus, stopped.
Nutrition Plants And Animals
Introduction
nutrients. It is one of the fundamental characteristics of living things.
The nutrients obtained are useful to the living organisms in many ways:
a) The nutrients are required for growth and development of the living organisms.
b) The nutrients are required for energy provision as they are broken down to release
energy.
c) They nutrients are also required for repair of worn out tissues
d) Nutrients are required for synthesis of very vital macromolecules in the body such as
hormones and enzymes.
Modes of nutrition
There are two main nutrition modes:
a) Autotrophism mode of nutrition through which living organisms manufacture their own
food from simple inorganic substances in the environment such as carbon (IV) oxide,
water and mineral ions. Organisms that make their own food through this mode are
autotrophs.
b) Heterotrophism mode of nutrition in which living organisms depend on already
manufactured food materials from other living organisms. Heterotrophs are the organisms
that feed on already manufactured food materials.
Autotrophism
In this mode of nutrition, organisms manufacture their own food from readily available
materials in the environment. These organisms use energy to combine carbon (IV) oxide,
water and mineral salts in complex reactions to manufacture food substances. Depending
on the source of energy used to manufacture the food, there are two types of
autotrophism:
a)Chemosynthesis
This is the process whereby some organisms utilize energy derived from chemical
reactions in their bodies to manufacture food from simple substances in the environment.
This nutrition mode is common in non green plants and some bacteria which lack the sun
trapping chlorophyll molecule.
b) Photosynthesis
the environment such as carbon (IV) oxide and water using sunlight energy.
and bacteria are also photosynthetic.
Importance of Photosynthesis
1. Photosynthesis helps in regulation of carbon (IV) oxide and oxygen gases in the
environment.
2. Photosynthesis enables autotrophs make their own food, thus, meet their nutritional
requirements.
3. Photosynthesis converts sunlight energy into a form (chemical energy) that can be
utilized by other organisms that are unable to manufacture their own food.
is important to understand the leaf structure.
External leaf structure
lamina- the broad flat surface, margin- the outline and the leaf apex.
leaves with some leaves reduced to needle like shape.
This helps reduce the rate of water
loss in such plants. However, the plants in areas of water abundance have broad leaves to
enable them lose the excess Water.


a) Cuticle
lower leaf surfaces.
Functions of the cuticle
a) Being waterproof, it minimizes water loss from the leaf cells to the environment through
transpiration and evaporation.
b) It protects the inner leaf tissues from mechanical damage.
c) It prevents entry of pathogenic microorganisms into the leaf.
b) Epidermis
are flattened and lack chloroplasts.
Functions of the epidermis:
a) It protects the leaf from mechanical damage.
b) It also protects the leaf from entry of disease-causing microorganisms.
c) It secretes the cuticle.
which exchange of materials occur. The opening and closing of the stomata is controlled
by the guard cells. Each stoma is controlled by two guard cells.
and thinner outer cell wall.
Adaptations of the guard cells
osmosis from the neighboring cells making them to open the stomata.
guard cells. As they draw water through osmosis, they bulge making the stomata to open.
c) Palisade mesophyll
sunlight for photosynthesis.
greener than the lower surfaces.
d) Spongy mesophyll layer
the cells which permits free circulation of gases carbon (IV) oxide and oxygen into the
photosynthetic cells. Spongy mesophyll cells contain fewer chloroplasts compared to
palisade cells.
e) Vascular bundle/tissue
tissues. Xylem tissues conduct Water and some dissolved mineral salts from the roots to
other plant parts while phloem translocates manufactured food materials from
photosynthetic areas to other plant parts.
Chloroplast
membrane bound organelle.
called stroma.
are contained in the grana.
place.
Adaptations of the leaf to photosynthesis
and for gaseous exchange.
molecules which trap sunlight energy for photosynthesis.
absorption of sunlight energy.
the photosynthetic cells and phloem to translocate manufactured food materials to other
plant parts.
Raw materials for photosynthesis
Conditions for photosynthesis
Photosynthesis Process
summarized into two main reactions.
a)Light reaction/Light stage
cannot take place.
i) Photolysis of water
and oxygen gas.
energy for photolysis.
plant for respiration.
Water– Hydrogen atoms + Oxygen gas
ii) Formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
plant tissues with a phosphate molecule to form Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP). ATP is
an energy rich molecule that stores energy for use in the dark stage when sunlight energy
could be unavailable.
ADP + P = ATP
b) Dark reaction/Dark stage
from the ATP formed during light stage.
(IV) oxide molecule with hydrogen ions to form a simple carbohydrate and a water
molecule.
synthesis reactions.
inactive. When a lot of simple sugars accumulate in the chloroplasts, osmotic pressure of
the guard cells would increase causing the guard cells to draw a lot of water through
osmosis. This makes the guard cells to bulge and open the stomata. This can result into
excessive water loss.
photosynthesis has taken place in a leaf, therefore, a test for presence of starch and not
simple sugars is carried out.

Testing for starch in a leaf
Requirements
Procedure
that the leaf has photosynthesized.
enzymes and stops any chemical reactions in the leaf.
boil in a water bath. Methylated spirit is highly flammable hence should be boiled
indirectly. Boiling with methylated spirit or alcohol decolourises the leaf (removes the
chlorophyll). This ensures that the leaf becomes white so that colour changes can be
observed easily when iodine is added.
leaf.
Observations
Factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis
a) Carbon (IV) oxide concentration
0.03%, an increase in carbon (IV) oxide concentration translates into an increase in the
rate of photosynthesis up to a certain point when the rate of photosynthesis becomes
constant.
At this point, other factors such as light intensity, water and temperature
become limiting factors.

b)Light intensity
level. Beyond the optimum light intensity the rate of photosynthesis becomes constant.
To this effect, plants photosynthesize faster on bright and sunny days than on dull cloudy
days.
and blue wavelengths of light for photosynthesis. Light duration also affects
photosynthesis rate.

c)Temperature
photosynthesis is slow because the enzymes are inactive. As temperature increases, the
rate of photosynthesis increases because the enzymes become more active.
Rate of
photosynthesis is optimum at (35-40) °C. Beyond 40°C the rate of photosynthesis
decreases and eventually stops since the enzymes become denatured.

d) Water
photosynthesis will be severely affected.
Experiment to investigate the gas produced during photosynthesis
Requirements
wooden blocks, test tubes, wooden splints and sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Procedure
a) Set up the apparatus as shown in the figure below
b) Place the set up in the sunlight to allow photosynthesis to take place.
c) Leave the set up in the sun until sufficient gas has collected in the test tube.
d) Test the gas collected with a glowing splint.
e) Record your observations.
Note:
of carbon (IV) oxide in the water since water has a low concentration of carbon (IV)
oxide.
the low light intensity in water where terrestrial plants cannot easily photosynthesize.
photosynthesis:
1) Carbon (IV) oxide concentration: Carry out the experiment using different
amounts of dissolved sodium hydrogen carbonate e. g 5 g, 10g, 15g, 20g and
examine the rate at which the gas collects.
2) Light intensity: An artificial light source can be used. Illuminate the plant and
vary the distance between the set up and the light source While recording the time
it takes for the gas jar to fill or counting the number of bubbles peer unit time.
3) Temperature: carry out the experiment at varying temperatures and record the
rate at which the gas collects.
Experiments on factors necessary for photosynthesis
Light
Requirements
boiling tube, light proof material e.g. aluminium foil, potted plant and clips.
Procedure
to ensure that all the starch in it is used up. This makes the leaves ideal for investigating
whether starch would form in the experimental period. This is called destarching).
leaves and one that was not covered.
Carbon (IV) oxide
Requirements
Procedure
Chlorophyll
lack chlorophyll.
place in them.
Procedure
Chemicals Of Life
and their reactions.
Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides
Properties of Monosaccharides
Benedict’s solution to red brown copper (I) oxide when heated.
Note:
a process known as condensation. Water molecules are produced in the process.
Functions
body.
Disaccharides
condensation.
is called glycosidic bond.
transported in plants
Properties of Disaccharides
as a complex reducing sugar.
Hydrolysis is the process through which complex molecules are broken down in the
presence of water molecules.
hydrolysis can be carried out by boiling the disaccharide in dilute aid such as
hydrochloric acid.
Functions
and inert nature.
Polysaccharides
condensation.
Properties of polysaccharides
Examples of polysaccharides
a) Starch– Made by linking numerous glucose molecules. It is a form in which
carbohydrates are stored in plants.
b) Glycogen– Is a storage carbohydrate in liver and muscles of animals. It is broken down to
glucose in animals when blood glucose falls.
c) Cellulose– This is a structural polysaccharide in plants. It is a component of the cell wall
d) Chitin– A structural carbohydrate found in cell wall of fungi and arthropod exoskeletons
Functions of polysaccharides
storing carbohydrates.
Lipids
oxygen but higher hydrogen compared to carbohydrates.
three fatty acids and a glycerol molecule are linked through a condensation reaction.
type of fatty acids that link up with the glycerol.
also form through condensation.
Properties of lipids
form emulsions
Functions
carbohydrates when oxidized per unit weight. However, they are less preferred as source
of energy because they require a lot of oxygen to oxidize. In addition, they are insoluble
hence not easy to transport to respiratory sites.
This explains why some desert animals such as camels store large quantities of fat in their
bodies.
shock absorbers.
conductors of heat hence do not conduct heat away from the body. Organisms in cold
areas tend to be short and plump as they have fatter fat adipose.
Proteins
nitrogen and sometimes phosphorous or sulphur or both.
Some proteins molecules contain other elements. In particular, haemoglobin contains
iron.
acids are of two kinds:
a) Essential– These are those amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the body
systems hence have to be supplied in the diet.
b) Non essential– These are amino acids that can be synthesized by the body
mechanisms hence do not need to be supplied in the diet.
group. Amino acids differ from each other by the alkyl group.
a) First class proteins– Contain all essential amino acids
b) Second class proteins– Proteins lack one or more essential amino acids
Protein synthesis
Several amino acids link up to form a polypeptide chain. Proteins are made up of long
chain polypeptides.
sequence in which the amino acids link up in the polypeptide chain.
Properties of Proteins
suspended in water.
organic solvents also denature proteins.
conjugated proteins such as:
Functions of proteins
a) They are structural compounds of the body. Cell membrane is protein in nature. Hair,
nails and hooves are made up of protein keratin.
b) Proteins are broken down to release energy during starvation when all carbohydrate and
lipid reserves are depleted.
c) Functional proteins play vital roles in metabolic regulation. Hormones are chemical
messengers while enzymes regulate the speed of metabolic reactions.
d) Proteins such as antibodies provide protection to the body against infections
e) Some protein molecules are transport molecules. Haemoglobin molecule plays a crucial
role in transportation of respiratory gases.
f) Proteins play a vital role in blood clotting e. g. fibrinogen.
g) Contractile proteins such as actin and myosin bring about movement.
Enzymes
What are enzymes?
Types of enzymes
a) Extracellular: Are produced within the cells but used outside the cells e. g. digestive
enzymes.
b) Intracellular: Are enzymes produced and used within the cells e. g. respiratory enzymes.
Importance of Enzymes
life.
DNA.
utilized by the cells.
poisonous substances less harmful.
Enzyme nomenclature
a).Trivial naming
Examples
b). Use of suffix -ase
or by adding the suffix to the reaction being catalyzed by the enzyme.
Substrates
Processes/Reactions
Hydrolysis ……………….. ..hydrolase
Reduction ………………… ..reductase
Oxidation …………………. ..oxidase
Mechanism of action of Enzymes
which the substrate molecules bind to the enzymes. The reaction is then catalyzed and the
end products released. The enzyme is free to bind with another substrate molecule. The
enzymes can be used again and again.

Properties of Enzymes
Factors affecting enzyme activity
a)Temperature
collisions leading to low enzyme activity.
increases leading to increased collisions hence increase in enzyme activity.
enzymes get denatured and their active sites get destroyed.
b)pH
under acidic conditions e. g. pepsin. However, most intracellular enzymes work better
under neutral conditions.
c)Enzyme Specificity
particular reaction.
d)Substrate Concentration
activity is low.
sites of the enzymes will be occupied and there will also be an increase in enzyme-
substrate collisions leading to increased reaction.
sites are utilized. The enzymes become the limiting factor of reaction. Increasing enzyme
concentration would increase the rate of enzyme activity.
e) Enzyme Concentration
beyond which the rate of reaction becomes constant.
and also fewer enzyme-substrate collisions that would lead to reactions.
increase in number of active sites and enzyme-substrate collisions.
Increasing substrate concentration increases the rate of reaction.
f) Enzyme co-factors
as vitamins.
reactions.
g) Co-enzymes
functioning. Some enzymes will not function without them.
Examples
NAD- Nicotine Adenine Dinucleotide.
FAD- Flavine Adenine Dinucleotide.
NADP- Nicotine Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate.
h) Enzyme inhibitors
1. Competitive
2. Non- competitive
Competitive inhibitors
up the shape of the substrates and compete for the active sites of the enzymes.
site for a long time) thereby slowing down the rate of enzyme activity.
Non competitive inhibitors
the enzyme at any site other the active site and alter the structure of the active site of the
enzyme. The normal substrate, therefore, fails to bind to the active site leading to
decreased rate of reaction.
Examples of non competitive inhibitors
Heavy metals (such as lead, mercury, silver), Cyanide, organophosphates such as malathion.
Heterotrophism
food substances such as carbohydrates, proteins and lipids.
food substances that can be absorbed and be utilized by the cells.
Modes of Heterotrophism
substances.
decomposition.
nutrients on another organism, the host.
mutually benefit from each other.
a) Parasitism
hosts and damage their tissues thereby weakening them.
b) Symbiosis
> Rhizobium and leguminous plants: rhizobium fixes nitrogen for the legume while
the bacteria obtains manufactured food from the legumes.
> Lichen: association of fungi (absorbing water and nutrients) and algae
(manufacturing food for the association.
> Catalase digesting bacteria and ruminants.
Dentition
utilized by the cells. The breakdown is both physical and chemical.
substances.
Types of Dentition
the same size and shape. Fishes and birds have homodont dentition.

incisors, canines, premolars and molars. Heterodont dentition is common with mammals
and reptiles.
a) Incisors

a. Canines
carnivores.
b. Premolar and molar

Classes of Holozoic Heterotrophs
a) Herbivores: heterotrophs that exclusively feed on vegetation.
b) Carnivores: heterotrophs exclusively feed on flesh.
c) Omnivores: heterotrophs that feed on both flesh and vegetation.
Dental Formula
a) i-incisors.
b) c-canines.
c) pm-premolars.
d) m-molars.
premolars and four molars on the upper jaw. On the lower jaw, it had eight incisors, no
canines, six premolars and six molars.
a) Write down its dental formula.
b) State its mode of feeding.
c) Give a reason.
Herbivores
pressed and cut by the lower incisors.
which allows the tongue to manipulate food.
out surfaces due to grinding.
grinding of grass.

Carnivores
carnassial teeth which have smooth sides and sharp edges to slice through flesh and crush
bones

Dental Diseases
a) Dental Carries
of vitamin D, lack of cleaning teeth and general ill-health. The bacteria in the mouth
break down the sugars to form energy and organic acids. The acids corrode the enamel.
b) Periodontal Diseases
of gums.
than children.
Are of two types:
a) Gingivitis– Characterized by reddening of gums, bleeding and pus in the gums.
b) Pyorrhea– The teeth become loose due to infection of the fibres holding the teeth in
the sockets.
Dental Hygiene
Digestion
chemically into simpler food substances that can be absorbed by body cells.
absorbed into the bloodstream without undergoing digestion.
bladder, salivary glands.


Digestion in the mouth
process is called mastication.
action.
from the salivary glands. The salivary glands are:
a) Sublingual salivary gland; beneath the tongue
b) Sub mandibular gland: under the jaw
c) Parotid gland: Found in the cheeks in front of the ears.
then pushed to the back of the mouth to initiate the swallowing process. The boluses are
then moved to the stomach via oesophagus. Movement is facilitated by a wave of
muscular contractions of longitudinal and circular muscles of the oesophagus known as
peristalsis.
swallowing.
Digestion in the stomach
the stomach via the cardiac sphincter (a muscular valve).
produce movements that mix the contents of the stomach. The mixing process is known
as churning and results in formation of a fluid called chyme
stimulates the gastric glands in the stomach walls to secrete gastric juice which contains:
a) Pepsinogen-This is activated to pepsin which breaks down proteins to peptides.
b) Rennin– Digests caseinogens protein in milk to casein (curd).
e) Hydrochloric acid– This:
d) Mucus– Forms a protective barrier to the stomach wall against corrosion by the
HC1. Mucus is secreted by goblet cells in the epithelial membrane of the
alimentary canal.

Duodenum
chyme is let down into the duodenum in small quantities.
a) Gall bladder in the liver- Secretes bile.
b) Pancreas- Secrete hormones and digestive enzymes.
i. Secretin hormone from the pancreas: Secretin stimulates secretion of pancreatic
juice into the duodenum
ii. Cholecystokinin from the duodenal wall: This stimulates secretion of bile from
the gall bladder.
a) Pancreatic amylase– This facilitates breakdown of the remaining starch into maltose
b) Trypsin– Digests proteins into peptides.
c) Pancreatic juice-Digests lipids into fatty acids and glycerol
d) Sodium hydrogen carbonate– This:
Provides alkaline medium for activity of the duodenum enzymes.
taurocholate. These salts:
i. Aid in emulsification (breakdown of fat molecules into tiny fat droplets to
increase surface area for digestion).
ii. The salts also provide a suitable alkaline medium for action of the duodenal
enzymes.
iii. In addition they neutralize the acidic chyme.

Digestion in the ileum
an alkaline fluid known as succus entericus (intestinal juice). The arrival of chyme in
ileum stimulates secretion of intestinal juice which contains:
a) Maltase: speeds up breakdown of maltose to glucose
b) Sucrase: speeds breakdown of sucrose to glucose and fructose
c) Peptidase: speeds breakdown of peptides to amino acids
d) Lipase: speeds breakdown of lipids to fatty acids and glycerol.
e) Lactase: speeds breakdown of lactose to glucose and galactose.
f) Polypeptidase: speeds breakdown of plypeptides into amino acids
Note:
The mucus secreted by the goblet cells lubricates food along the alimentary canal and
also protect the canal from being digested by enzymes.
At the end of digestion in the ileum, the resulting watery emulsion is called chyle; it
contains soluble end products of digestion ready to be absorbed.
Absorption
cellular lining of the villi.
are absorbed at the stomach. Alcohol is equally absorbed here without undergoing
digestion.
walls into the blood system by active transport.
transported to the liver before they are circulated to other body parts.
vessels. The lymphatic vessels later join the blood circulatory system which transports
them to other body parts.
a) It is long to provide a large surface area for absorption
b) It has a narrow lumen so as to bring the digested food into close contact with the
walls of the ileum for easier absorption
c) It is highly coiled to slow down movement of food thus allowing more time for
digestion and absorption of food.
d) The inner surfaces have numerous villi and microvilli to increase surface area for
absorption of end products of digestion.
e) The epithelial lining is one cell thick to reduce the distance through which
digested food diffuses.
f) Has a dense network of blood capillaries into which digested food materials
diffuse to increase transport and thus maintain a steep concentration gradient.
g) Have lacteal vessels in the villi for absorption of fatty acids and glycerol.

Egestion
> This is the process through which the undigested and indigestible food substances are
eliminated from the body.
Caecum and Appendix
herbivores.
digest cellulose since most digestive systems cannot secrete cellulose digesting enzyme.
The bacteria and the herbivores are in a symbiotic relationship.
Assimilation
a) Glucose
important structural compound in plants.
b) Fatty acids and glycerol
c) Amino acids
Vitamins
are also obtained in fresh fruits and vegetables.
quantities.
influence the intake of certain substances. In particular, vitamin C influences uptake of
iron while vitamin D influences absorption of calcium ions in the gut.
deficiency diseases. These deficiency diseases can be corrected by inclusion of the
deficient vitamins in the diet or taking the vitamin supplements.
a) Fat soluble vitamins– They dissolve in fats and are often stored in the liver.
Include Vitamins A, D, E, K.
b) Water soluble vitamins– Dissolve in water. Include vitamins B1, B2, B5, B12 and
C.
Vitamin A (retinol)
main food source
uses in the body
deficiency disease symptoms
Vitamin B1 (thiamine)
main food source
uses in the body
deficiency disease symptoms
Vitamine B2 (riboflavine and nicotinic acid)
main food source
uses in the body
deficiency disease symptoms
Vitamin B5 (pentathonic acid)
main food source
uses in the body
deficiency disease symptoms
Vitamin B12 (cobalamine)
main food source
uses in the body
deficiency disease symptoms
Vitamin C (absorbic acid)
main food source
uses in the body
deficiency disease symptoms
Vitamin D (calciferol)
main food source
uses in the body
deficiency disease symptoms
Vitamin E (tosopherol)
main food source
uses in the body
deficiency disease symptoms
Vitamin K (quinone)
main food source
uses in the body
deficiency disease symptoms
Mineral salts
body functioning. Depending on body requirements, mineral salts are of two classes:
a) Macro-nutrients: Nutrients required in large quantities. These include nitrogen,
sulphur, phosphorous, calcium, sodium, iron and magnesium.
b) Micro-nutrients: Nutrients required in small quantities. Include copper,
manganese, boron, iodine and cobalt.
Element: Nitrogen
source
function in the body
deficiency symptoms
–
Element: Phosphorous
source
function in the body
deficiency symptoms
Element: Calcium
source
function in the body
deficiency symptoms
Element: Iodine
source
function in the body
deficiency symptoms
Element: Potassium
source
function in the body
deficiency symptoms
Element: Iron
source
function in the body
deficiency symptoms
Element: Sodium
source
function in the body
Element: Chlorine
source
function in the body
Element: Sulphur
source
function in the body
Element: Magnesium
source
function in the body
deficiency symptoms
Roughage
walls.
vegetables.
Importance of roughage
a) It rubs against the walls of the alimentary canal stimulating secretion of digestive
enzymes and mucus to lubricate the epithelial lining.
b) Roughage enhance peristalsis since as they rub against the walls of the alimentary canal,
they stimulate contraction and relaxation of the muscles.
c) Roughage is an absorbent; it extracts water from the alimentary canal making the fecal
matter bulky and moist hence can be easily propelled by peristaltic movements. This
prevents constipation.
Factors affecting energy requirements in humans
Discuss how the following factors affect energy requirements in humans:
KCSE Biology Questions and Answers Form 2 – Biology Form Two Notes
K.C.S.E ONLINE REVISION
BIOLOGY NOTES FORM 2
1. a) i) Define transport
ii) Explain the necessity of transport in plants and animals
b) i) Describe the structure and function of root hair
particles
salts
ii) State ways in which the root hairs are adapted to their functions
mineral salts
c) i) Compare the internal structure of a dicotyledonous root and a monocotyledonous root
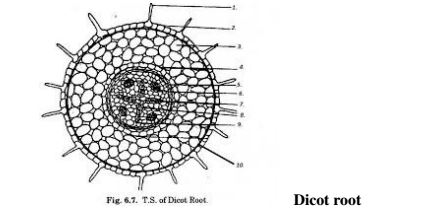
Monocot root
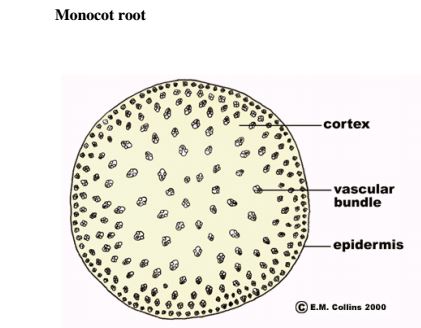
root
Similarities
Differences
Monocotyledonous
Dicotyledonous
iii) Compare the internal structure of a monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous stem
Monocotyledonous stem
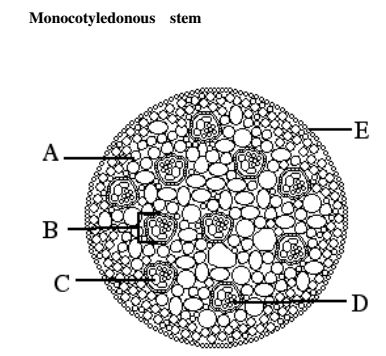
Dicotyledonous stem
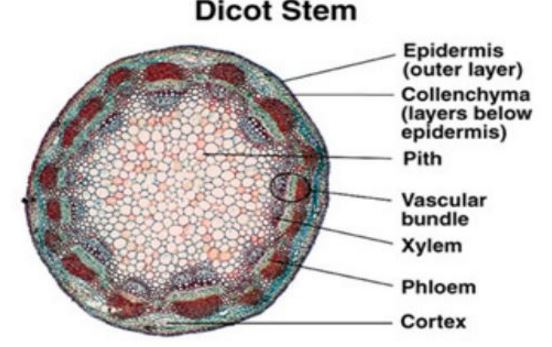
i) Give the similarities and differences between a monocotyledonous and
dicotyledonous stem
Similarities
Differences
Monocotyledonous
Dicotyledonous
arranged in a concentric ring near
the epidermis
State the differences between the internal structure of a root and a stem.
c) i) Name the transport structures of a flowering plant
ii) State the ways in which xylem vessels are adapted to their function
a) i) Why do flowering plants need water?
ii) Describe the movement of water from the soil to the leaves of a tall plant
the soil, thus drawing the Water molecules across the cell wall and cell membrane into the
root hair by osmosis
that in the adjacent cortex cells of the root
from cell to cell by osmosis, across the endodermis by active transport into xylem vessels
of the root that conduct water into xylem vessels of the stem into xylem vessels of the
leaves
Stem
(capillary), root pressure, attraction of water molecules to each other (cohesion).
xylem of leaves
column up to the tree leaves
Leaves
from the spongy mesophyll cells their sap becomes more concentrated than the adjacent
cells as the result water flows into the cell from other surrounding cells which in turn
takes in water from xylem vessels within the leaf veins this creates a pull(suction force)
called transpiration pull that pulls a stream of water from xylem vessels in the stem and
roots .
the leaves.
iii) Name the process by which mineral salts enter into a plant
i) Explain the forces that make water and mineral salts move through a plant
the mineral ions in sap and those in soil solution
salts through a plant against a concentration gradient
cells of stem
the air
/exudation
ii) Explain the uptake of mineral salts by plants
then carried to the stems and leaves
b) i) What is transpiration?
ii) Name the sites through which transpiration takes place in a plant
iii) State the importance of transpiration to plants
excess transpiration causes wilting
i) Explain the structural factors that affect the rate of transpiration in plants
are open transpiration rate is high
transpiration
rate. Absence of cuticle also increase rate of transpiration
ii) Explain the environmental factors that affect rate of transpiration in plants
leading to higher rate of transpiration
atmosphere
rate evaporation of water
iii) State the structural differences between xylem vessels and sieve tubes
iv) State the adaptations of plants which enable them to reduce water loss
water vapour concentration gradient leading to lower rate of evaporation
v) State the factors that cause increase in the rate of transpiration from leaves
vi) Explain how drooping of leaves on a hot sunny day is advantageous to a plant
c) Explain how aquatic and terrestrial plants are adapted to deal with problems of
transpiration
a. Mesophytes
b. Xerophytes
c. Hydrophytes
d) i) What is translocation
ii) Name the tissue which is responsible for translocation of manufactured food in flowering plants
iii) Name the processes that bring about the translocation of manufactured food
iv) Draw a labeled diagram to represent phloem tissue
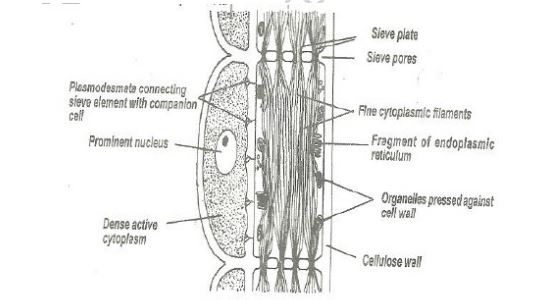
ii) State the functions of the labbeled structures cytoplasmic strands
Companion cell
supply nutrients to sieve tube element
Sieve tubes element
iii) name the compounds that are translocated in phloem
Describe an experiment you would carry out in order to demonstrate that phloem
transports manufactured food substances in a plant
a. Ringing experiment
ii) Use the radio-active tracers
iii) Collecting exudate from stylets of aphids
e) Describe an experiment you would carry out to demonstrate that xylem transports
water
i. Either
young plant in a beaker
ii. OR
2. a) i)List the components of animal transport systems
ii) Distinguish between closed and open circulatory systems
arthropoda
iii) What are the advantages of the closed circulatory system over open circulatory system?
iv) Distinguish between single circulatory system and double circulatory system Single
circulatory
b) i) Describe the general layout of the transport system in mammals
oxide and metabolic wastes
arteries to veins
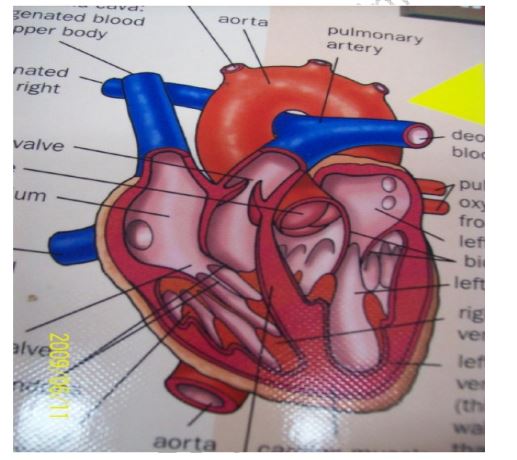
ii) Describe the structure and function of the mammalian heart
chambers, the auricles
ventricle
over again
iii) Explain how the mammalian heart is adapted to performing its functions
nervous stimulation
the tricuspid valve
right ventricle
valve(mitral)
aorta for distribution into the whole body
ventricle to be able to generate enough pressure to push blood to the whole body
carbon IV oxide removal, it is supplied with blood by the coronary arteries and drained
by the coronary veins
iv) Explain why blood leaving the lungs may not be fully oxygenated
e) Describe the structure and functions of the blood vessels
i. Arteries
lungs for oxygen
ii. Capillaries
movement of blood into them
iii. Veins
lungs
b) i) State the ways in which the composition of blood in the pulmonary arterioles differs from that in the pulmonary venules
pulmonary arterioles
pulmonary venules
ii) Give the reasons why pressure of blood is greater in the arterioles than I the veins of
mammals
reduces pressure
less/thinner muscular walls which reduce pressure
iii) Name the common heart diseases in humans
c) i) State the functions of mammalian blood
ii) Describe how mammalian blood components carry out their functions Plasma
from small intestines to liver and other body tissues
Red blood cells (Erythrocytes)
White blood cells (leucocytes)
Blood platelets (thrombocytes)
iii) State the Ways in which the red blood cells are adapted to their functions
oxide
oxide
oxygen and carry away carbon IV oxide
iv) State the structural differences between a red blood cell and a white blood cell.
Red blood cells
White blood cells
v) State the functional differences between a red blood cell and a White blood cell
Red blood cell
White blood cell
How does the heart increase blood flow to some parts of the body during exercise
Explain how oxygen and carbon Iv oxide are transported in the blood
Oxygen
and capillary walls into plasma and red blood cells
to form oxygen and haemoglobin
capillaries diffuses into body cells for respiration
Carbon IV oxide
red blood cells due to concentration gradient
the lungs
diffuses into alveolar cavity due to concentration gradient
Most carbon IV oxide is transported from tissues to lungs within the red blood cells and
not in the blood plasma. Give the advantages of this mode of transport.
loading(combining) and offloading of carbon (iv) oxide
vessel
ii) Name a protein, vitamin, an enzyme and a mineral element involved in blood clotting
iii) describe the blood clotting process
K
iv) State the role of blood clotting on wounds
v) Explain why blood flowing in blood vessels does not normally clot
iii. Explain the meaning of :
Universal donor
Universal recipient
iii) What is the difference between rhesus positive and Rhesus negative blood samples?
vi) What is blood transfusion?
v) Under what conditions would blood transfusion be necessary in people?
vi) How can low blood volume be brought back to normal?
How may excessive bleeding result in death?
leading to low oxygen, loss of nutrients and dehydration.
State the precautions that must be taken before blood transfusion
factor
j) i) What is immunity?
ii) Distinguish between natural and acquired immunity
iii) What are allergic reactions?
e.g. dust, pollen, perfumes, smoke etc.
vi) How does an allergic reaction occur?
ii) State the role of vaccination against certain diseases
3. a) i) What is gaseous exchange?
ii) Why is gaseous exchange important to organisms?
b) i) name the structure used for gaseous exchange by plants
ii) Briefly describe the structure of stomata
photosynthesis to occur
iii) State the factors which affect stomatal opening
iv) Name the theories suggesting the mechanism of opening and closing of stomata
v) Describe the mechanism of opening and closing of stomata
flaccid
concentration is lowered, pH increases, guard cells become turgid causing stomata to
open.
and causes then to open
guard cells therefore causes stomata to open.
i) What is the advantage of having stomata open during daytime and having them
closed at night?
take place and allows diffusion of oxygen out of the leaf
mineral slats
water available in the soil.
c) i) State the ways in which leaves of plants are adapted to gaseous exchange
ii) Describe how gaseous exchange takes place in terrestrial plants
oxide is produced
diffusion/concentration gradient
cell
iii) State the ways in which floating leaves of aquatic plants are adapted to gaseous
exchange
iv) How is aerenchyma tissue adapted to its function?
v) Explain stomatal distribution in plants of different habitats
sides then upper side has very few
d) i) List the types of respiratory surfaces of animals
ii) State the characteristics of respiratory surfaces in animals
iii) Describe gaseous exchange in protozoa
e) i) Make a labeled drawing of a fish gill
ii) How is a fish gill adapted to its function?
iii) Discuss gaseous exchange in bony fish
increased and pressure is lowered
this raises the pressure, forcing water over gills and out through the operculum
pressure) into the blood stream.
gradient, and is transported to the gills and diffuses out into the water.
iv) What is counter-flow system?
vi) What is the advantage of counter-flow system?
f) i) Describe the mechanism of gaseous exchange in terrestrial insects
abdominal muscles
gradient
the air.
ii) State how traceholes are adapted to gaseous exchange
g) i) What is breathing?
surrounding.
ii) Name the structures in humans that are used in gaseous exchange
iii) Describe the mechanism of gaseous exchange in a mammal
Breathing in
Breathing out
the ribcage downwards and inwards
iv) Explain how mammalian lungs are adapted to gaseous exchange
and carbon IV oxide to the lungs
v) Name the features of alveoli that adapt them to their function
vii) How is the trachea of a mammal suited to its function?
viii) State the advantages of breathing through the nose rather than through the
mouth
ix) Give the conditions under which the carbon iv oxide level rises above normal in
mammalian blood
x) Explain the physiological changes that occur in the body to lower the carbon iv
oxide level back to normal when it rises
tissues and supply more oxygen
carbon iv oxide from the lungs
h) i)Describe the factors which control the rate of breathing in humans
ii) Name the respirator diseases
4. a) i) Define respiration
ii) Explain the significance of respiration in living organisms
iii) Where does respiration take place?
b) i) Draw and label a mitochondrion
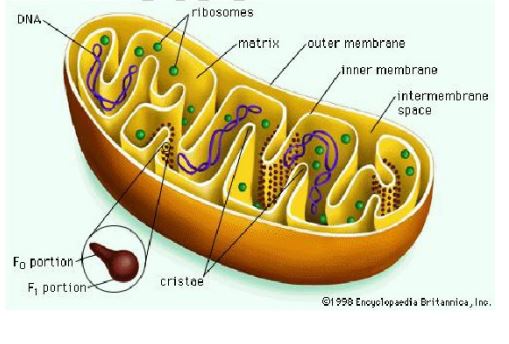
ii) State the most important function of mitochondria
iii) Give the functions of the labeled parts
Outer membrane
Cristae
Matrix
c) Explain the roles of enzymes in respiration
d) i) What is aerobic respiration
ii) Give a word equation for aerobic respiration
iii) What are the end products of aerobic respiration?
e) i) What is anaerobic respiration
ii) What are obligate anaerobes?
iii) What are facultative anaerobes?
iv) State the Word equation representing anaerobic respiration in plants
v) Name the end products of anaerobic respiration in plants
g) i) Give a word equation of anaerobic respiration in animals
Glucose —> lactic acid + energy
ii) Name the end products of respiration in animals when there is insufficient oxygen
supply
iii) Why is there a high rate of lactic acid production during exercise?
iv) Why does lactic acid level reduce after exercise?
v) State why accumulation of lactic acid during vigorous exercise lead to an increase in
heartbeat
State the economic importance of anaerobic respiration
What is oxygen debt?
and energy
h) i) What is respiratory quotient(RQ)?
RQ = volume of CO2 produced
volume of oxygen consumed
ii) Why are respiratory quotient important
iii) Name the respiratory substrates
iv) Why does anaerobic respiration of a given substrate yield a smaller amount of energy
than aerobic respiration?
animals
iv) Explain the disadvantages of anaerobic respiration
v) Mention the types of experiments carried out for respiration
5. a) i) Define the following terms
Excretion
process which occur in living cells
Secretion
glands
Egestion
Homeostasis
ii) Explain Why excretion is necessary in plants and animals
-products of excretion are usually harmful while some are toxic
– if allowed to accumulate in the cells they would destroy tissues and interfere with normal
metabolism
– They are therefore removed through excretion
b) i) Describe how excretion takes place in green plants
ii) Why do plants lack complex excretory structures like those of animals?
animals which produce toxic wastes derived from protein metabolism
ii) State the excretory products of plants and some of their uses to humans
humans
anesthesia, also causes damage to the brain, may cause addiction if not well used and is
an illegal drug
tanning (softening) of leather.
addiction if much is used or consumed. It is used to make cigarettes, cigars and is
poisonous. It is a precursor of lung cancer
fibres
quantities
c) i) Describe excretion in unicellular organisms
-examples are amoeba and paramecium
-They have to remove waste products such as carbon IV oxide and nitrogenous substances e. g
urea and ammonia
– These diffuse from the body surface into the surrounding Water
– Diffusion is due to large surface area
ii) List excretory organs and products of mammals
d)i) Draw and label a mammalian skin
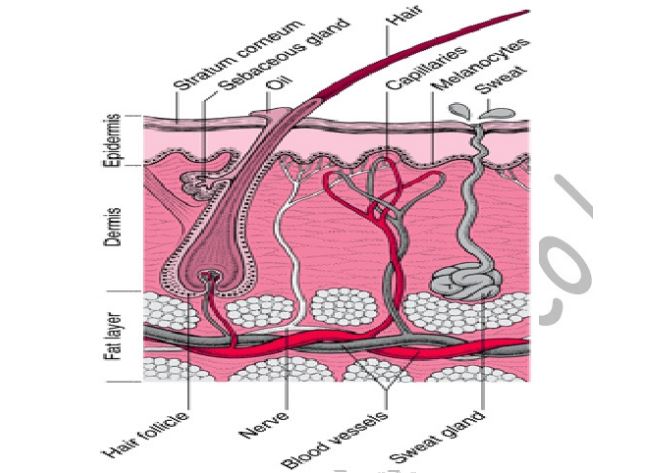
ii) Explain how the mammalian skin is adapted to its functions
the skin is made up of dermis and epidermis
Epidermis
microorganisms, prevent physical damage and dessication
cells/granular layer it contains melanin that protects the body against ultra violet
rays(radiations)
Dermis
evaporates cooling the body by lowering body temperature. When it is cold, no sweat is
produced, conserving water
excretory organ
loss/insulation. It lies flat to allow heat loss when temperature is high.
touch
excretory products. Arterioles vasodilate when temperatures are high to lose heat by
radiation, and convention. Arterioles constrict when temperatures are low to conserve
heat i.e. reduce heat loss
prevents drying and cracking the skin by making the skin supple
e) What is the role of lungs in excretion?
water vapour which are by-products of respiration
f) State the functions of the liver
i. Excretion
transported to skin and kidney for removal
transported to kidneys for removal
ii) Homeostasis
used in respiration
secretes glucagon which stimulates the liver to convert glycogen to glucose until the
normal sugar level is attained
Deamination
g) i) Draw a labeled diagram of mammalian nephrone
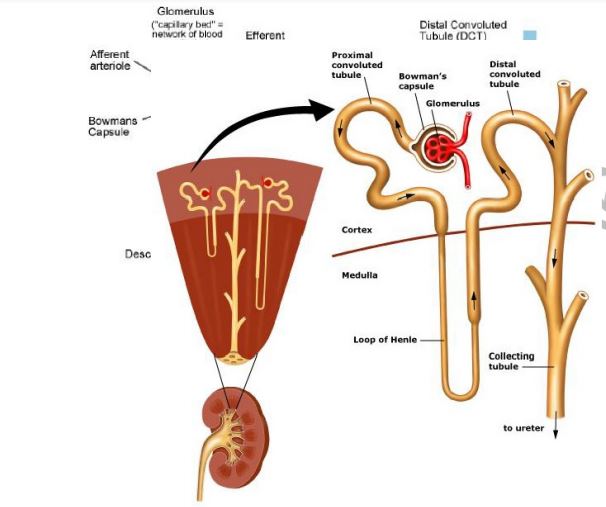
ii) Describe how the human kidney functions
glomerulus
ultra filtration
glomerular filtrate
large to pass through the capillary walls hence remain in blood capillary
glucose are selectively reabsorbed back into the blood stream
concentration gradient by active transport
blood capillaries
reabsorbed into blood stream
pressure of blood
pelvis and ureter into bladder and out of body through urethra
iii) State the adaptations of proximal convoluted tubule to its function
absorption numerous mitochondira to provide energy for reabsorption dense capillary network to transport reabsorbed products
iv) Name the common kidney diseases
6. a) i) Why is homeostatic control necessary?
optimum (best) condition for their survival
ii) What is internal environment?
b) i) Why is constant body temperature maintained by mammals?
ii) Explain the advantage gained by possessing a constant body temperature
iii) How do mammals regulate body temperature?
heat gain
hypothalamus it transmits impulses to the skin and the blood stream in response to
temperature changes hypothalamus acts as a thermostat for the body
of sweat.
respiration, or chemical activities
body hence lowering the body temperature
and reduction of metabolic rate
body and reduce heat loss to the environment
around the skin because still air is a good insulator of heat and by generation of heat by
increasing metabolic rate.
iv) Why does body temperature of a healthy person rise up to 37 C on a hot humid day?
body causing temperature to rise
v) Name the structures in the human body that detect external temperature changes
Ruffinni (cold)
vi) State the advantages that organisms with small surface area to volume ratio experience
over those with larger
Explain why individuals with smaller sizes require more energy per unit body weight than
those with larger sizes.
smaller heat is lost faster by smaller ones than larger ones
c) i) What is the meaning of osmoregulation?
ii) State the importance of osmoregulation
conditions for metabolism suitable for cellular functions
iii) State the ways by which desert mammals conserve water fewer glomeruli longer loop of
Henle
iv) Explain why some desert animals excrete uric acid rather than Water
v) Explain why eating a meal with too much salt leads to production of a small volume of
concentrated urine
higher rate of water reabsorption by kidney tubules
vi) Explain how marine fish regulate their osmotic pressure
for elimination
d) i) What is the biological significance of maintaining a relatively constant sugar level in a
human body?
cytoplasm
increasing the concentration of the contents
ii) Discuss the role of the following hormones in blood sugar control
Insulin
Glucagon
glycogen to glucose thus raising blood sugar level
e) Explain the part played by antidiuretic hormone in homeostasis
concentration) in the blood.
blood stream, thus restoring osmotic pressure
blood, little or no ADH is produced, less water reabsorbed hence water loss in urine
(more dilute urine) hence raising the osmotic pressure in body fluids/blood
f) What is the role of blood clotting in homeostasis?
g) Describe the role of the following hormones in homeostasis
i. Aldosterone
(and therefore water) in the kidneys)
blood
effect of sodium ions
an inhibiting effect, and a fall in sodium ions has a stimulating effect on the adrenal
cortex
produced in the anterior of the pituitary gland however, the main method of control is
dependent on the fact that adrenal cortex itself is somehow sensitive to the relative
concentration of potassium and sodium in the blood
ii. Adrenaline
h) i) Distinguish between diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus
hyperglucaemia and presence of glucose in urine
hence a high volume of water is passed out in urine in a condition called diuresis
ii) How can high blood sugar level in a person be controlled?
iii) Why does glucose not normally appear in urine even though it is filtered in the
mammalian Bowman’s capsule?
iv) When is glycogen which is stored in the liver converted into glucose and released into
the blood?
v) How would one find out from a sample of urine whether a person is suffering from
diabetes mellitus?
KCSE Biology Questions and Answers Form 3 – Biology Form Three Notes
Biology Questions and Answers Form 3
1. a) i) What is meant by the term binomial nomenclature?
ii) State briefly the general principles of classification of living organisms
genus Rana become Ranaidea
b) State the main characteristics of the five kingdoms of organisms
i. Monera
ii. Protista(protoctista)
iii. Fungi
iv. Plantae
v. Animalia
c) Describe the economic importance of:
i. Fungi
ii. Bacteria
d) State the main characteristics of the following division of kingdom plantae
i. Bryophyte
ii. Pteridophyta
iii. Spermatophyte
e) Name sub-divisions of spermatophyte and state the characteristics of each class
i. Gymnospermae (cornifers)
ii. Angiospermae (flowering plants)
iii. Name the classes and state characteristics of angiospermae
Dicotyledonae
Monocotyledonae
iv)State the importance of plants
respiration
influence water cycle
earn money from sales of products
f) i) Give the general characteristics of phylum arthropoda
ii. State the characteristics of the following classes of arthropoda
Diplopoda
Chilopoda
Insecta
Crustacean
Arachnida
iii) State the economic importance of insects
Beneficial effects
Harmful effects
g) i) State the general characteristics of chordate
Give the characteristics of the following classes of chordate
Pisces
Amphibian
Reptilia
Aves
Mammalian
a) i) What is a dichotomous key?
opting between two alternative observable characteristics
i. State the necessity of using a dichotomous key
of a characteristic which is not to be found in other specimens
ii. List the rules followed in constructing a dichotomous key
iv) Describe the procedure of using a dichotomous key. Make a list of major features of the
characteristics to be identified
iv You are provided with a specimen kale leaf. Use the dichotomous key below to identify
the taxonomic group to which the specimen belongs. Show the steps (number and letter) in
the key that you followed to arrive at the identify of the specimen
1 a) Leaf broad……. Go to 2
b) Leaf narrow……. Araicaria
2 a) Leaf parallel vein……. Cynodon
b) Leaf net veined……. Go to 3
3 a) Leaf with one lobe (simple Leaf)……. Go to 4
b) Leaf with many lobes (compound Leaf)……. Grevellea
4 a) Leaf Fleshy……. Kalanchoa
b) Leaf not fleshy……. Go to 5
5 a) Leaf petiole modified to form sheath……. Go to 6
b) Leaf petiole not modified to form sheath……. Brassica
6 a) Leaf purple……. Tradescantia
b) Leaf green……. commelina
Steps 1a, 2b, 3a, 4b, 5b
Identify- Brassica
v) You have been provided with four animals labeled K (mature adult housefly), L (mature
adult grasshopper, M(maize flour beetle) and N(Worker termite) use the dichotomous key
below to identify the specimens. Write down in the correct order, the steps (number and
letter) in the key that you followed to arrive at your answer.
Dichotomous key
1 a) Animal with wings……. Go to 2
b) Animal without wings……. Go to 7
2 a) With two pairs of wings……. Go to 3
b) With one pair of wings……. Diptera
3 a) With membranous wings……. Go to 4
b) Hind pair of membranous wings……. Go to 6
4 a) With long abdomen ……. Odontata
b) Medium sized abdomen……. Go to 5
5 a) Wings with colored scales……. Lepidoptera
b) Wings without scales……. Hymenoptera
6 a) Forewings hard and shell-like……. Coleoptera
b) Forewings hard but not shell-like……. Orthoptera
7 a) Body horizontally flattened……. Isoptera
b) Body laterally flattened……. Symphonopteria
Identify the orders of the various specimen as per the table below
Specimen Order Step followed
K- housefly Diptera 1a, 2b
L- grasshopper Orthoptera 1a, 2a, 3b, 6b
M- beetle Coleoptera 1a, 2a, 3b, 6a
M- termite Isoptera 1b, 7a
2 a) Define the following ecological terms
i. Ecology
ii. Environment
iii. Habitat
an organism lives.
iv. Ecological niche
v. Population
vi. Community
existing or interacting (living) with each other and the environment in which they live
vii. Ecosystem
they live
vm. Biosphere
ix. Autecology
ecosystem, habitat or environment.
x. Synecology
ecosystem.
xi. Carrying capacity
xii. Biome
xiii. Biomass
b) i) What are abiotic factors?
ii) Explain how abiotic factors affect living organisms
Wind
evaporation of water from the soil
replenishes oxygen concentration necessary for life
Temperature
and animals
metabolism and enzyme reaction
Light
Humidity
transpiration
pH
Salinity
Topography
side
of species
Rainfall (Water) or precipitation
mineral salts. Provides turgidity for plant support, medium for transport, disperses fruits,
seeds and spores
Pressure
and less carbon iv oxide for photosynthesis and this affects distribution of organisms
Mineral salts (trace elements)
obtaining it.
c) i) What are biotic factors?
interacts with in various ways
ii) Give examples of biotic factors affecting ecosystems
d) Discuss how the various biotic factors affect living organisms
i. Competition
e.g. for mates
food and space.
ii. Predation
die due to environment depletion
iii. Parasitism
food(and other benefits) from it, causing harm to it (without necessary killing it)
iv. Diseases and parasites
v. Symbiotic
and association of organisms of different species where both benefit from the association
i.e. there is mutual benefit
vi. Human activities
poaching, fishing conservation, population control
Saprophytism
decaying tissues of plants and animals
e)i) What is nitrogen cycle?
eventually returns to the air.
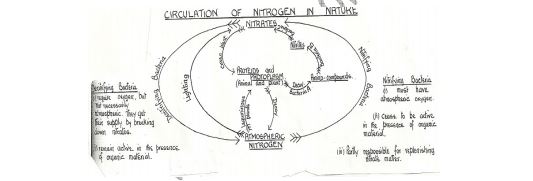
iii) Describe the nitrogen cycle
oxides
form nitrates which are absorbed by plants
free nitrogen to nitrates
to nitrites by Nitrosomonas and nitrococcus bacteria
pseudomonas and theobaccilus bacteria generally called denitrifying bacteria
iii. Nitrogen in the atmosphere cannot be directly utilized by plants. State two ways
by which this nitrogen is made available for plant use
lightning
f) i) Describe how energy flows from the sun through the various trophic levels in an
ecosystem
chemical energy9food or carbohydrates
trophic level
level
organisms feed on them thus causing them to decompose into simple substances e. g.
mineral salts
releases nutrients for plants, linking biotic and a biotic components
Give the reasons for loss of energy from one trophic level to another in a food chain
Why are green plants referred to as primary producers in an ecosystem?
trophic level (consumers) and other organisms
vi. Explain the following terms giving suitable examples
Food chain
straight line i.e. linear representation of feeding relationship between different organisms
in an ecosystem
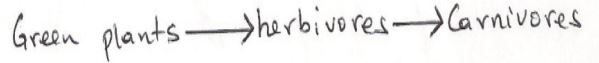
Food web
while several herbivores feed on one type of plant
consumers are usually fewer to ensure survival of both
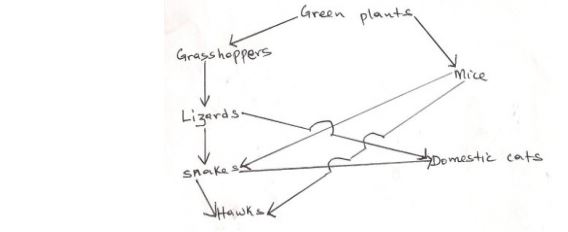
Pyramid of numbers
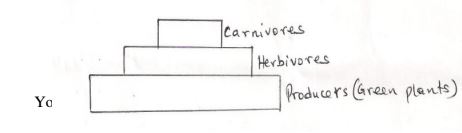
food chain
camivores feed on many herbivores
on a herbivore
Pyramid of biomass
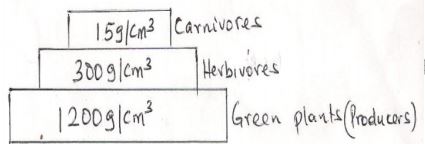
levels in a food chain
Account for the decrease of biomass in the successive trophic levels
energy is lost by respiration and indigested (unconverted) materials hence less biomass
supported at each level
h) i) Describe the three characteristics of a population growth
Dispersion
Density
ii) Explain how the following methods are used to estimate population of organisms
quadrat method
the total area of habitat Q
Line transect
Belt transect
Capture-recapture method
second sample multiplied by the number of marked grasshoppers in the first sample
divided by number of grasshoppers marked in the second sample that were recaptured
2. a) Describe the adaptations of plants to various habitats
i. Xerophytes
(rolled) leaves. Some have thick waxy cuticle, reduced number of stomata to reduce
water loss by transpiration
ii. Hyrophytes
buoyancy (floating in water)
support
or for increased rate of transpiration
diffusion
iii. Mesophytes
carry out photosynthesis in low light intensities (those that form undergrowth)
both leaf surfaces
iv. Halophytes
plant
osmosis
e.g. mangrove
b) 1) What is pollution?
ii) Explain the various human activities that have caused pollution
Causes and effects of air pollution
sewage, decomposing organic matter and fumes affect gaseous exchange, makes acid rain
and damage plant leaves
sprayed to control diseases, pests and weeds affect respiratory organs of animals. The
chemicals are residual and persistent (not easily broken down) and bring depletion of the
ozone layer
bum fuel, oil, wood and coal cause carbon ii oxide, poisoning affect respiratory systems
and affect visibility
of heating the lower layers of atmosphere
hearing in animals
radio-active emissions from nuclear reactors, mines and bombs cause cancer, mutations
and death.
Control of air pollution
State the causes, effects and methods of controlling and prop roots for support water
pollution
Causes and effects
population
rates of photosynthesis and gaseous exchange. It also leads to reduction of algae which
causes reduction of consumers i.e. animal population
organism while oily substances in wastes may clog gills of fish and may change pH of
water oxygen solubility is also reduced by oily surfaces
reduces oxygen supply and sewage provides food for bacteria increasing their population
and demand for oxygen thus depriving fish of oxygen.
faecal matter changes pH of water interferes with photosynthesis and may clog fish gills
or block light penetration which interferes with producers thereby decreasing
productivity.
amount of oxygen in the water causing organism to suffocate and die
Control of water pollution
biotechnology, banning the use ofphosphate-based detergents, using plastic pipes instead of
those made from lead, recycling gabbage, using biodegradable detergents.
carrying out environmental impact assessment before establishing industries
biological control of weeds and pests, biodegradable organic fertilizer herbicides, insecticides
pesticides, organic farming educate farmers on the use of correct amount of agrochemicals
reafforestation, building gabions and terracing
iv) State the causes /effects and control methods of soil pollution
Causes and effects
rain alters soil pH therefore affecting plants that cannot tolerate acidic soil
by plants which make its concentration many times higher, increasing the toxicity in the
plants which absorb them
obtain oxygen in oil saturated soils, therefore plants are killed
plants and eventually soil microorganisms cannot inhabit the soils
towns and cities. commodities packaged in metal tins, rubber, plastic containers, scrap
metal, glass bottles, different types of paper are nuisance to the environment, rendering it
useless for agricultural purposes
Control of soil pollution
v) Define biological control give suitable examples
e.g beetles to feed on water hyacinth, fish to feed on mosquito larvae.
vi) What is eutrophication?
growth of surface plants
i) What are the effects of eutrophication?
growth of surface plants
vii) What are the effects of eutrophication?
The plants die and decompose leading to lack of oxygen hence animals also die
c) Describe the symptoms, mode of transmission and control of cholera, typhoid, malaria and amoebic dysentery in humans
Cholera
causative agent
Transmission
Symptoms
Control
Typhoid
Causative agent
Transmission
Symptoms
Control
Malaria
Causative agent
Transmission
Symptoms
Control
Amoebic dysentery (amoebiasis)
Causative agent
Transmission
Symptoms
Control
d) Discuss Ascaris lumbricoides under the following sub-headings
i. Mode of transmission
ii. Effects of parasite on the host
iii. Adaptations
iv. Control and prevention
e) Discuss schistosoma under the following sub-headings
i. Mode of transmission
ii. Effects on host
iii. Adaptations
penetration
Control and prevention
on which snails feed.
3. a) i) What is reproduction?
resemble the parents
ii) Why is reproduction important?
iii) Name the types of reproduction
new individuals
b) i) What is cell division?
ii) What are chromosomes?
c) i) What is mitosis?
ii) Describe the five stages of mitosis
Interphase
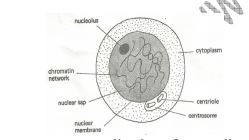
Prophase
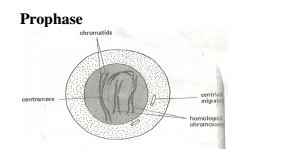
Metaphase
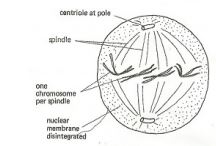
Anaphase
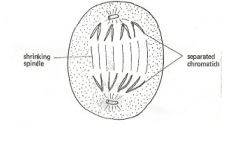
Telophase
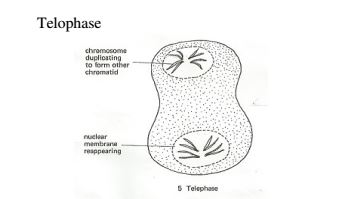
ii) State the significance of mitosis
d) i) What is meiosis?
ii) State the significance of meiosis
iii) Give a summary of the stages of meioeis
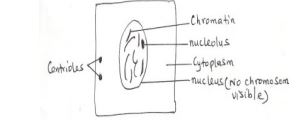
Prophase I
Metaphase I
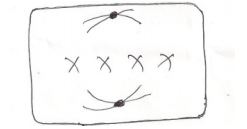
Anaphase I
Telophase I
Second meiotic division
Prophase II
Metaphase II
Anaphase II
Telophase II

iv) Give the similarities between mitosis and meiosis
v) What are the differences between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis
meiosis
d) i) What is asexual reproduction
ii) What is the significance of sexual reproduction in living organisms?
iii) State the advantages of sexual reproduction
iv) Give the disadvantages of sexual reproduction
e) i) What is asexual reproduction?
ii) State the advantages of asexual reproduction
iii) Give the disadvantages of asexual reproduction
iv) Explain how reproduction occurs by the following methods of asexual reproduction
Sporulation
Budding
Binary fission
f) i) What is a flower?
ii) Draw a longitudinal section of a labeled diagram of a flower
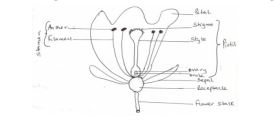
iii) Give the functions of the parts of a flower
Receptacle
Calyx
Corolla
Androecium
Gynaecium
iv) What is inflorescence?
v) Explain the meaning of the following terms which describe flowers
Hermaphrodite
Unisexual
Carpelate
Staminate
Dioecious plants
Monoecius plants
Complete flower
Incomplete flower
vi) Explain the meaning of the following types of ovary
Superior
Q ovary occurs above other floral parts on the receptacle
Inferior (epigynous)
Q other floral parts arise above ovary on the receptacle
g) i) What is pollination?
ii) Explain the types of pollination
same flower
flower of the same species
iii) State the advantages of pollination
iv) List the agents of pollination
v) How are flowers adapted to wind and insect pollination?
Insect pollinated flowers (entomophilus)
of contact by insects
Wind pollinated flower (anemophilus)
land/to trap pollen grains
vi) State the Ways in which plants prevent self-pollination
vii) Give the characteristics that ensure cross pollination takes place in flowering plants
viii) State the advantages of cross pollination
h) i) What is fertilization?
ii) Describe how fertilization takes place in a flower
to produce a pollen tube/to germinate
antipodal cells
fuses with the egg cell/ovum to form a zygote
nuclei/endosperm)food storage used by developing embryo)

iii) What is double fertilization?
form a triploid primary endosperm nucleus
iv) Name the changes that Occur in a flower after fertilization
b) i) Distinguish between a fruit and a seed
ii) How is a seed formed?
into endosperm, interguments harden to form testa, hence the whole ovule becomes the
seed
iii) Draw a labeled diagram of a seed

iv) Describe the main parts of a seed
Testa
Hilum
Micropyle
Radicle
Cotyledons
v) Draw a labeled diagram of a fruit
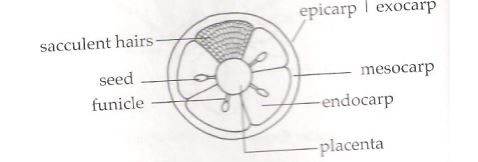
vi) How is a fruit formed?
stimulate the young ovary
vii) Explain the importance of fruits in the survival of plants
vii. Distinguish between parthenogenesis and parthenocarpy
iv) state the differences between a seed and a fruit
A Seed
fruit
j. i) What is placentation?
ii) Explain the following types of placentation
Marginal
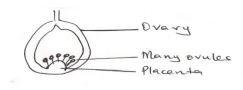
Basal
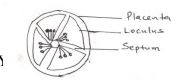
Parietal
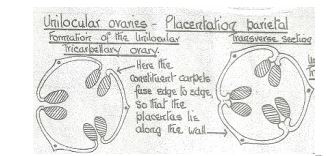
Axile
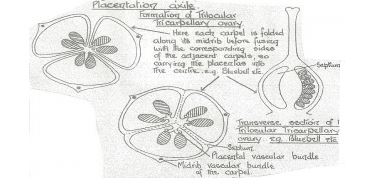
Free central placentation
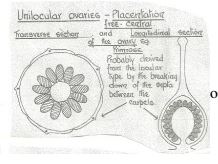
c) i) How are fruits grouped?
Simple fruits
Aggregate fruits
Multiple (compound) fruits
ii) What are succulent fruits?
iii) Give types of juicy fruits
Berry
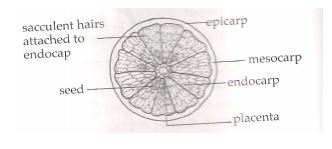
Drupe
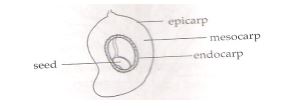
Pome
iv) What are dry fruits?
v) What are dehiscent fruits?
vi) Give types of dehiscent fruits
Legumes
Follicle
Capsule
vii) What are indehiscent fruits?
ii) Give main types of indehiscent fruits
Nut
Achene
d) i) What is seed and fruit dispersal?
suitable for their germination
ii) Why is dispersal of seeds and fruits necessary?
iii) Explain how seeds and fruits are adapted to various methods of dispersal
Adaptations for wind dispersal
them easily/buoyancy
carried away by wing
loosely attached which allows swaying so that movements of capsule by wind releases
the seeds
Water dispersal seeds
Animal dispersal seeds
from mother plant
Self dispersal/explosive
from parent plant
5. a) i) Distinguish between external and internal fertilization in animals
body of the female e. g. amphibians and fish
ii) State the advantages and disadvantages of external fertilization
Advantages
Disadvantages
iii) State the advantages and disadvantages of internal fertilization
Disadvantages
Advantages
iii) Give a reason why it is necessary for frogs to lay many eggs
iv) Compare external and internal fertilization


b) i) Draw and label the human male reproductive system
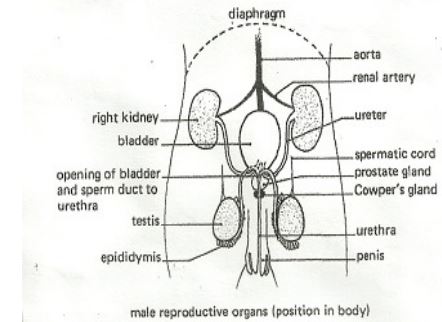
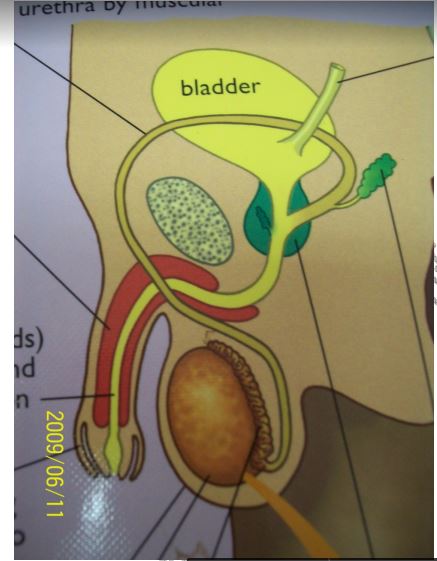
ii) Describe how the mammalian male reproductive system is adapted to perform its
functions
Penis
Scrotum
place
Epididymis
Vas deferens
Gametes
energy/allow swimming to reach the egg
Accessory glands
iii) How is the sperm adapted to perform its function?
the lashing movement of the tail enables the sperm to move/propulsion in fluid medium
towards the egg
c) i) Draw and label the human female reproductive system
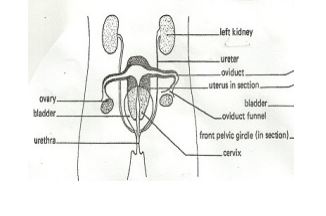
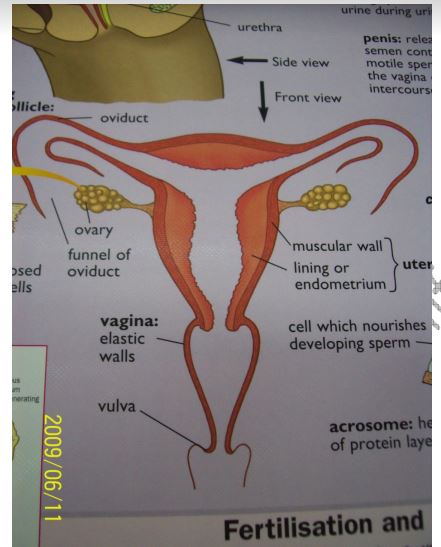
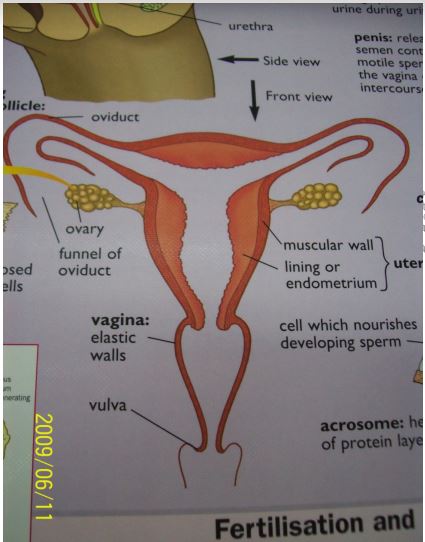

ii) Describe how the various structures of the human female reproductive system are
adapted to their function
Ovaries
characteristics
and subsequent nourishment of the embryo
Oviducts (Fallopian tube)
implantation
Uterus
developing embryo
Cervix
gestation period
to uterus
at the right point
Vagina
proper deposition of sperms and for easy parturition
during parturition
Clitoris
iii) Explain how the ovum is adapted to its function
iv) Explain the differences between sperm and ovum
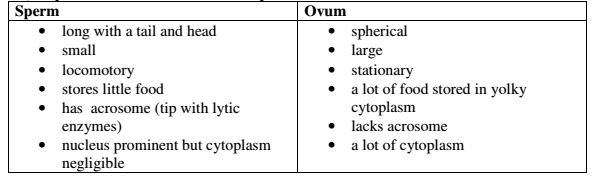
d) i) Explain the process of fertilization
blastocyst
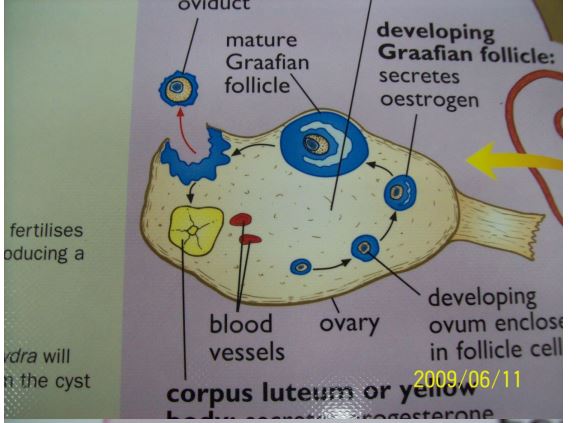
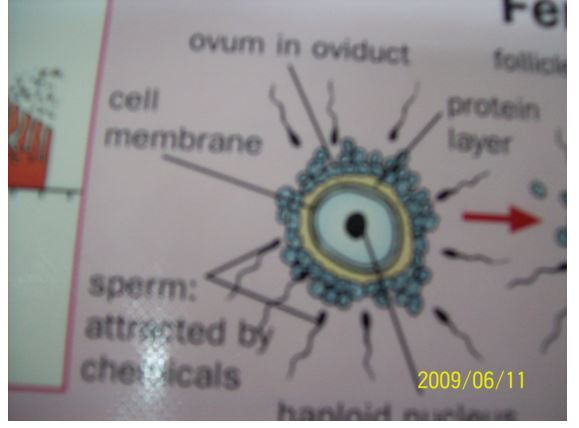
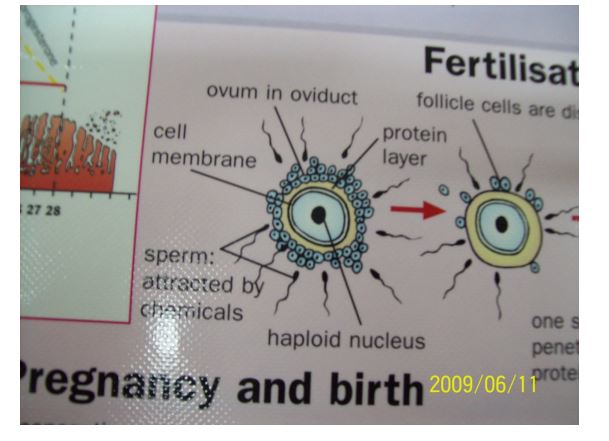
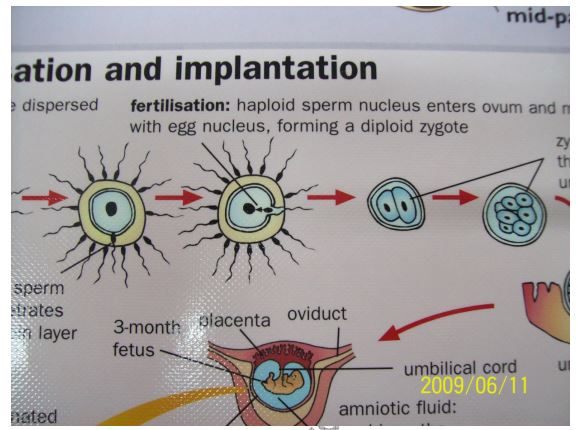
i) Explain the process of implantation
ectopic pregnancy which is fatal
uterine wall for attachment
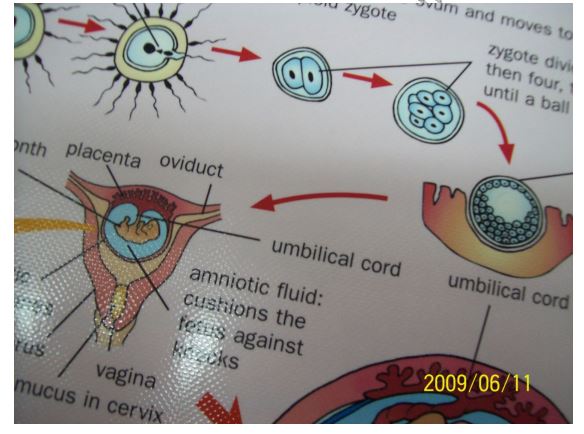
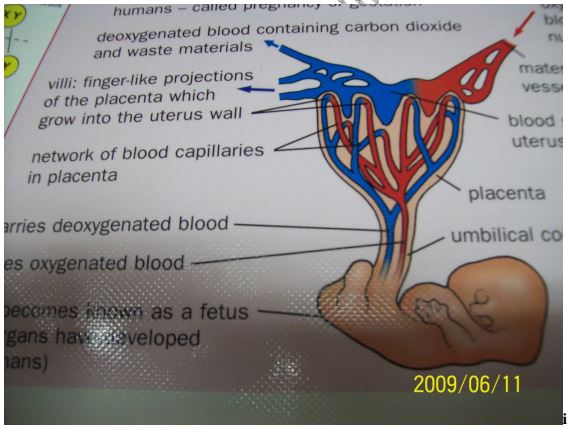
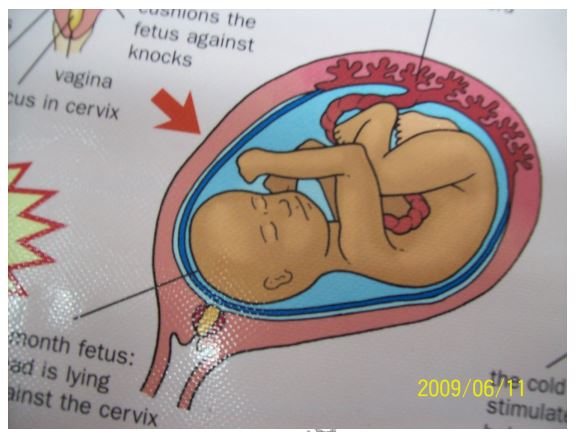
State the functions of umbilical cord
State the role of placenta
e) i) What is gestation period?
ii) Explain the functions of the membranes associated with placenta
Chorion
Amnion
Yolk sac
Allantois
iii) Explain the events that take place to facilitate parturition
iv) State the reasons why later in pregnancy the ovary will b e removed without disturbing
the pregnancy
development of foetus after conception
f) i) What are secondary sexual characteristics
influence of male and female hormones
ii) State the main secondary changes in
Boys
Girls
iii) Describe the role of hormones in secondary sexual characteristics in
Boys
Follicle stimulation hormone (FSH)
Testosterone
Girls
FHS
LH
Oestrogen
Progesterone
Prolactin
Oxytocin
g) i) What is menstruation?
ii) Describe the role of hormones in the human menstrual cycle
characteristics and also control of the menstrual cycle
menstruation
stimulates tissues of the ovary/wall (theca) to secrete oestrogen
stimulates corpus luteum to secrete progesterone
no more follicles develop and oestrogen production reduces
anterior lobe of pituitary“
of progesterone drops
iii) What is menopause?
h) Explain the symptoms, methods of transmitting and prevention (control) of the following
sexually transmitted diseases
i) Gonorrhea
ii) Herpes
iii) Syphilis
iv) Trichomoniasis
v) Hepatitis
vi) Candidiasis
vii) HIV/AIDS
infected mother to foetus, infant and baby
fatigue, loss of appetite, diarrhea, headache, a opportunistic infections and tumors
using sterile piercing instruments.
6. a) Define the terms
i) Growth
ii) Development
differentiation)
iii) Differentiation
perform specific functions
b) i) Differentiate growth in plants and animals
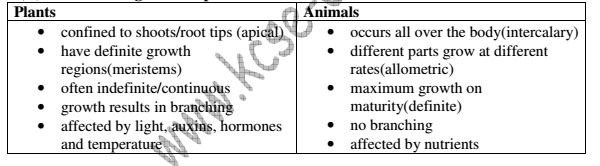
More differences between Plant Growth and Animal Growth
Plant Growth:
1. Growth continues throughout the life of the plant.
2. Here the growth involves increases in the number of parts.
3. Growth take place during definite seasons.
4. Growing pattern is distinct each species.
5. Plant possess well-defined growing regions.
6. A seedling does not resemble an adult plant.
7. A juvenile stage with distinct may be present in the life-history of a plant.
8. Growth is by addition of new parts ahead or around the older ones.
Animal Growth:
1. Growth takes place for definite periods before maturity.
2. Here it does not involve increase in the number of parts.
3. Each species has a distinct season for growth.
4. Growing pattern is absent.
5. They have no such defined growing regions.
6. The young one are identical to adults except in the body size and sexual maturity.
7. A juvenile stage with different morphology does not occur in higher animal.
8. Growth is diffused by all round increases in different organs of the body.
ii) List the processes involved in growth
iv) List the parameters used to measure growth
iv) Name the patterns of growth in organisms
c) i) Name the different types of growth curves
ii) Draw a sigmoid growth curve and explain its different phases/stages
A-lag phase
– Slow growth rate at first
Organism adapting to the environment
B-exponential phase
– organisms already adapted
– first growth due to birth rate that is higher than death rate
C- Stationery phase (plateau)
– Birth rate equals death rate (equilibrium)
Lack of nutrients, accumulation of toxic waste products
D-phase of decline
– due to depletion of nutrients, accumulation of toxic wastes, lack of space
– some individuals old hence not reproducing
– death rate higher than birth rate
iii) Draw an intermittent curve and explain the various stages
A-growth
B-no growth
C- moulting/ecdysis
– seen in arthropods
– growth in in arthropods is intermittent(takes place during some time only because their
hard cuticles (exoskeleton) does not expand to cause growth
– the cuticle must be shed off first to allow further growth
– the shedding is called ecdysis or moulting
– when moulting has taken place animal grows but growth stops when the exoskeleton
hardens again
d) i) What is seed dormancy?
– A state where a viable seed is incapable of germinating when all conditions are
favorable.
ii) State the biological importance of seed dormancy
– gives embryo time to reach maturity
– gives time for dispersal
– allows plant to survive adverse conditions
iii) State the factors which cause seed dormancy
Internal factors
– presence of abscisic acid/ABA/ presence of germination inhibitors
– embryo not fully developed
– absence of hormones/enzymes/inactivity of hormones/enzymes/gibberellins/cytokinins
– impermeability of seed coat
External factors
– unsuitable temperature
– absence of light
– lack of oxygen
– lack of oxygen
– lack of water
iv) Give the conditions necessary to break seed dormancy
– scarification/scratching to make seed coat impermeable
– vernalisation/cold treatment in some seeds like wheat
– burning/nicking/expose to heat e.g. wattle seeds
– destruction of germination inhibitors
e) i) What is seed germination?
– process by which a seed develops in a seedling
ii) What is viability
– ability of a seed to germinate
iii) Discuss the various conditions necessary for the germination of seeds
Water
– medium for enzymatic activity
– hydrolysis of food into simpler substances
– medium of transport
– softens the seed
– acts as a solvent
Air
– in form of oxygen
– oxygen is used for respiration/oxidation of food to release energy
Suitable (optimum) temperature
– activates enzymes involved in mobilization of food reserves
Enzymes
-breakdown and subsequent oxidation of food
– conservation of hydrolyzed food products in to new plant tissues
Viability
– only viable seed are able to germinate and grow
iv) Name and describe the types of germination
Epigeal
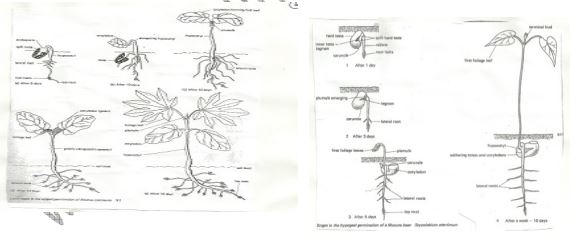
cotyledons are brought above the ground level during germination due to elongation of
the bean seed that elongates to bring about epigeal germination
Hypogeal
– the cotyledons remain below the surface during germination due to elongation of epicotyl
e.g maize
vi) Account for the loss in dry weight of cotyledons in a germinating bean seed
vii) Describe the physiological changes that occur in a seed during germination
hydrolysed or broken down into soluble diffusible form by enzymes
viii) Explain the biological significance of cotyledons being brought above the ground in
epigeal germination
during germination
f) i) Distinguish between primary and secondary growth
Primary growth
Secondary growth
ii) What are meristems
iii) State the characteristics of meristematic cells
iv) State the location and function of the following meristematic tissues
Apical meristem
Intercalary meristem
Lateral meristems
v) Describe primary growth
vi) Describe secondary growth in plants
intervascular cambium
secondary xylem each year
parenchyma, thereby increasing growth of medullary rays
outward
the bark of perennial plants
on outside and secondary cortex on the inside
gaseous exchange.
vii) State the significance of secondary growth
g) i) Describe one method which can be used to measure the average growth rate of a single
leaf of a plant
Either
– chose/identify a young leaf (just unfolded)
– use the same leaf throughout
– measure (total) length of (whole) leaf
– record
– repeat at regular intervals until no more change occurs/constant length
– average rate of growth is equal to total increase in length divided by the period taken to
achieve full length
Average rate of growth = total increase in length divide by
period taken to achieve full length
OR
– choose/identify a young leaf(just unfolded)
– use the same leaf throughout
– trace the outline on a graph paper and work out the area
– record
– repeat at regular intervals until regular area
– average rate of growth equals to total increase in area divided by the period of time taken
to achieve full area
Average rate of growth = total increase in area divide by
period of time taken to achieve final area
i) Describe how the growth of a root can be determined
Materials
– fine thread, marking ink, germinating bean seedlings, blotting paper, ruler marked in
millimeters, pins, cork, a boiling tube and moist cotton wool
Procedure
– dry seedlings using blotting paper
– place inside against the ruler marked in mm
– dip the fine thread in waterproof ink
– mark the radicle at equal intervals
– pin the seedling to the cork
– suspend the seedling into the boiling tube containing moist cotton wool
– allow the seedling to grow for two days/some
time observe the intervals with the marks
– record your observations the Widest intervals are found in the region just behind the tip
indicating/showing region of greatest growth
iii) A boy hammered a nail in the bark of a tree at a height of 1.5 metres above the ground
Four years later, the nail was found at the same height although the tree had grown 3
meters taller. Explain the above observation
The nail was hammered at a point where vertical growth had stopped/further growth was
confined to increase in width/diameter.
Vertical growth is confined to tips/apex/vertical apical meristem
h) i) Describe the role of hormones in growth and development of plants
Cytokinnins (Kinnins/Kinnetin/Zeatin)
– breaks dormancy
– promotes flowering
– promotes cell division
– stabilizes protein and chlorophyll
– promotes root formation on a shoot
– low concentration encourages leaf senses
– normal concentration increases cell enlargement in leaves
– stimulates lateral bud development
Ethylene (ethynel C2H4)
– accelerates ripening in fruits
– encourages fruit fall/leaf fall
– induces thickening in stern/inhibits stem elongation
– promotes flowering (in pineapples)
– promotes germination in certain seeds
Abscisic acid (ABA) abscisin hormone/dormin)
– causes bud dormancy
– encourages fruit/leaf fall
– high concentration causes closing of stomata
– causes seed dormancy
– inhibits cell elongation
Traumatin
– heals wounds by callous formation
Florigen
– promotes flowering
ii) State the applications of plant hormones in agriculture
– induce root growth in stem cuttings
– selective weed killers
– encourage sprouting of lateral buds
– breaking seed dormancy
– induce parthenocarpy
– accelerate ripening of fruits
– promote flowering
– cause dormancy
iii) Explain apical dominance
– a phenomenon whereby production of auxins by a growing apical bud of a shoot inhibits
growth of lateral buds
– this inhibition is due to high concentration of auxins (indoleacetic acid/IAA) in apical
bud
– removal of terminal/apical bud causes development and sprouting of several buds which
later develop into branches
– applied in pruning coffee, tea and hedges
– this leads to more yield
iv) Describe the role of hormones in the growth and development of animal
somatotrophin (growth hormones)
– from anterior pituitary
– promotes cell division
– overproduction causes gigantism
– underproduction causes dwarfism
Thyroxine
– promotes growth and metamorphosis
– underproduction leads to a child becoming a cretin (mentally retarted)
Androgens
– in males
– growth of male reproductive organs
Oestrogen
– in females
– growth of female reproductive organs
Ecdysone
– in arthropods
– moulting (ecdysis)
t) i) What is metamorphosis?
– change in form during which there are changes in structure and function in body of
organism
– prepares organism for life in a different habitat
ii) Explain complete metamorphosis
radical changes in the body during the life cycle of an organism
called holometabolous development
example is egg larva pupa adult (imago)
occurs in animals such as butterfly and bee
iii) What is the significance of each of the four stages in complete metamorphosis?
Larval stage
– feeding takes place
– larva is quite different from adult
– larva sheds its cuticle (exoskeleton) several times to emerge as pupa
– dispersal stage avoids overcrowding
Pupa
– enclosed in a case called puparium (cocoon)
– no feeding
– organ formation takes place
Adult
– emerges from puparium
– reproductive stage of the life cycle
iv) Describe incomplete metamorphosis
– called hemimetabolous development
– changes are gradual
– eggs develop into nymphs which develop into adults
– nymph resembles adult but are sexually immature
– a nymph moults several times as some parts develop before it becomes an adult
– stage of development between one moult and another is called instar
– occurs in insects such as locust and cockroach
v) Name the hormones that control metamorphosis in insects
– brain hormone responsible for moulting because it simulates production of ecdyson
(moulting hormone)
– ecdysone(moulting hormone) causes moulting
– juvenile hormone causes moulting in larvae
vi) State the advantages of metamorphosis in the life of insects
– the adult and larvae exploit different niches
– do not compete for food
– pupa cam survive adverse pupa can survive adverse conditions eg-feeding stage
– dispersal prevents overcrowding
KCSE Biology Questions and Answers Form 4 – Biology Form Four Notes
Biology Questions and Answers Form 4
Biology Form 4 Notes
a) i) Define the term genetics
characteristics are passed from parents to offspring
ii) List some characteristics which are inherited
iii)State the importance of genetics
b) i) Explain the meaning of the following terms
Heredity
Trait
Gene
Allele
Chromosomes
DNA
cystosine (C)
ii) List the types of chromosomes
c) i) What is variation?
ii) State the causes of variation in organisms
iii) Name the types of variation
intelligence etc. They are quantitative and show intermediates
grouping system, RH factor, patterns of fingerprints, and ability to taste PTC. They are
qualitative and have no intermediates
iv) Explain the following terms
Acquired characteristics
Inherited characteristics
Genotype
Phenotype
character
Dominant gene (character)
Recessive gene
Homozygous
Heterozygous
F1 and F2
be crossed
d) i) Explain Mendels first law of inheritance
character can be inherited.
ii) Give an example of this law
short wings. Assume letter L denotes gene for wing size. The gene for long wings is
dominant to that for short wings
iii) What is monohybrid inheritance?
ratio of 1:2:1 in a complete dominance
i) What is complete dominance?
is recessive is not expressed in the heterozygous state e. g. the case of wing size above
e) i) What is meant by co dominance?
dominant over the other/where two or more alleles does not show complete
dominance/recessiveness due to the failure of any allele to be dominate in a heterozygous
condition.
ii) Give an example of co dominance
In a certain plant species, some individual plants may have only white, red or pink flowers.
In an experiment a plant with white flowers was crossed with a parent with red flowers. Show results
of Fl generation. Use letter R for red gene and W for white gene.
If the plants form F1 were selfed, work out the phenotype ratio for the F2 generation
Phenotypic ratio 1 red:2 pink: 1 white
Genotypic ratio 1:2:1
f) i) What is a test cross?
heterozygous) with a homozygous recessive individual
OR
individual
ii) State the importance of a test cross in genetics
iii) What are multiple alleles?
example is blood group which can be determined by any two of three alleles i.e. A,B and
O
iv) Explain the inheritance of ABO blood groups
ii) Explain the inheritance of Rhesus factor (Rh) in human beings
people who have Rh antigen are Rh(+ve) while those without Rh antigen in their blood
are Rh(-ve)
recessive the result is as shown below
Let the gene for dominant Rh factor be R while gene for recessive be r
iii) How is sex determined in human beings .
chromosome
g) i) What does the term linkage mean?
– These are genes which occur together on a chromosome and are passed to offspring without
being separated
ii) Define the term sex-linked genes
sex
iii) What is meant by the term sex linkage?
iv) Name the sex-linked traits in humans
v) Give an example of a sex linked trait in humans on:
Y Chromosome
X Chromosome
vi) In humans red-green colour blindness is caused by a recessive gene C, which is sex-
linked. A normal man married to a carrier Woman transmits the trait to his children. Show
the possible genotypes of the children.
Let C represent the gene for normal colour vision (dominant)
Let c represent the gene for colour blindness
Parental phenotype Norman man x carrier woman
iv) State the importance of sex linkage
possible to determine sex of day old chicks
v) Haemophilia is due to a recessive gene. The gene is sex-linked and located on the
x chromosome. The figure below shows sworn offspring from phenotypically
normal parents
What are the parental genotypes?
Work out the genotypes of the offspring
h) i) What is mutation?
ii) Describe how mutations arise
dleltion/duplication/substitution/inversion/translocation/crossing over
chemicals e. g. mustard gas/colchicines
iii)State the factors that may cause mutation
Radiations Effects
X-rays gene/chromosome alteration
Ultra violet rays structural distortion of DNA
Chemicals Effect
colchicines prevents spindle formation
Cyclamate chromosome aberrations
Mustard gas chromosomes aberrations
Nitrous acid adenine in DNA is deaminated so behaves like guanine
Acridone orange addition and removal of bases of DNA
Formaldehyde
iv) State the characteristics of mutations
v) Explain chromosomal mutation
– Change in nature, structure or number of chromosomes
vi) Explain how the following types of chromosomal mutations occur
Duplication
Inversion
and joins in an inverted position
Deletion
Translocation
chromatid of another chromosome
Non-disjuntion
Polyploidy
vii) What are gene mutations?
i) Explain how the following occur during gene mutation
Deletion
Inversion
Insertion
Substitution
ii) Name the disorders in humans caused by gene mutation
I. State the practical applications of genetics
i. Breeding programmes (research)
ii. Genetic engineering
iii. Law
– legal questions of paternity knowledge of blood groups or blood transfusion
iv) Genetic counseling
v) Others
– Pre-sex determination
Understanding human evolution and origin of other species.
2. a) i) Explain the meaning of evolution
a long period of time.
ii) Differentiate organic evolution from chemical evolution as theories of origin of life
pre-existing forms (some of which no longer exist)
compounds reacted to form the simplest life forms
iii) What is special creation?
of a supernatural being
b) Discuss the various kinds of evidence for evolution
i) Fossils
years
ago/millions of years ago
a long period of time e. g. human skull, leg of horse
ii) Comparative anatomy
a group of organisms
system] urinary system/nervous system/vestigial structures and vertebrate heart
vertebrate forelimb/beak structure in birds/birds feet/parts of a flower. These are called
homologous structures
different functions e.g. the pentadactyl limb
common embryonic origin which is modified to perform different functions to adapt
organisms to different ecological niches/habitats e.g. beaks of Darwinian finches(birds)
wings of birds and insects/eyes of humans and octopuses. These are called analogous
structures
appendix/caecium/coccix in humans, wings of kiwi (flightless bird), presence of hind
limb pad in python, halters in insects, human hair nictitating membrane in human eye,
human ear muscle, pelvic girdle in whale and third digit of wing of bird.
iii) Comparative embryology
possibility of a common ancestry
(tocophere)
iii) Comparative serology/physiology
show immunological similarities of tissues therefore showing relatedness of different
organisms
relationship among organisms/common ancestry
iv) Geographical distribution
as a result of continental drift isolation of organisms occurred bring about different
patterns of evolution
species/divergence/convergence
Examples
vi) Cell biology (cytology)
c) i) State the evolutionary characteristics that adopt human beings to the environment
– Brain
– Eyes
– Upright posture/bipedal locomotion
– prehensible arm/hand
– Speech
ii) State the ways in which Homo sapiens differs from Homo habilis
d) i) Explain Larmarck’s theory of evolution
– Inheritance of acquired characteristics/environment induces production of a favorable
trait which is then inherited
ii) Explain why Lamarck’s theory of evolution is not accepted by biologists today
– evidence does not support Lamarck’s theory
– acquired characteristics are not inherited/inherited characteristics are found in
reproductive cells only
iii) Explain Darwin’s theory of evolution
– inheritance of genetically acquired characteristics
– a character happens to appear spontaneously which gives advantage to an organism
therefore adapted then inherited through natural selection
e) i) What is natural selection?
– Organisms with certain characteristics are favoured by the environment
Such organisms tend to survive and produce viable offspring
Others not favored are eliminated from subsequent generations
ii) With examples, explain how natural selection takes place
– organism with certain characteristics are favored by their environment
– such organisms tend to survive and produce viable offspring
– others not favored are eliminated from subsequent generations
– as the environmental conditions change the survival value of a character may alter with
time so that characteristics which were favored may no longer have advantage and other
characters may then become favorable
– if a favorable character is inherited, then offspring produce generations which are better
adapted to survive in a population
– more offspring are produced than can survive which results in struggle for survival
– the fittest survive
iii) State the advantages of natural selection to organisms
– assist to eliminate disadvantageous characteristics/perpetuates advantageous
characteristics
– allows better adapted organisms to survive adverse changes in the environment/less
adapted organisms are eliminated
iv) State the ways in which sexual reproduction is important in the evolution of plants and
animals
– brings about useful variations/desirable characters
– variations make offspring better adapted for survival/more resistant to diseases
– may lead to origin of new species
v) Explain the significance of mutation in evolution
– Mutation bring about variation which can be inherited
– Some of these variations are advantageous to the organism
– Others are disadvantageous
– The advantageous variations favour the organism to compete better in the struggle for survival
– This results into a more adapted organism to its environment or new species/varieties
– Those with disadvantageous characters will be discriminated against therefore eliminated from
the population/death/perish
vi) Plain why it is only mutations in genes of gametes that influence evolution
– gametes form the new offspring
vii) How would you prove that evolution is still taking place?
– resistance of organism to antibiotics, pesticides and drugs
– new varieties of bacteria are resistant to certain antibiotics such as penicillin
– houseflies and mosquitoes are resistant to DDT
vii) Explain why some bacteria develop resistance to a drug after they have bee
subjected to it for some time
– bacteria mutates/develops a new strain/chemical composition is altered hence is able to
produce enzymes/chemicals which degrade the drug rendering it non-susceptible to the
drug
– the new strain is favoured by selection pressure natural selection
f) How has industrial melaninism i.e. peppered moth contributed towards the mechanism
of evolution
– This is an example of natural selection
– The peppered moth exists in two distinct forms, the speckled white form (normal form) and a
melanic form (the black/dark)
– They usually rest on leaves and barks of trees that offer camouflage for protection
– Originally the “speckled white” form predominated the unpolluted area of England
– This colouration offered protection against predatory birds
– Due to industrial pollution tree barks have blackened with soot
– The white form underwent mutation
– A black variety/mutant emerged suddenly by mutation
– It had selective advantage over the white forms that were predated upon in the industrial areas
– The speckled white form is abundant in areas without soot/smoke
3. a) i) Define irritability, stimulus and response irritability
-also called sensitivity
– Responsiveness to change in environment
Stimulus
A change in the environment of organism which causes change in organism’s activity
Response
– change in activity of an organism caused by a stimulus
ii) State importance of irritability to living organisms
– Adjusting to environmental conditions. Sensitive/defect/responding
iii) List the examples of external stimuli to organisms
– air/oxygen (aero)
– light(photo)
– osmotic pressure (osmo)
– current (Rheo)
– chemical concentration (chemo)
– water/moisture (hydro)
– Touch/contact (hapto/thigmo)
– Gravity/soil (geo)
– Temperature (thermo)
b) i) What are tactic responses?
– response in which whole organism or its motile parts move e. g. gamete
ii) What causes tactic responses?
– caused by unidirectional stimulus
– usually doesn’t involve growth
– response is either positive or negative
– named according to source of stimulus
– e.g phototaxis, aerotaxis, chemotaxis
iii) State the importance of tactic response to:
Members of kingdom protista
– move towards favorable environment/move away from unfavorable environment
– move towards their prey/food
Microscopic plants
– escape injurious stimuli/seek favorable habitats
iv) Name the type of response exhibited by:
Euglena when they swim towards the source of light
– phototaxis
– sperms when they swim towards the ovum
– chemotaxis
v) State the advantages of tactic responses to organisms
– to avoid unfavorable environment/injurious stimuli
– escape from predators
– to seek favorable environment
– to seek for food/prey
c) i) Define the term tropism
– growth movement of plants in response to external unilateral/unidirectional stimuli
ii) Explain the various types of tropism in plants
Phototropism
– growth movements of plant shoots in response to unilateral sources of light
– the tip of the shoots produce auxins down the shoot
– light causes auxins to migrate to outer side/darker side causing growth on the side away
from light hence growth curvature towards source of light roots are negatively
phototrophic
Geotropism
– response of roots/pans of a plant to the direction of force of gravity
– auxins grow towards the direction of force of gravity causing positive geotropism in roots
while shoot grows away from force of gravity (negatively geotrophic)
Thimotropism/Haptotropism
– growth response of plant when in contact with an object
– contact with support causes migration of auxins to outer side causing faster growth on the
side away from contact surface
– this causes tendrils/stem to twin around a support
Hydrotropism
– growth movement of roots in response to unilateral source of water/moisture
– the root grows towards the source of water/ positively hydrotropic while leaves are
negatively hydrotropic
chemostropism
– growth movement of parts of plant to unilateral source of chemicals
– the chemicals form a gradient between two regions e.g. pollen tube growing towards the
ovary through the style
iii) State the ways in which tropisms are important to plants
– expose leaves/shoots in positions for maximum absorption of sunlight for photosynthesis
– enables roots of plants to seek/look/search for water
– enables plant stems/tendrils to obtain mechanical support especially those that lack
woody stems.
– enables roots to grow deep into the soil for anchorage
– enables pollen tube grow to embryo sac to facilitate fertilization
iv) Explain the differences between tropic and tactic responses
Tropism
-growth curvature in response
-slow
-influenced by hormones
Taxes
-locomotory response
-fast
-external influence
d) The diagram below represents growing seedlings which were subjected to unilateral
light at the beginning of an experiment

i) State the results of P, Q and R after S days
– P will bend/grow towards light
– Q will remain straight/have little or no growth
– R will remain/grow straight/grow upwards
ii) Account for your results in (i) above
P- Growth substance/growth hormone/IAA/auxin are produced by the stem tip
– they move (downwards and get distributed) to the side away from light where they cause
rapid/more growth/cell division/elongation that results in bending
Q- Source of auxin has been removed
R- The auxins cannot be affected by light because the tip has been covered
iii) If the tin foil were removed from the tip of seedling R, what results would be
observed after two days
– it will bend/grow towards light
iv) State the expected results after 3 day is if the box were removed
– all seedlings will grow straight/upwards
e) In an experiment to investigate a certain aspect of plant response, a seedling was placed
horizontally as shown in diagram I below. After seven days the appearance of the seedling
was as shown in diagram 2
Account for the curvature of the shoot and root after the seven days
i) Shoot
– auxins accumulate on the lower side of the seedling due to gravity
– high concentration of auxins in shoot stimulates faster growth causing more elongation
on the lower side than the upper side hence curvature occurs upwards
ii) Root
– the high concentration of auxins inhibits growth hence the upper side with less auxins
grows faster than the lower side therefore the curvature occurs downwards
f) What is etiolation?
– phenomenon exhibited by plants when grown in darkness
– such plants are pale yellow due to absence of chlorophyll, have small leaves, long
stems/hypocotyle and slender stems
– plants exhibit etiolation to reach light/obtain light
– this is a survival response
4. a) i) What is coordination in animals
– The linking together of all physiological activities that occur in the body so that they take place
at the night time and in the correct place
ii) Name the main systems for coordination in animals
– Nervous system/sensory system
– Endocrine (hormonal system)
iii) List the components of the mammalian sensory system
– Central nervous system (CNS), brain & spinal cord
– Peripheral nervous system (PNS) cranial and spinal nerves
– Sense organs
– Autonomic nervous system (ANS) nerve fibers and ganglia
iv).Explain the terms receptors, conductors and effectors
– Receptors are structures that detect stimuli i.e. sense organs
– Conductors transmit impulses from receptors to effectors e. g. neurons
– Effectors are the responding parts e.g. muscles, glands
v) What are the functions of the central nervous system?
– provides a fast means of communication between receptors and effectors
– coordinates the activities of the body
vi) State the differences between somatic and autonomic systems of peripheral nervous
system
– Somatic is concerned with controlling the conscious or voluntary actions of the body i.e. skin,
bones, joints and skeletal muscles
– the autonomic (automatic) nervous system controls involuntary actions of internal organs,
digestive system, blood vessels, cardiac muscles and glandular products.
b) i) What is a neurone?

ii) Name the parts of a typical neurone and state the functions of each part
impulse transmission
process
i) Describe the structure and function of a motor neurone
muscles/glands)

ii) Describe the structure and of sensory neurone

iii) State structural differences between motor and sensory neurons
iv) Describe the structure and function of a relay neurone

c) State the function of the major parts of the human brain

i) Cerebrum
ii) Mid brain
i) Hind brain
coordination and muscle tone
sneezing
a) i) What is reflex action?
hot object
ii) Describe a reflex action that will lead to the Withdrawal of a hand from a hot object
nervous system (White matter), through the relay neurone into grey matter, then to the
motor neurone and finally to the effect muscle which contracts

iii) Explain how an impulse is transmitted across the synapse (gap)
neurone
ii) Briefly describe the transmission of a nervous impulse across a neuro-muscular
junction
membrane
membrane
iii) What are the functions of a synapse?
b) i) What is a conditioned reflex?
normal stimulus
ii) Explain a conditioned reflex
of neurone necessary to bring about conditioning
iii) Compare a simple reflex action with a conditioned reflex

c) i) What are endocrine glands?
ii) State the functions of hormones in animals
iii) Name the main endocrine glands, their secretions and functions in the human body
Hormone:
Thyroxine
Function:
increases the rate of metabolism
Hormone:
Parathyroid hormone
Function:
regulates calcium and phosphate levels
Hormone:
growth hormone
Function:
regulates growth of the body
gonadotrophic hormone
Function:
stimulates the growth of male and female organs
lactogenic hormone (prolactine)
Function:
stimulates secretion of milk after child birth
thyrotropic hormone( TSH)
Function:
proper functioning of thyroid glands/thyroxine production
adrenocorthicotropic hormone (ACTH)
Function:
stimulate release of adrenal cortex hormone
oxytocine hormone
Function:
regulates blood pressure
stimulates smooth muscles
stimulates contraction of uterus during child birth
aids flow of milk from mammary glands
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Function:
causes maturition of egg in females
stimulates sperm production in male
Vasopressin (ADH) antidiuretic hormone
Function:
regulates water balance by kidney
adrenaline (epinephrine hormone)
Function:
for emergency
prepares body to cope up with stress
aldosterone hormone
Function:
maintain balance of salt and water in blood
cortisone hormone
Function:
break down the stored proteins to amino acids
aids in the break down of adipose tissue
regulates sugar levels in the blood
prevents inflammation
sex hormone
Function:
supplements sex hormones produced by gonads
promotes development of sexual characteristics
Hormone:
insulin
Function:
regulates levels of sugar in blood
enables liver to store sugars
glucagon
Function:
regulates levels of sugar in blood
Hormone:
oestrogen
Function:
causes secondary sexual characteristics in female
prepares the uterus for pregnancy
progesterone
Function:
growth of mucus lining of uterus
maintains the uterus during pregnancy
Hormone:
androgen testosterone
Function:
causes secondary sexual characteristics in male
Hormone:
gastrin
Function:
stimulates release of gastric juice
Hormone:
secretin
Function:
stimulates secretion of pancreatic juice
iv) Give the differences between nervous and endocrine (hormonal) communication
nervous
hormonal(endocrine)
v) State the effects of over secretion and under secretion of adrenaline and thyroxine in
humans


g) i) Define the following terms
Drug
Drug abuse
ii) State the types of drugs, examples and side effects
Sedatives
Pain-killers
Hallucinogens
behavior that can lead to murder or suicide
Stimulants
iii) State the general effects of drug abuse on human health
may cause poor health
h) i) List the special sense organs in mammals and the major function of each
– Eye for sight
– Ear for hearing and balance
– Nose for smell
– Skin for touch, temperature detection, pain detection
iii) How is the human eye adapted to its function?

Sclerotic layer is made up of (collagen) fibers/fibrous. It maintains shape of the
eyeball/protects the eye
of light in the eye/contains blood vessels that supply oxygen/nutrients/remove
(metabolic) wastes from the eye
interpretation)
objects allow light to pass through/for refraction of light rays
pupil
comea/lens/maintains shape of the eyeball/refracts light rays
iii) What is accommodation of the eye?
the retina
iv) Explain how an eye viewing a near object adjusts to viewing a far object
v) What changes occur in the eye if it changes from observing an object at a distance to one
at a closer range?
– ciliary muscles contract
– Tension in suspensory ligaments reduces/relaxes slackens
– Lens bulges/thickens/increases curvature
– Radial muscles contract
– Circular muscles relax
– Size of pupil becomes large to allow in more light.
viii) State the changes which would take place in the eye if a person in a dark room
had lights switched on
ix) Explain how the eye forms an image
x) Name the defects of the eye and state how they can be corrected
Short sight (Myopia)

Long sight (Hypermetropia)
image on the retina
near image is formed behind the retina but a distant one is correctly focused on the retina

Presbyopia
of light rays
Squinting
Astigmatism
xi) State the advantages of having two eyes in human beings
i) What are the functions of the human ear?
iv) How are the structures of the human ear suited to perform the function of
hearing?


auditory canal/auditory mateus
membrane/tympanum/eardrum
vibrations
sound vibrations
(perilymph and endolymph) then to cochlea.
sensory cells
ear with the atmospheric air pressure (in outer ear)
ear to middle ear
iii) Explain how the structure of the human ear performs the function of balancing
planes at right angles to each other
sensory impulses are generated
body/posture/balance
iv) State what would happen if the auditory nerve was completely damaged
5. a) i) What is support?
ii) What is locomotion?
iii) State the importance of support systems in living organisms
crushing each other
eyes, heart
iv) State the importance of locomotion in animals
b) i) Name the tissues in higher plants that provide mechanical support
ii) State the importance of support in plants
iii) Name the types of plant stems
iv) Name the tissues in plants that are strengthened with lignin
v) What makes young herbaceous plants remain upright?
vi) State the ways by which plants compensate for lack of ability to move from one place to
another
c) i) Explain the Ways in which erect posture is maintained in a Weak herbaceous stem
– This is the function of turgidity and presence of collencyma
Cells take in water and become turgid
ii) Explain how support in plants is achieved
upright
support
and setting inward pressure against turgid cells and this causes a force to hold plant
upright
d) i) Give the reasons why support is necessary in animals
ii) Why is movement necessary in animals?
e) i) Name the organ used for support by animals
– Skeleton
ii) Name the different types of skeletons in animals, giving an example of an animal for
each type of skeleton named
iii) State the difference between exoskeleton and endoskeleton
iv) State the advantages of having an exoskeleton
v) Explain the importance of having an endoskeleton
f) i) Explain how a fish is adapted to living in Water
ii) Explain how a finned fish is adapted, to locomotion in Water
flexible
of water pushing the fish sideways and forwards in a direction opposed to thrust
controlling pitch and slow down movement/unpaired fins (dorsal, ventral, anal) for
yawing and rolling (caudal) for swimming/propulsion and steering/change of direction
g) i) Name the main parts of the vertebral column giving the types of bones found in each
part
Axial skeleton
Appendicular skeleton
hind limbs are connected to the pelvic girdle (hips)
tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges, ilium, ischium and pubis
ii) What are the vertebrae?
iii) State the functions of the vertebral column
iv) State the general characteristics of vertebrae


v) Name the bones of the vertebral column
– Cervical vertebra
— Thoracic vertebra
– Lumbar vertebra
– Sacral vertebra
– Caudal vertebra

vi) Describe how the various vertebrae are adapted to their functions

Bone:
skull
Structure:
Function:
Bone:
cervical region Atlas (first cervical)
Structure:
Function:
Bone:
axis (second cervical)
Structure:
Function:
Bone:
cervical (others)
Structure:
Function:
Bone:
Thoracid
Structure:
Function:
Bone:
lumbar
Structure:
anapophysis,metapophysis
Function:
Bone:
sacral
Structure:
Function:
Bone:
Rib
Structure:
Function:
vii) Describe the bones that form the appendicular skeleton
Bone:
pectoral girdle (scapular shoulder bone)
Structure:
Function:
Bone:
Humerous
Structure:
Function:
Bone:
Ulna and radius
Structure:
Function:
Bone:
pelvic girdle (hip bone)
Structure:
Function:

Bone:
Femur
Structure:
Function:
Bone:
tibia and fibula
Structure:
Function:
6. a) What is a joint?
ii) State the functions of joints
iii) Name the main types of joints
iv) Give the features of movable joints
membrane
b) Describe the synovial joints
iv) Ball and socket
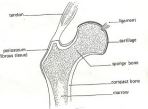
v) Hinge joint
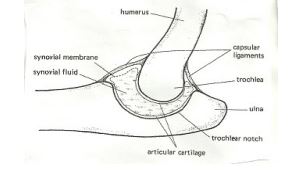
vi) Pivot joint
c) i) What is synovial fluid?
ii) State the functions of synovial fluid
d) Explain the following terms
v) Ligament
vi) Cartilage
vii) Tendon
7. Muscles
e) i) What is a muscle?
ii) State the functions of muscles
f) Describe the structure and function of various types of muscles
i) skeletal muscles
ii) Involuntary muscles
organs, bladder, uterus, urinary tract, reproductive system, respiratory tract, ciliary body
iris
iii) Cardiac muscles
g) Explain how muscles cause movement of the human arm
h) i) State the structural differences between skeletal muscles e.g. biceps and smooth
muscles e.g. gut muscle
skeletal (biceps)
smooth muscles
ii) Name the cartilage found between the bones of the vertebral column
iv) What are the functions of the cartilage named in (d) ii) above
Biology Notes FAQ Form
Please insert your question in the form below. Check and ensure that your question has not been asked and answered in the enquiries appearing beneath the form.
Biology Notes Questions and Answers
Click below to see contributions from other visitors to this page…
aa biology form 3 questions and answers
10th grade biology questions and answers
10th grade biology test
11th ncert biology
12th class biology book free download
2017 biology hsc answers
9th grade biology study guide
a level biology biological molecules questions
a level biology exam questions by topic
a level biology notes edexcel
a level biology notes xtremepapers
a level biology questions and answers
a level biology questions and answers (pdf)
a level biology questions and answers pdf
a level biology questions by topic – kidney questions with markschemes
a level biology revision
a level biology revision edexcel
a level biology revision guide
a level biology revision notes
a level biology revision notes pdf
a level biology textbook pdf
a level biology year 1 / as aqa exam questions by topic
a level edexcel notes – a* biology
aerobic respiration in plants
all biology essays
anaerobic respiration equation
animal cell organelles quiz answers
animal cell questions and answers
animal cell quiz
animal cell quiz labeling
ap bio quizzes
ap biology essay questions and answers
as level biology notes
bbc bitesize biology ks3
biology 101
biology 12th
biology 12th class notes pdf
biology 2019 syllabus
biology book 3 klb
biology book 3 notes
biology book for class 11
biology book pdf free download
biology cell structure test
biology class 12 ncert solutions
biology class 12 pdf
biology communication syllabus
biology diagrams for class 12 – biology diagram software – biology diagrams for class-10 – biology diagrams for class 11 – biology diagrams for class 9 – biology diagrams to label – biology diagram of female reproductive system – biology diagrams pdf – biology diagrams in form 1 – biology diagrams in form 2 – biology diagrams in form 3 – biology diagrams in form 4 – kcse biology diagrams -biology revision tips
biology essay questions and answers
biology essay questions and answers 2018
biology essay questions and answers form 1
biology essay questions and answers form 2
biology essay questions and answers form 3
biology essay questions and answers form 4
biology essay questions and answers form 4 pdf
biology essay questions and answers pdf
biology essays and answers
biology essays kcse
biology essays pdf
biology exam 2 test
biology exam form four
biology exam form one
biology exam form three
biology exam form two
biology exam practice test
biology exam questions and answers
biology exam questions and answers pdf
biology exam study guide
biology excretion notes
biology exercise form 4 with answers
biology final exam answer key
biology final exam answer key 2016
biology final exam answer key 2017
biology final exam answers 2018
biology final exam answers 2019
biology final exam questions and answers
biology form 1 & 2 and answers
biology form 1 chapter 1
biology form 1 diagrams
biology form 1 notes
biology form 1 notes pdf
biology form 1 past papers
biology form 1 questions
biology form 1 questions and answers
biology form 1 questions and answers pdf
biology form 1 revision questions
biology form 1 syllabus
biology form 2 chapter 1
biology form 2 chapter 2
biology form 2 diagrams
biology form 2 notes
biology form 2 notes pdf
biology form 2 past papers
biology form 2 pdf
biology form 2 questions
biology form 2 questions and answers
biology form 2 questions and answers pdf
biology form 2 revision notes
biology form 2 syllabus
biology form 3 chapter 3
biology form 3 classification
biology form 3 diagrams
biology form 3 ecology
biology form 3 notes
biology form 3 notes pdf
biology form 3 past papers
biology form 3 questions
biology form 3 questions and answers
biology form 3 questions and answers pdf
biology form 3 questions and answers term 3
biology form 3 questions and answers+pdf
biology form 3 revision notes
biology form 3 syllabus
biology form 3 topics
biology form 4 all chapter
biology form 4 chapter 4
biology form 4 diagrams
biology form 4 notes
biology form 4 notes all chapter pdf
biology form 4 notes chapter 1
biology form 4 notes pdf
biology form 4 past papers
biology form 4 questions
biology form 4 questions and answers
biology form 4 questions and answers pdf
biology form 4 syllabus
biology form 4 textbook pdf
biology form four notes pdf
biology form four questions and answers
biology form four questions and answers pdf
biology form one
biology form one exam
biology form one notes pdf
biology form one questions
biology form one questions and answers
biology form one questions and answers pdf
biology form one term three test
biology form three questions and answers
biology form three questions and answers pdf
biology form three reproduction
biology form three reproduction.
biology form three-questions and answers
biology form two diagrams
biology form two notes pdf
biology form two questions and answers
biology form two questions and answers pdf
biology form2
biology form2 textbook
biology grade 10 exam papers
biology hsc pdf
biology human reproduction video
biology kcse 2017
biology kcse 2017 paper 1
biology kcse questions
biology made familiar
biology mcq for class 11
biology mcq for class 12
biology mcq for competitive exams
biology mcq for competitive exams pdf
biology mcq for neet pdf
biology mcq with answers pdf
biology mcqs for class 12 pdf
biology mid familia form one
biology multiple choice questions and answers cxc
biology multiple choice questions and answers pdf
biology multiple choice questions with answers pdf
biology notes
biology notes for high school students
biology notes for igcse 2014
biology notes form 1
biology notes form 2
biology notes form 3
biology notes form 4
biology notes form 4 chapter 2
biology notes form one pdf
biology notes form three
biology notes form two
biology objective answer
biology objective questions for competitive exams pdf
biology paper 1
biology paper 1 notes
biology paper 1 questions
biology paper 1 questions and answers
biology paper 1 topics
biology paper 2 2017
biology paper 2 questions and answers
biology paper 2 revision
biology paper 2018
biology paper one questions and answers
biology past papers 2017
biology past papers form 3
biology practical book class 12 pdf
biology practical exam
biology practicals questions and answers
biology practice test 9th grade
biology practice test answers
biology practice test questions and answers
biology question and answers note
biology questions
biology questions and answers
biology questions and answers for high schools
biology questions and answers for high schools pdf
biology questions and answers form 1
biology questions and answers form 2
biology questions and answers form 3
biology questions and answers form 4
biology questions and answers multiple choice
biology questions and answers on cells
biology questions and answers online
biology questions and answers pdf
biology questions for high school
biology questions for high school students with answers
biology questions multiple choice
biology questions quizlet
biology questions to ask your teacher
biology quiz for class 9
biology quiz questions and answers for class 10
biology quiz questions and answers for class 12
biology quiz questions and answers for class 9
biology quiz questions and answers for high school
biology quiz questions and answers pdf
biology quiz questions for class 12
biology quiz questions for college students
biology quiz with answers
biology quiz with answers pdf
biology revision
biology revision a level
biology revision notes form 1
biology revision notes form 2
biology revision notes form 3
biology revision notes form 4
biology revision notes igcse
biology revision questions
biology study guide
biology study guide – biology questions and answers
biology study guide answer key
biology study guide answers
biology study guide ib
biology study guide pdf
biology study notes
biology syllabus in kenya
biology test questions and answers
biology test questions and answers pdf
biology topics form one
biology unit 1 quiz
biology | revision science
cell biology exam questions and answers
cell biology exam questions pdf
cell biology mcq with answers
cell biology multiple choice questions and answers pdf
cell biology multiple choice questions pdf
cell biology previous question papers
cell biology question bank
cell biology question bank pdf
cell biology question paper pdf
cell biology questions and answers multiple choice
cell biology questions and answers multiple choice pdf
cell biology questions and answers pdf
cell biology questions and answers pdf in hindi
cell biology short answer questions
cell biology test bank questions
cell biology test questions and answers
cell biology test questions and answers pdf
cell mcq pdf
cell organelles labeling quiz
cell organelles multiple choice questions and answers
cell questions and answers
cell questions and answers pdf
cell questions quizlet
cell structure and function pdf
cell structure and function pdf class 11
cell structure and function quiz answers
cell structure and function test answer key
cell structure and function test pdf
cells
cells questions
cellular organization pdf
chemical equation for aerobic respiration
chemistry form 1 questions and answers
chemistry form 2 exams
chemistry form 2 questions and answers
chemistry form 2 questions and answers pdf
chemistry form 3 questions and answers
chemistry form 3 revision questions
chemistry form 4 questions and answers
chemistry form one questions and answers pdf
chemistry kcse questions and answer
chemistry paper 2 questions and answers
chemistry paper 3 question and answer
cie a level biology notes 2016
cie a level biology notes pdf
class 10 biology chapter 1 mcqs
college biology practice test
college biology quiz
college biology quiz chapter 1
college biology quizlet
college biology study guide
college biology study guide pdf
college biology test questions and answers
complete biology for cambridge igcse revision guide pdf
cytology mcqs with answers pdf
difficult questions on gaseous exchange in animals
download form three biology notes
download klb biology book 2
easy biology questions
easy cell questions
edexcel a level biology b
edexcel a level biology notes pdf
edexcel a level biology salters nuffield
edexcel a2 biology notes
edexcel as biology revision guide pdf
edexcel biology a2 revision notes pdf
edexcel biology unit 2 revision notes
edexcel gcse science revision guide pdf
energy questions science bowl
essential cell biology test bank answers
essential cell biology test bank download free
exam notes for biology 101
excretion question and answer form 4 work
excretion questions and answers
excretory system questions and answers pdf
excretory system structure
f3 biology test paper
form 1 biology exam
form 1 biology notes
form 1 biology questions and answers
form 1 biology syllabus
form 1 mathematics questions and answers
form 1 mathematics test paper pdf
form 1 revision papers
form 2 biology exam
form 2 biology notes pdf
form 2 biology questions and answers
form 2 biology questions and answers >
form 2 biology syllabus
form 2 mathematics questions and answers
form 3 biology book
form 3 biology exam
form 3 biology questions and answers
form 3 chemistry exam paper
form 3 chemistry questions and answers pdf
form 3 english exam paper
form 3 history exam paper
form 3 maths exam paper
form 4 biology exam
form four biology book
form four biology revision questions
form four biology syllabus
form four biology topics
form one biology book
form one biology questions
form one biology revision questions
form one biology syllabus
form one biology topics
form one geography questions and answers
form one notes of biology
form one past papers
form three biology book
form three biology notes
form three biology revision questions
form three biology syllabus
form three biology topics
form three cre notes pdf
form two biology book
form two biology examination
form two biology notes
form two biology revision questions
form two biology syllabus
form two biology topics
form two chemistry cat
form two chemistry past papers
form two chemistry questions and answers
form two chemistry questions and answers pdf
form two notes
free a-level biology revision app | pass your biology exams
free biology form 1 notes
free college biology practice test
free kcse revision notes
fun biology questions
funny biology questions and answers
funny biology quotes
funny science questions
funny science questions to ask
gas exchange exam questions
gas exchange practice test
gas exchange quiz
gcse biology exam questions and answers
gcse biology past papers
gcse biology revision
gcse biology revision notes
gcse biology revision notes pdf
gcse biology revision notes pdf 9-1
gcse biology revision questions and answers
gcse biology textbook pdf
gcse biology topics – pass my exams: easy exam revision notes
general biology practice test with answers
general biology quiz
general biology test questions and answers
general knowledge in biology human body
general science mcq for ssc
general science mcqs with answers pdf
general science notes pdf
geography form 1 questions and answers pdf
geography form 1 revision questions
geography form 3 questions
good biology questions to ask
gre biology practice test
gre biology subject test pdf
hard biology quiz questions
hard science questions and answers
hard science questions to ask your teacher
high school biology final exam doc
high school biology final exam pdf
high school biology final exam questions
high school biology final exam questions and answers
high school biology practice test
high school biology test questions and answers pdf
how does the excretory system work
how many chromosomes do gametes have
how many copies of each gene do gametes have
how much genetic information is found in a gamete
how to study biology: 5 study techniques to master biology
hsc biology 2018
hsc biology 2019
ial biology notes
ib biology question bank by topic
igcse biology alternative to practical revision
igcse biology notes 2017 pdf
igcse biology notes edexcel
igcse biology paper 6 notes
igcse biology revision guide
igcse biology revision notes pdf
igcse biology revision worksheets
igcse biology znotes
igcse notes chemistry
igcse physics revision notes pdf
interesting biology questions
interesting questions to ask about biology
interesting science questions and answers
intro to biology quiz
k.c.s.e mathematics paper 1 2017
kcse 2015 biology paper 3
kcse 2016 biology paper 1
kcse 2016 biology paper 2
kcse 2017 biology paper 2
kcse 2017 papers
kcse biology essay questions and answers
kcse biology essay questions and answers pdf
kcse biology essays
kcse biology essays pdf
kcse biology notes
kcse biology notes pdf
kcse biology paper 1
kcse biology paper 1 2017
kcse biology paper 1 2017 pdf
kcse biology paper 2
kcse biology paper 2 2013
kcse biology paper 2 2015
kcse biology paper 2 2017
kcse biology paper 3 2016
kcse biology paper 3 past papers
kcse biology past papers and answers
kcse biology practical past papers
kcse biology practicals
kcse biology questions and answers
kcse chemistry notes
kcse chemistry paper 1 2013
kcse chemistry paper 1 2016
kcse chemistry paper 2 2014
kcse chemistry paper 2 2016
kcse chemistry past papers
kcse chemistry past papers and answers
kcse chemistry practical
kcse cre past papers and answers
kcse english paper 3 2016
kcse essays
kcse made familiar chemistry
kcse made familiar geography
kcse made familiar kiswahili
kcse made familiar mathematics pdf
kcse mathematics paper 1 2016
kcse mathematics past papers pdf
kcse mock papers pdf
kcse past papers
kcse past papers 2012
kcse past papers biology
kcse revision question for biology
kcse syllabus pdf
kenya secondary school chemistry syllabus
kenya secondary school syllabus pdf
klb biology book 2
klb biology book 2 notes
klb biology book 2 pdf
klb biology book 3 pdf
klb biology form 1
klb biology form 1 notes
klb biology form 1 pdf
klb biology form 2 book
klb biology form 2 notes
klb biology form 2 pdf
klb biology form 3 notes
klb biology form 3 pdf
klb biology form 4 notes
klb biology form 4 pdf
klb biology form one
klb geography form 3
knec biology syllabus
kusoma biology notes
kusoma biology notes pdf
kusoma.com past papers
made familiar biology pdf
made familiar mathematics
mathematics form 3 questions and answers
mathematics form 3 questions and answers pdf
mcq on cell biology class 9
mcqs about gaseous exchange
middle school science bowl biology questions
more than 1800 biology questions and answers to help you study
multiple choice questions on biology
multiple choice questions on cell structure and function
o level biology practical experiments
orm three biology notes
page navigation
past paper questions by topic biology
pdf biology form 3
physics form 1 questions and answers pdf
physics form one questions and answers
physics questions and answers pdf for competitive exams
plant and animal cell organelles quiz
plant and animal cell organelles quiz answers
plant and animal cell quiz for 5th grade
plant and animal cell quiz grade 8
plant and animal cell quiz pdf
plant cell
plant cell pdf download
plant cell questions and answers
plant cell test questions
practical biology experiments pdf
practical biology question and answer pdf
preliminary biology
questions about cells biology
questions and answers on gaseous exchange
questions and answers pdf biology form 1
questions and answers pdf biology form 2
questions and answers pdf biology form 3
questions and answers pdf biology form 4
questions and answers pdf biology form four
questions and answers pdf biology form one
questions and answers pdf biology form three
questions and answers pdf biology form two
questions based to introduction to biology
questions on cell structure and function
questions on gaseous exchange in humans
questions to ask in biology class
questions to confuse your science teacher
respiration and gas exchange worksheet
respiration notes my elim form two
revision quiz for biology for form three
science bowl biology study guide
science bowl questions biology
science bowl questions chemistry
science bowl questions earth science
science bowl questions math
science bowl questions middle school
science bowl questions physics
science quiz for class 9 biology
science quiz questions and answers for class 10
science quiz questions and answers for class 10 pdf
science quiz questions and answers for class 9 pdf
simple scientific questions
smart questions to ask a physics teacher
smart questions to ask a science teacher
snab biology revision notes
the animal cell quiz answers
the excretory system answer key
the excretory system worksheet answers
the plant cell quiz answer key
tricky biology questions and answers
tricky science questions for adults
tricky science quiz questions
two biology revision questions
types of respiration
what are gametes
what are gametes in biology
what are gametes in plants
what are gametes in punnett squares
what are gametes quizlet
what are the types of gametes
working of excretory system
year 11 biology
znotes as biology
“Pdf” Revision Questions Biology Form 2
“Pdf” Revision Questions Biology Form 3
“Pdf” Revision Questions Biology Form 4
“Pdf” Revision Questions Biology Form Four
“Pdf” Revision Questions Biology Form One
“Pdf” Revision Questions Biology Form Three
“Pdf” Revision Questions Biology Form Two
1 a a KCSE Past Papers
10th Grade Biology Questions and Answers
10th Grade Biology Test
11th Ncert Biology
12th Class Biology Book Free Download
2014 KCSE Marking Schemes
2014 Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2015
2015 Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 4
2016 KCSE Papers
2016 KCSE Prediction Questions
2017 Biology Hsc Answers
2017 KCSE Prediction Questions
2018 Biology KCSE Leakage
2018 Biology KCSE Questions
2018 KCSE Busineness Studies
2018 KCSE Exam
2018 KCSE Leakage
2018 KCSE Prediction Questions
2018 KCSE Questions
2019 Biology KCSE Leakage
2019 Biology KCSE Questions
2019 KCSE Leakage
2019 KCSE Questions
9th Grade Biology Study Guide
A a a Biology Notes
a a a Biology Notes!
a a a BiologyNotes!
A a KCSE Past Papers
A Biblical View of Social Justice
A Level Biology Biological Molecules Questions
A Level Biology Exam Questions by Topic
A Level Biology Notes Edexcel
A Level Biology Notes Xtremepapers
A Level Biology Past Papers
A Level Biology Questions and Answers
a Level Biology Questions and Answers
A Level Biology Questions and Answers (Pdf)
A Level Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
A Level Biology Questions by Topic Kidney Questions With Markschemes
A Level Biology Revision
A Level Biology Revision Edexcel
A Level Biology Revision Guide
A Level Biology Revision Notes
A Level Biology Revision Notes Pdf
A Level Biology Textbook Pdf
A Level Biology Year 1 / as Aqa Exam Questions by Topic
A Level Edexcel Notes a* Biology
aa Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers
Advance KCSE Past Papers
Advance-africa.com KCSE Rev Quiz
Advantages and Disadvantages.
Aerobic Respiration in Plants
All Biology Essays
All Biology Notes for Senior Two
All KCSE Past Papers Biology With Making Schemes
All Marking Schemes Questions and Answers
All Past K.c.s.e Questions With Answers
Alliance Mocks 2017
Anaerobic Respiration Equation
Animal Cell Organelles Quiz Answers
Animal Cell Questions and Answers
Animal Cell Quiz
Animal Cell Quiz Labeling
Ap Bio Quizzes
Ap Biology 1 Textbook Pdf
Ap Biology Essay Questions and Answers
Are Sourced From KNEC.
As Level Biology Notes
Atika Biology Notes
Atika School Biology Notes
B/s Book 2 Notes
Basic Biology Books Pdf
basic Biology Interview Questions and Answers Pdf
Basic Biology Interview Questions and Answers Pdf
Basic Biology Pdf
Basic Biology Questions and Answers
Basic Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Bbc Bitesize Biology Ks3
Bihar Board Biology Objective Answer 2017
Bihar Board Biology Objective Answer 2018
Bio Answers
Bio Quesions
Biology 0478
Biology 101
Biology 12th
Biology 12th Class Notes Pdf
Biology 2019 Syllabus
Biology All KCSE Short Notes
Biology Answers
Biology Answers Online Free
Biology Answers Quizlet
Biology Bk 2 Notes
Biology Book 1
Biology Book 1 Notes
Biology Book 2
Biology Book 2 Notes
Biology Book 3
Biology Book 3 KLB
Biology Book 3 Notes
Biology Book 4
Biology Book 4 Notes
Biology Book 4 Pdf
Biology Book for Class 11
Biology Book Four
Biology Book Four Notes
Biology Book One
Biology Book One Notes
Biology Book Pdf Free Download
Biology Book Three
Biology Book Three Notes
Biology Book Three Pdf
Biology Book Two
Biology Book Two Notes
Biology Books Form Three
Biology Bowl Biology Study Guide
Biology Bowl Questions Biology
Biology Bowl Questions Earth Biology
Biology Bowl Questions Math
Biology Bowl Questions Middle School
Biology Brekthrough Form Two Notes
Biology Cell Structure Test
Biology Class 12 Ncert Solutions
Biology Class 12 Pdf
Biology Communication Syllabus
Biology Diagram of Female Reproductive System
Biology Diagram Software
Biology Diagrams for Class 11
Biology Diagrams for Class 12
Biology Diagrams for Class 9
Biology Diagrams for Class-10
Biology Diagrams in Form 1
Biology Diagrams in Form 2
Biology Diagrams in Form 3
Biology Diagrams in Form 4
Biology Diagrams Pdf
Biology Diagrams to Label
Biology Essay Questions and Answers
Biology Essay Questions and Answers 2018
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 1
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 2
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 3
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 4
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Form 4 Pdf
Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Essay Revision Q
Biology Essays and Answers
Biology Essays Form One to Form Four
Biology Essays Form One to Form Three
Biology Essays KCSE
Biology Essays Pdf
Biology Exam 1 Multiple Choice
Biology Exam 2 Advance
Biology Exam 2 Test
Biology Exam 2016
Biology Exam Form Four
Biology Exam Form One
Biology Exam Form Three
Biology Exam Form Two
Biology Exam Practice Test
Biology Exam Questions
Biology Exam Questions and Answers
Biology Exam Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Exam Study Guide
Biology Exams
Biology Excretion Notes
Biology Exercise Form 4 With Answers
Biology Final Exam Answer Key
Biology Final Exam Answer Key 2016
Biology Final Exam Answer Key 2017
Biology Final Exam Answers 2018
Biology Final Exam Answers 2019
Biology Final Exam Questions and Answers
Biology Fom 1 Notes
Biology Fom 2 Notes
Biology Fom 3 Notes
Biology Fom 4 Notes
Biology Form 1
Biology Form 1 & 2 and Answers
Biology Form 1 and 2 Essays
Biology Form 1 and 2 Essays Questions and Answers
Biology Form 1 Chapter 1
Biology Form 1 Diagrams
Biology Form 1 Exams
Biology Form 1 Mid Year Exam
Biology Form 1 Notes
Biology Form 1 Notes and Questions
Biology Form 1 Notes Download
Biology Form 1 Notes Free Download
Biology Form 1 Notes GCSE
Biology Form 1 Notes KCSE-kcse
Biology Form 1 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 1 Notes Pdf Download
Biology Form 1 Past Papers
Biology Form 1 Pdf
Biology Form 1 Pressure
Biology Form 1 Question Papers
Biology Form 1 Questions
Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 1 Quiz
Biology Form 1 Revision Questions
Biology Form 1 Summary Notes
Biology Form 1 Syllabus
Biology Form 1 Work
Biology Form 1-4 Notes
Biology Form 2
Biology Form 2 Chapter 1
Biology Form 2 Chapter 2
Biology Form 2 Diagrams
Biology Form 2 Exam Paper 2014
Biology Form 2 Exams
Biology Form 2 Notes
Biology Form 2 Notes and Questions
Biology Form 2 Notes GCSE
Biology Form 2 Notes KCSE-kcse
Biology Form 2 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 2 Notes Pdf Download
Biology Form 2 Past Papers
Biology Form 2 Pdf
Biology Form 2 Question Papers
Biology Form 2 Questions
Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 2 Quiz
Biology Form 2 Revision Notes
Biology Form 2 Salts
Biology Form 2 Structure and Bonding
Biology Form 2 Summary Notes
Biology Form 2 Syllabus
Biology Form 2 Work
Biology Form 3
Biology Form 3 and 4 Essays
Biology Form 3 and 4 Essays Questions and Answers
Biology Form 3 Chapter 3
Biology Form 3 Classification
Biology Form 3 Diagrams
Biology Form 3 Ecology
Biology Form 3 Exams
Biology Form 3 Notes
Biology Form 3 Notes and Questions
Biology Form 3 Notes GCSE
Biology Form 3 Notes KCSE-kcse
Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf Download
Biology Form 3 Notes Topic 1
Biology Form 3 Past Papers
Biology Form 3 Pdf
Biology Form 3 Question Papers
Biology Form 3 Questions
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Term 3
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers+pdf
Biology Form 3 Quiz
Biology Form 3 Revision Notes
Biology Form 3 Revision Questions
Biology Form 3 Summary Notes
Biology Form 3 Syllabus
Biology Form 3 Syllabus Pdf
Biology Form 3 Topics
Biology Form 3 Work
Biology Form 4
Biology Form 4 All Chapter
Biology Form 4 Chapter 1 Conversion of Units
Biology Form 4 Chapter 1 Exercise
Biology Form 4 Chapter 1 Exercise and Answers
Biology Form 4 Chapter 1 Exercise Pdf
Biology Form 4 Chapter 1 Mind Map
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Exercise and Answers
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Exercise Pdf
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Experiment
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Formula
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Mind Map
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Momentum
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Objective Questions and Answers
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Paper 2
Biology Form 4 Chapter 2 Slideshare
Biology Form 4 Chapter 3
Biology Form 4 Chapter 3 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 4 Chapter 4
Biology Form 4 Chapter 4 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 4 Chapter 5 Light Questions and Answers
Biology Form 4 Chapter 5 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 4 Diagrams
Biology Form 4 Exam Paper 1
Biology Form 4 Exams
Biology Form 4 Exercise
Biology Form 4 Exercise Pdf
Biology Form 4 Module With Answer
Biology Form 4 Note
Biology Form 4 Notes
Biology Form 4 Notes (Pdf)
Biology Form 4 Notes All Chapter Pdf
Biology Form 4 Notes and Questions
Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 1
Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 2
Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 3
Biology Form 4 Notes Download
Biology Form 4 Notes Free Download
Biology Form 4 Notes GCSE
Biology Form 4 Notes KCSE-kcse
Biology Form 4 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 4 Notes Pdf Download
Biology Form 4 Paper 2 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 4 Past Papers
Biology Form 4 Question Papers
Biology Form 4 Questions
Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers
Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 4 Quiz
Biology Form 4 Revision Notes
Biology Form 4 Schemes of Work
Biology Form 4 Summary Notes
Biology Form 4 Syllabus
Biology Form 4 Textbook Pdf
Biology Form 4 Work
Biology Form 5 Chapter 1 Exercise and Answers
Biology Form 5 Chapter 1 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 5 Chapter 2 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 5 Chapter 2 Slideshare
Biology Form 5 Chapter 3 Notes Pdf
Biology Form 5 Notes Pdf
Biology Form Four Book
Biology Form Four Notes
Biology Form Four Notes and Questions
Biology Form Four Notes GCSE
Biology Form Four Notes Pdf
Biology Form Four Past Papers
Biology Form Four Questions
Biology Form Four Questions and Answers
Biology Form Four Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Four Quiz
Biology Form Four Study Notes
Biology Form Four Syllabus
Biology Form Four Topic 2
Biology Form Four Topic 4
Biology Form Four Topics
Biology Form Four Work
Biology Form One
Biology Form One Book
Biology Form One Book Pdf
Biology Form One Download Topic 1 Upto 3
Biology Form One Exam
Biology Form One Notes
Biology Form One Notes and Questions
Biology Form One Notes GCSE
Biology Form One Notes Pdf
Biology Form One Pdf
Biology Form One Questions
Biology Form One Questions and Answers
Biology Form One Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form One Questions and Their Answers
Biology Form One Quiz
Biology Form One Revision Question
Biology Form One Schemes of Work
Biology Form One Study Notes
Biology Form One Syllabus
Biology Form One Term Three Test
Biology Form One to Three Notes
Biology Form One Work
Biology Form Three
Biology Form Three Book
Biology Form Three Notes
Biology Form Three Notes and Questions
Biology Form Three Notes GCSE
Biology Form Three Questions and Answers
Biology Form Three Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Three Quiz
Biology Form Three Reproduction
Biology Form Three Reproduction.
Biology Form Three Study Notes
Biology Form Three Work
Biology Form Three-questions and Answers
Biology Form Two
Biology Form Two Book
Biology Form Two Diagrams
Biology Form Two Notes
Biology Form Two Notes and Questions
Biology Form Two Notes GCSE
Biology Form Two Notes Pdf
Biology Form Two Notes-pdf
Biology Form Two Pdf
Biology Form Two Questions
Biology Form Two Questions and Answers
Biology Form Two Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Two Quiz
Biology Form Two Study Notes
Biology Form Two Topics
Biology Form Two Work
Biology Form Two,schemes of Work
Biology Form2
Biology Form2 Textbook
Biology Game Form Four Question End Answers
Biology Grade 10 Exam Papers
Biology Hsc Pdf
Biology Human Reproduction Video
Biology IGCSE Past Papers Xtremepapers
Biology K.c.s.e 2017
Biology KCSE
Biology KCSE 2016
Biology KCSE 2017
Biology KCSE 2017 Paper 1
Biology KCSE Past Papers
Biology KCSE Questions
Biology KCSE Questions and Answer
Biology KCSE Quizzes & Answers
Biology KCSE Revision
Biology KCSE Revision Notes
Biology KCSE Setting Questions Form One and Two
Biology Ksce 2015
Biology Last Year K.c.s.e Questions
Biology Lesson Plan Form Two
Biology Made Familiar
Biology Mcq for Class 11
Biology Mcq for Class 12
Biology Mcq for Competitive Exams
Biology Mcq for Competitive Exams Pdf
Biology Mcq for Neet Pdf
Biology Mcq for Ssc
Biology Mcq Questions With Answers
Biology Mcq With Answers Pdf
Biology Mcqs for Class 12 Pdf
Biology Mcqs With Answers Pdf
Biology Mid Familia Form One
Biology Mock Papers
Biology Module Form 5
Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Cxc
Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Multiple Choice Questions With Answers Pdf
Biology Note
Biology Note Form Two All Chapters
Biology Notes
Biology Notes and Guestion and Answear
Biology Notes and Syllabus
Biology Notes Class 10
Biology Notes for Class 11 Pdf
Biology Notes for Class 12 Pdf
Biology Notes for High School Students
Biology Notes for IGCSE 2014
Biology Notes Form 1
Biology Notes Form 1 4
Biology Notes Form 1 Free Download
Biology Notes Form 1 KLB
Biology Notes Form 1 Pdf
Biology Notes Form 1-4
Biology Notes Form 1-4(1) Biology
Biology Notes Form 14
Biology Notes Form 2
Biology Notes Form 2 KLB
Biology Notes Form 2 Pdf
Biology Notes Form 2; Biology Notes
Biology Notes Form 3
Biology Notes Form 3 KLB
Biology Notes Form 3 Pdf
Biology Notes Form 4
Biology Notes Form 4 Chapter 2
Biology Notes Form 4 KLB
Biology Notes Form 4 Pdf
Biology Notes Form 4-pdf
Biology Notes Form Four
Biology Notes Form Four KLB
Biology Notes Form Four Pdf
Biology Notes Form One
Biology Notes Form One KLB
Biology Notes Form One Pdf
Biology Notes Form One to Form Four
Biology Notes Form Three
Biology Notes Form Three KLB
Biology Notes Form Three Pdf
Biology Notes Form Two
Biology Notes Form Two KLB
Biology Notes Form Two Pdf
Biology Notes Form2
Biology Notes IGCSE
Biology Notes Kenya
Biology Notes on Agroforestry
Biology Notes Pdf
Biology Notes:
Biology Objective Answer
Biology Objective Answer 2018
Biology Objective Questions for Competitive Exams
Biology Objective Questions for Competitive Exams Pdf
Biology Oral Exam Questions
Biology Paper 1
Biology Paper 1 2018 Marking Rules
Biology Paper 1 Notes
Biology Paper 1 Questions
Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers
Biology Paper 1 Topics
Biology Paper 1 With Answers
Biology Paper 2
Biology Paper 2 2017
Biology Paper 2 2018 Marking Rules
Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers
Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Paper 2 Revision
Biology Paper 2 Topics
Biology Paper 2018
Biology Paper 3 2018 Marking Rules
Biology Paper 3 Question and Answer
Biology Paper 3 Question Paper 2014 KCSE
Biology Paper 3 Question Paper 2015 KCSE
Biology Paper 3 Question Paper 2016 KCSE
Biology Paper 3 Question Paper 2017 KCSE
Biology Paper 3 Question Paper 2018 KCSE
Biology Paper 3 Questions and Answers
Biology Paper One Questions and Answers
Biology Paper One Topics
Biology Paper Two Qestions With Answers
Biology Paper1
Biology Paper2
Biology Paper3
Biology Paper4
Biology Past Papers
Biology Past Papers 2017
Biology Past Papers a Level
Biology Past Papers Form 1
Biology Past Papers Form 2
Biology Past Papers Form 3
Biology Past Papers O Level
Biology Pdf Download
Biology Pp1 KCSE 2016
Biology Practical Book Class 12 Pdf
Biology Practical Exam
Biology Practicals Form One
Biology Practicals Questions and Answers
Biology Practice Test 9th Grade
Biology Practice Test Answers
Biology Practice Test Questions and Answers
Biology Practice Test Quizlet
Biology Predicted Questions This Year KCSE
Biology Preparation Notes
Biology Pretest High School Pdf
Biology Question and Answer With Explanation
Biology Question and Answers 2019
Biology Question and Answers 2020
Biology Question and Answers 2021
Biology Question and Answers 2022
Biology Question and Answers Note
Biology Questions
Biology Questions and Answers
Biology Questions and Answers for High School
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf
Biology Questions and Answers for Secondary Schools
Biology Questions and Answers Form 1
Biology Questions and Answers Form 2
Biology Questions and Answers Form 3
Biology Questions and Answers Form 4
Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice
Biology Questions and Answers Notes
Biology Questions and Answers O
Biology Questions and Answers on Cells
Biology Questions and Answers Online
Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Questions and Answers Pdf for Class 12
Biology Questions and Answers Pdf for Competitive Exams
Biology Questions and Answers-form 2
Biology Questions for High School
Biology Questions for High School Students With Answers
Biology Questions for Senior 1
Biology Questions for Senior 2
Biology Questions for Senior 3
Biology Questions for Senior 4
Biology Questions for Senior 5
Biology Questions for Senior 6
Biology Questions for Senior Five
Biology Questions for Senior Four
Biology Questions for Senior One
Biology Questions for Senior Six
Biology Questions for Senior Three
Biology Questions for Senior Two
Biology Questions Form One
Biology Questions Multiple Choice
Biology Questions Quizlet
Biology Questions to Ask Your Teacher
Biology Quetion and Answer Form Four
Biology Quetion and Answer Form One
Biology Quetion and Answer Form Three
Biology Quetion and Answer Form Two
Biology Quiz for Class 9
Biology Quiz for Class 9 Biology
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10 Pdf
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 12
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 9
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 9 Pdf
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers for High School
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers Multiple Choice
Biology Quiz Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Quiz Questions for Class 12
Biology Quiz Questions for College Students
Biology Quiz With Answers
Biology Quiz With Answers Pdf
Biology Quizlet
Biology Revision
Biology Revision a Level
Biology Revision Biology Notes Biology
Biology Revision Exam
Biology Revision Examination
Biology Revision Form One
Biology Revision Notes
Biology Revision Notes Biology
Biology Revision Notes Form 1
Biology Revision Notes Form 2
Biology Revision Notes Form 3
Biology Revision Notes Form 4
Biology Revision Notes IGCSE
Biology Revision Paper One
Biology Revision Questions
Biology Revision Questions and Answers
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form 1
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form 2
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form 3
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form 4
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form Four
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form One
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form Three
Biology Revision Questions and Answers Form Two
Biology Revision Questions Form 1
Biology Revision Questions Form 2
Biology Revision Questions Form 3
Biology Revision Questions Form 4
Biology Revision Questions Form Four
Biology Revision Questions Form One
Biology Revision Questions Form Three
Biology Revision Questions Form Two
Biology Revision Quiz
Biology Revision Test
Biology Secondary School Revision
Biology Simple Notes
Biology Spm Notes Download
Biology Spm Notes Pdf
Biology Spm Questions
Biology Study Form 2
Biology Study Guide
Biology Study Guide Answer Key
Biology Study Guide Answers
Biology Study Guide Biology Questions and Answers
Biology Study Guide Ib
Biology Study Guide Pdf
Biology Study Guides
Biology Study Notes
Biology Study Notes Materials Form 1 Pdf
Biology Study Notes Materials Form 2 3 Pdf
Biology Study Notes Materials Form 2 Pdf
Biology Study Notes Materials Form 3 Pdf
Biology Study Notes Materials Form 4 Pdf
Biology Syllabus in Kenya
Biology Syllabus Pdf
Biology Test 1 Quizlet
Biology Test Questions
Biology Test Questions and Answers
Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Topic One Form Four
Biology Topics Form One
Biology Unit 1 Quiz
Biology Vol 3
Biology | Revision Biology
Biology,form 4
Biology.form Four.topic Three
BiologyExam Form Three
BiologyModule Form 5
BiologyNotes
BiologyNotes for Class 11 Pdf
BiologyNotes for Class 12 Pdf
BiologyNotes Form 1
BiologyNotes Form 1 Free Download
BiologyNotes Form 2
BiologyNotes Form 3
BiologyNotes Form 3 Pdf
BiologyNotes IGCSE
BiologyNotes Pdf
BiologyPast Papers
BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf
BiologySimple Notes
BiologySpm Notes Download
BiologySpm Notes Pdf
BiologySpm Questions
BiologyStudy Guide Answers
BiologyStudy Guide Pdf
BiologyStudy Guides
Blologytextpapers
Bridge Biology
Business Past KCSE Past Papers
Business Studies Form 3 Notes Pdf
Business Studies Form 4 Notes Pdf
C R E Form One KLB
C R E Form One Oli Topic
C.r.e Form 1 Notes Kenya
C.r.e Form 2 Notes Kenya
C.r.e Form 3 Notes
C.r.e Form 3 Notes Kenya
C.r.e Form 3 Pdf
C.r.e Form 4 Notes Kenya
C.r.e Form One Notes Pdf
C.r.e Notes Form 1
C.r.e Revision Notes
C.r.e Short Notes
Cambridge IGCSE Biology
Cambridge IGCSE Biology 3rd Edition
Cambridge IGCSE Biology 3rd Edition Plus Cd South Asia Edition
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Answers
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Coursebook Pdf Download
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Practical Workbook
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Pdf
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Study and Revision Guide 2nd Edition Pdf
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Study and Revision Guide Pdf
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Workbook Free Download
Cambridge IGCSE Biology Workbook Pdf
Cambridge IGCSE® Biology Coursebook
Caucasian Chalk Circle Essay Questions
Cell Biology Exam Questions and Answers
Cell Biology Exam Questions Pdf
Cell Biology Mcq With Answers
Cell Biology Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf
Cell Biology Multiple Choice Questions Pdf
Cell Biology Previous Question Papers
Cell Biology Question Bank
Cell Biology Question Bank Pdf
Cell Biology Question Paper Pdf
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Multiple Choice Pdf
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Cell Biology Questions and Answers Pdf in Hindi
Cell Biology Short Answer Questions
Cell Biology Test Bank Questions
Cell Biology Test Questions and Answers
Cell Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf
Cell Mcq Pdf
Cell Organelles Labeling Quiz
Cell Organelles Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Cell Questions and Answers
Cell Questions and Answers Pdf
Cell Questions Quizlet
Cell Structure and Function Pdf
Cell Structure and Function Pdf Class 11
Cell Structure and Function Quiz Answers
Cell Structure and Function Test Answer Key
Cell Structure and Function Test Pdf
Cells
Cells Questions
Cellular Organization Pdf
Chapter 1 Introduction to Biology
Chapter 1 Introduction to Biology Studies
Chemical Equation for Aerobic Respiration
Cie a Level Biology Notes 2016
Cie a Level Biology Notes Pdf
Cie Past Papers
Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 Mcqs
Class 8 Biology Notes KCSE-kcse
College Biology Notes
College Biology Practice Test
College Biology Quiz
College Biology Quiz Chapter 1
College Biology Quizlet
College Biology Study Guide
College Biology Study Guide Pdf
College Biology Test Questions and Answers
College Biology Volume 3 Pdf
College BiologyNotes
Complete Biology for Cambridge IGCSE
Complete Biology for Cambridge IGCSE Revision Guide Pdf
County Mocks 2017
Cse Past Papers Biology 2017
Cytology Mcqs With Answers Pdf
Difficult Questions on Gaseous Exchange in Animals
Dl Biology Form 3 Pdf Kusoma
Download Biology Form 1
Download Biology Form 2
Download Biology Form 2 Notes
Download Biology Form 3
Download Biology Form 3 Notes
Download Biology Form 4
Download Biology Form Four
Download Biology Form One
Download Biology Form Three
Download Biology Form Two
Download Biology Notes Form 3
Download Biology Notes Form One
Download BiologyNotes Form 3
Download Form Three Biology Notes
Download Free KCSE Past Papers Biology
Download Free KCSE Past Papers From KNEC.
Download KCSE Past Papers With Answers
Download KCSE Revision Notes
Download KLB Biology Book 2
Download KLB Biology Book 3
Download KLB Biology Book 4
Download Notes of Biology
Downloads | Biology | Form Four Exams | Exams
Downloads | Biology | Form One Exams | Exams
Downloads | Biology | Form Three Exams | Exams
Downloads | Biology | Form Two Exams | Exams
Downloads | KCSE Papers and Marking Schemes |
Dvance KCSE Past Papers
Easy Biology Questions
Easy Cell Questions
Edexcel a Level Biology B
Edexcel a Level Biology Notes Pdf
Edexcel a Level Biology Salters Nuffield
Edexcel A2 Biology Notes
Edexcel as Biology Revision Guide Pdf
Edexcel Biology A2 Revision Notes Pdf
Edexcel Biology Unit 2 Revision Notes
Edexcel GCSE Biology Revision Guide Pdf
Edexcel IGCSE Biology Past Papers
Edexcel IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Free Pdf Download
Edexcel IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Pdf
Edexcel IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Pdf Download
Electronics Form Four Notes
Energy Questions Biology Bowl
Essay Questions and Answers KCSE Biology Notes
Essay Questions and Answers on Betrayal in the City
Essay Questions Based on Betrayal in the City
Essential Cell Biology Test Bank Answers
Essential Cell Biology Test Bank Download Free
Evolving World Biology Book 1 Pdf
Evolving World Biology Book 4 Notes
Evolving World Biology Book Form 1
Evolving World-history Book 3
Exam Notes for Biology 101
Exams KCSE Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers
Excretion Question and Answer Form 4 Work
Excretion Questions and Answers
Excretory System Questions and Answers Pdf
Excretory System Structure
F3 Biology Test Paper
Find Download KCSE Past Papers With Answers
Find KCSE Biology Essay Questions and Answers
Form 1 Biology Exam
Form 1 Biology Notes
Form 1 Biology Questions and Answers
Form 1 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form 1 Biology Revision Notes
Form 1 Biology Summurized Revision Pdf
Form 1 Biology Syllabus
Form 1 Biology Test Paper Pdf
Form 1 Biology Topics
Form 1 BiologyNotes
Form 1 BiologyQuestions and Answers
Form 1 BiologyRevision Notes
Form 1 BiologySyllabus
Form 1 BiologyTest Paper Pdf
Form 1 Past Papers
Form 1 Past Papers With Answers
Form 1 Revision Papers
Form 1 Subjects in Kenya
Form 2 Biology Exam
Form 2 Biology Exam Paper
Form 2 Biology Exam Paper 2016
Form 2 Biology Exam Paper Free Download
Form 2 Biology Exam Paper With Answer
Form 2 Biology Final Year Exam Paper 2
Form 2 Biology Notes
Form 2 Biology Notes and Revision Questions
Form 2 Biology Notes Pdf
Form 2 Biology Past Papers
Form 2 Biology Questions
Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers
Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers >
Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form 2 Biology Revision Notes
Form 2 Biology Short Notes
Form 2 Biology Syllabus
Form 2 BiologyExam Paper
Form 2 BiologyExam Paper Free Download
Form 2 BiologyExam Paper With Answer
Form 2 BiologyFinal Year Exam Paper 2
Form 2 BiologyPast Papers
Form 2 BiologyRevision Notes
Form 2 BiologyShort Notes
Form 2 BiologySyllabus
Form 2 Revision Papers
Form 2 Subjects in Kenya
Form 3 Biology Book
Form 3 Biology Exam
Form 3 Biology Exam Paper
Form 3 Biology Notes
Form 3 Biology Past Papers
Form 3 Biology Questions
Form 3 Biology Questions and Answers
Form 3 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form 3 Biology Revision Notes
Form 3 Biology Syllabus
Form 3 BiologyExam Paper
Form 3 BiologyNotes
Form 3 BiologyPast Papers
Form 3 BiologyQuestions
Form 3 BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf
Form 3 BiologyRevision Notes
Form 3 BiologySyllabus
Form 3 C.r.e
Form 3 Notes of Biology Topic on Fish
Form 3 Past Papers
Form 3 Revision Papers
Form 3 Subjects in Kenya
Form 4 Biology Exam
Form 4 Biology Notes
Form 4 Biology Notes Pdf
Form 4 Biology Questions and Answers
Form 4 Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form 4 Biology Revision Notes
Form 4 Biology Syllabus
Form 4 Biology Topics
Form 4 BiologyNotes
Form 4 BiologyRevision Notes
Form 4 BiologySyllabus
Form 4 BiologyTopics
Form 4 Exam Papers
Form 4 Revision Papers
Form 4 Subjects in Kenya
Form 5 Biology Topics
Form 5 BiologyTopics
Form Five Biology Notes
Form Five BiologyNotes
Form Four Biology Book
Form Four Biology Notes
Form Four Biology Notes Pdf
Form Four Biology Questions and Answers
Form Four Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form Four Biology Revision Questions
Form Four Biology Syllabus
Form Four Biology Topics
Form Four BiologyNotes
Form Four BiologyQuestions and Answers
Form Four BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf
Form Four BiologyTopics
Form Four Notes
Form Four Revision Papers
Form Four Subjects in Kenya
Form One Biology Book
Form One Biology Examination
Form One Biology First Topic
Form One Biology Lesson Plan
Form One Biology Notes Pdf
Form One Biology Past Papers Pdf
Form One Biology Questions
Form One Biology Questions and Answers
Form One Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form One Biology Revision Questions
Form One Biology Short Notes
Form One Biology Syllabus
Form One Biology Topics
Form One BiologyExamination
Form One BiologyPast Papers Pdf
Form One BiologyQuestions and Answers
Form One BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf
Form One BiologyTopics
Form One Exams
Form One Notes of Biology
Form One Past Papers
Form One Subjects in Kenya
Form One Term One Biology Exam
Form One Term One BiologyExam
Form Three Biology Book
Form Three Biology Book Pdf
Form Three Biology Notes
Form Three Biology Notes Pdf
Form Three Biology Questions and Answers
Form Three Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form Three Biology Revision Questions
Form Three Biology Syllabus
Form Three Biology Topics
Form Three BiologyNotes
Form Three BiologyNotes Pdf
Form Three BiologyQuestions and Answers
Form Three BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf
Form Three BiologyTopics
Form Three Subjects in Kenya
Form Two Biology Book
Form Two Biology Cat
Form Two Biology Examination
Form Two Biology Notes
Form Two Biology Notes Pdf
Form Two Biology Past Papers
Form Two Biology Questions and Answers
Form Two Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Form Two Biology Revision Questions
Form Two Biology Syllabus
Form Two Biology Topics
Form Two BiologyNotes
Form Two BiologyNotes Pdf
Form Two BiologyQuestions and Answers
Form Two BiologyQuestions and Answers Pdf
Form Two BiologySyllabus
Form Two BiologyTopics
Form Two Notes
Form Two Subjects in Kenya
Free a-level Biology Revision App | Pass Your Biology Exams
Free Biology Form 1 Notes
Free Biology Notes Form 1
Free Biology Notes Pdf
Free BiologyNotes Pdf
Free College Biology Practice Test
Free Form1,form2,form3 Past Papers Free KCSE Past Papers
Free KCSE Mocks 2015
Free KCSE Past Papers 2014
Free KCSE Past Papers KCSE Past
Free KCSE Past Papers Kenya,
Free KCSE Past Papers With Answers
Free KCSE Questions and Answers on Biology
Free KCSE Revision Notes
Free Marking Schemes
Free Mocks Online KCSE Answers Past Exams Question Papers
Free Revision Papers
From Three Notes Topic One KLB
Fun Biology Questions
Funny Biology Questions
Funny Biology Questions and Answers
Funny Biology Questions to Ask
Funny Biology Quotes
Gas Exchange Exam Questions
Gas Exchange Practice Test
Gas Exchange Quiz
GCSE Biology Exam Questions and Answers
GCSE Biology Past Papers
GCSE Biology Revision
GCSE Biology Revision Notes
GCSE Biology Revision Notes Pdf
GCSE Biology Revision Notes Pdf 9-1
GCSE Biology Revision Questions and Answers
GCSE Biology Textbook Pdf
GCSE Biology Topics Pass My Exams: Easy Exam Revision Notes
General Biology Notes Pdf
General Biology Practice Test With Answers
General Biology Quiz
General Biology Quiz Pdf
General Biology Test Questions and Answers
General Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf
General Knowledge in Biology Human Body
Good Biology Questions to Ask
GRE Biology Practice Test
GRE Biology Subject Test Pdf
Handbook of Biology Pdf Free Download
Hard Biology Questions
Hard Biology Questions and Answers
Hard Biology Questions to Ask Your Teacher
Hard Biology Quiz Questions
Hard Form 3 Biology Question
High School Biology Final Exam Doc
High School Biology Final Exam Pdf
High School Biology Final Exam Questions
High School Biology Final Exam Questions and Answers
High School Biology Notes
High School Biology Practice Test
High School Biology Pretest With Answers
High School Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
High School Biology Study Guide
High School Biology Test Questions and Answers Pdf
High School BiologyNotes
High School BiologyStudy Guide
How Does the Excretory System Work
How Many Chromosomes Do Gametes Have
How Many Copies of Each Gene Do Gametes Have
How Much Genetic Information Is Found in a Gamete
How to Answer KCSE Biology Question
How to Motivate a Form 4 Student
How to Motivate a KCSE Candidate
How to Motivate a KCSE Student
How to Pass Biology Questions & Answers Form 1&2 | Text Book
How to Revise Biology
How to Revise Effectively for KCSE
How to Study Biology: 5 Study Techniques to Master Biology
Hsc Biology 2018
Hsc Biology 2019
Https://www.knec.ac.ke/ Www.knec-portal.ac.ke/ KNEC Portal:
Ial Biology Notes
Ib Biology Cold War Notes
Ib Biology Notes
Ib Biology Notes Pdf
Ib Biology of the Americas Notes
Ib Biology of the Americas Study Guide
Ib Biology Paper 2 Study Guide
Ib Biology Question Bank by Topic
Ib Biology Study Guide Pdf
Ict Notes Form 1
IGCSE Biology Alternative to Practical Revision
IGCSE Biology Alternative to Practical Revision Notes
IGCSE Biology Book
IGCSE Biology Book Pdf Download
IGCSE Biology Notes
IGCSE Biology Notes 2017 Pdf
IGCSE Biology Notes Edexcel
IGCSE Biology Paper 2 Notes
IGCSE Biology Paper 6 Notes
IGCSE Biology Past Papers
IGCSE Biology Past Papers 2014
IGCSE Biology Past Papers 2017
IGCSE Biology Pdf
IGCSE Biology Pre Release Material 2018
IGCSE Biology Resources
IGCSE Biology Revision Guide
IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Free Download
IGCSE Biology Revision Guide Pdf Download
IGCSE Biology Revision Notes Pdf
IGCSE Biology Revision Worksheets
IGCSE Biology Workbook Pdf
IGCSE Biology Znotes
IGCSE BiologyPast Papers
IGCSE Notes Biology
Importance of Agroforestry
Inorganic Biology Multiple Choice Questions With Answers Pdf
Inorganic Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Interesting Biology Questions
Interesting Biology Questions and Answers
Interesting Questions to Ask About Biology
Intro to Biology Quiz
Introduction of Biology Form One
Introduction to Biology
Introduction to Biology Notes
Introduction to Biology Pdf
Introduction to BiologyNotes
Is Agroforestry Sustainable?
K.c.s.e Answers Biology Paper One 2018
K.c.s.e Biology 2017
K.c.s.e Biology 2018
K.c.s.e Biology Paper 1 2017
K.c.s.e Mocks 2018
K.c.s.e Papers 2015
K.c.s.e Papers 2016
K.c.s.e Past Papers 2014
K.c.s.e.Biology Paper 2 Year 2018
K.c.s.e.results 2018 for Busia County
K.l.b Biology Form 3
K.l.b Biology Notes
K.l.b BiologyNotes
Kasneb Past Papers for Colleges Biology Past Papers
KCSE 2010 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2010 Past Papers
KCSE 2011 Biology Paper 1
KCSE 2011 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2012 Biology Paper 2 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2012 Marking Schemes
KCSE 2013 Biology Paper 1
KCSE 2013 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2013 Marking Scheme Pdf
KCSE 2014
KCSE 2015 Biology Paper 2
KCSE 2015 Biology Paper 3
KCSE 2015 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2015 Past Papers
KCSE 2016 Biology Paper 1
KCSE 2016 Biology Paper 2
KCSE 2017 Biology Paper 1
KCSE 2017 Biology Paper 2
KCSE 2017 Hostory Papers With Answers.com
KCSE 2017 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2017 Papers
KCSE 2017 Papers and Marking Scheme
KCSE 2017 Papers Pdf
KCSE 2017 Past Papers
KCSE 2017 Prediction Pdf
KCSE 2018 Biology and Answers
KCSE 2018 Biology Prediction
KCSE 2018 Leakage
KCSE 2018 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2018 Papers
KCSE 2018 Prediction Pdf
KCSE 2018 Predictions
KCSE 2018 Questions
KCSE 2018 Questions and Answers
KCSE 2019 Leakage Biology
KCSE 2019 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2019 Questions
KCSE 2019 Questions and Answers
KCSE 2020 Questions
KCSE 2020 Questions and Answers
KCSE Answers
KCSE Answers Past Exams Question Papers Downloads |
KCSE Biology 2011
KCSE Biology 2016
KCSE Biology Diagramsbiology Revision Tips
KCSE Biology Essay Questions and Answers
KCSE Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf
KCSE Biology Essays
KCSE Biology Essays Pdf
KCSE Biology Marking Schemes
KCSE Biology Notes
KCSE Biology Notes Pdf
KCSE Biology Notes, Syllabus, Questions, Answers
KCSE Biology Paper 1
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2011
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2012
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2013
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2015
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2016
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2017
KCSE Biology Paper 1 2017 Pdf
KCSE Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers
KCSE Biology Paper 2
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2012
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2012 KCSE Biology Paper 2 2015
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2013
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2014
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2015
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2016
KCSE Biology Paper 2 2017
KCSE Biology Paper 3
KCSE Biology Paper 3 2012
KCSE Biology Paper 3 2016
KCSE Biology Paper 3 2017
KCSE Biology Paper 3 Past Papers
KCSE Biology Past Papers
KCSE Biology Past Papers and Answers
KCSE Biology Past Papers Pdf
KCSE Biology Practical
KCSE Biology Practical 2015
KCSE Biology Practical 2016
KCSE Biology Practical Past Papers
KCSE Biology Practicals
KCSE Biology Practicals KCSE Biology Paper 1
KCSE Biology Question and Answer
KCSE Biology Questions and Answers
KCSE Biology Questions and Answers Ap Biology
KCSE Biology Revision
KCSE Biology Revision Notes
KCSE Biology Revision Papers
KCSE Biology Revision Questions
KCSE Biology Revision Questions and Answers
KCSE Biology Syllabus
KCSE BiologyNotes
KCSE BiologyPaper 1
KCSE BiologyPaper 2
KCSE BiologyPaper 2 Pdf
KCSE BiologySyllabus
KCSE Business Paper 1 2016
KCSE Business Past Papers
KCSE Business Studies Past Papers
KCSE Essay Questions in Betrayal in the City
KCSE Essays
KCSE Exam Papers 2018
KCSE Exam Papers Answers
KCSE Form 1 Biology Revision
KCSE Form 2 Biology Revision
KCSE Form 3 Biology Revision
KCSE Form 4 Biology Revision
KCSE Form Four Biology Revision
KCSE Form One Biology Revision
KCSE Form Three Biology Revision
KCSE Form Two Biology Revision
KCSE KCSE Past Papers KNEC
KCSE Leakage
KCSE Leakage Biology
KCSE Made Familiar Biology
KCSE Made Familiar Biology Pdf
KCSE Marking Scheme 2016
KCSE Marking Schemes
KCSE Marking Schemes 2017
KCSE Marking Schemes Pdf
KCSE Mock Exams
KCSE Mock Papers 2015
KCSE Mock Papers 2017
KCSE Mock Papers 2018
KCSE Mock Papers Pdf
KCSE Mock Papers Pdf 2018
KCSE Mock Papers Pdf KCSE Past Papers
KCSE Mocks 2017
KCSE Mocks 2018
KCSE Notes
KCSE Online Notes
KCSE Online Past Papers
KCSE Online Registration
KCSE Papers 2015
KCSE Papers and Marking Schemes | Exams
KCSE Past Papers
KCSE Past Papers 2007
KCSE Past Papers 2009
KCSE Past Papers 2010
KCSE Past Papers 2011
KCSE Past Papers 2011 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2012
KCSE Past Papers 2013
KCSE Past Papers 2013knec
KCSE Past Papers 2014
KCSE Past Papers 2014 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2015
KCSE Past Papers 2015 Marking Schemes
KCSE Past Papers 2015 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2016
KCSE Past Papers 2016 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2017
KCSE Past Papers 2017 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2018
KCSE Past Papers Biology
KCSE Past Papers Biology and Answers
KCSE Past Papers Biology Pdf
KCSE Past Papers Biology With Answers
KCSE Past Papers Biologyand Answers
KCSE Past Papers Business Studies and Answers
KCSE Past Papers KCSE and Answers
KCSE Past Papers KCSE and Answers Free Mocks Online
KCSE Past Papers Marking Scheme
KCSE Past Papers Pdf Download
KCSE Past Papers Pdf Download KCSE 2013
KCSE Past Papers With Answers
KCSE Past Papers Woodwork and Answers
KCSE Prediction 2017
KCSE Prediction 2018
KCSE Prediction 2018 Pdf
KCSE Prediction Papers 2018
KCSE Prediction Questions
KCSE Prediction Questions 2018
KCSE Prediction Questions and Answers
KCSE Questions
KCSE Questions and Answers
KCSE Questions and Answers.
KCSE Questions on Biology
KCSE Results, Online Registration, KCSE Result Slip.
KCSE Revision
KCSE Revision Notes
KCSE Revision Notes Biology
KCSE Revision Notes Pdf
KCSE Revision Papers
KCSE Revision Papers 2014
KCSE Revision Papers With Answers
KCSE Revision Question for Biology
KCSE Revision Questions
KCSE Revision Questions and Answers
KCSE Revision | Secondary School | Text Books | Text Book Centre
KCSE Syllabus Pdf
KCSE Trial 2017
KCSE Trial Exams 2017
Kenya Secondary School Biology Syllabus
Kenya Secondary School Biology Syllabus Pdf
Kenya Secondary School BiologySyllabus Pdf
Kenya Secondary School Syllabus Pdf
Kenya-kcse-christian Religious Education Syllabus
Kenyaplex KCSE Past Papers
Kenyaplex Past Papers for Secondary
KLB Biology Book 1 Download
KLB Biology Book 1 Notes
KLB Biology Book 1 Pdf
KLB Biology Book 2
KLB Biology Book 2 Notes
KLB Biology Book 2 Notes Pdf
KLB Biology Book 2 Pdf
KLB Biology Book 3 Notes
KLB Biology Book 3 Pdf
KLB Biology Book 3 Pdf Download
KLB Biology Book 4 Notes
KLB Biology Book 4 Pdf
KLB Biology Book 4 Pdf Download
KLB Biology Book 4 Topics
KLB Biology Book One
KLB Biology Form 1
KLB Biology Form 1 Notes
KLB Biology Form 1 Pdf
KLB Biology Form 2
KLB Biology Form 2 Book
KLB Biology Form 2 Notes
KLB Biology Form 2 Pdf
KLB Biology Form 2 Pdf Download
KLB Biology Form 2 Schemes of Work
KLB Biology Form 3
KLB Biology Form 3 Notes
KLB Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf
KLB Biology Form 3 Pdf
KLB Biology Form 3 Pdf Download
KLB Biology Form 4
KLB Biology Form 4 Notes
KLB Biology Form 4 Pdf
KLB Biology Form Four
KLB Biology Form Four Notes
KLB Biology Form One
KLB Biology Form One Notes
KLB Biology Form Three
KLB Biology Form Three Notes
KLB Biology Form Two
KLB Biology Form Two Notes
KLB Biology Notes
KLB Biology Notes Form 4
KLB Biology Pdf
KLB BiologyNotes
KLB BiologyNotes Form 4
KLB BiologyPdf
KNEC Biology Syllabus
KNEC Examiners Portal KNEC Website
KNEC Ict Past Papers
KNEC Past Papers for Colleges
KNEC Past Papers Free Download
KNEC Past Papers Free Downloads
KNEC Past Papers Pdf
KNEC Portal Confirmation
KNEC Portal KCSE Results
KNEC Portal KNEC Past Papers for Colleges Kasneb Past Papers
KNEC Revision Papers
KNEC Technical Exams Past Papers
Kusoma Biology Notes
Kusoma Biology Notes Pdf
Kusoma Notes Biology
Kusoma.co.ke
Kusoma.com Past Papers
Learner Guide for Cambridge IGCSE Biology
Longhorn Biology Book 3 Pdf
Made Familiar Biology
Made Familiar Biology Pdf
Made Familiar Biology Questions
Maktaba Tetea Notes
Marking Scheme KCSE Biology Past Papers
Math Form2 Note
Mcq on Cell Biology Class 9
Mcqs About Gaseous Exchange
Middle School Biology Bowl Biology Questions
Mock Past Papers 2017
Mock Past Papers With Answers
Mokasa Mock 2017
More Than 1800 Biology Questions and Answers to Help You Study
Multiple Choice Questions on Biology
Multiple Choice Questions on Cell Structure and Function
Necta Biology Past Papers
Necta Biology Practicals
Necta BiologyPast Papers
Necta BiologyPracticals
Necta Form Four Past Papers
Necta Past Papers Form 4
Necta Past Papers Form 4 2016
Necta Past Papers Form Six
Necta Past Papers Form Two
Necta Questions and Answers
Necta Review Questions
Notes Biology Form 1
Notes Biology Form 2
Notes Biology Form 3
Notes Biology Form 3 Notes Pdf
Notes Biology Form 3 Syllabus
Notes Biology Form 4 Syllabus
Notes on Biology Studies
Notes Za Biology 4m 2
Notes Za Biology Form One
Notes Za Biology Form Three
O Level Biology Practical Experiments
O Level Biology Questions and Answers Pdf
Orm Three Biology Notes
Page Navigation
Papacambridge Biology IGCSE
Papers KNEC KCSE Online Past
Papers KNEC KCSE Results Past Papers
Past KCSE Papers
Past Paper Questions by Topic Biology
Past Papers 2014
Past Papers in Kenya
Pdf Biology Form 3
Pdf Biology Notes
Pdf Biology Notes Form 1
Pdf Biology Notes Form 2
Pdf Biology Notes Form 3
Pdf Biology Notes Form 4
Pdf Biology Notes Form Four
Pdf Biology Notes Form One
Pdf Biology Notes Form Three
Pdf Biology Notes Form Two
Pdf Form 1 Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form 2 Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form 3 Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form 4 Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form Four Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form One Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form Three Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Form Two Biology Questions and Answers
Pdf Free KCSE Past Papers and Marking Schemes
Pdf” Revision Questions Biology Form 1
Plant and Animal Cell Organelles Quiz
Plant and Animal Cell Organelles Quiz Answers
Plant and Animal Cell Quiz for 5th Grade
Plant and Animal Cell Quiz Grade 8
Plant and Animal Cell Quiz Pdf
Plant Cell
Plant Cell Pdf Download
Plant Cell Questions and Answers
Plant Cell Test Questions
Practical Biology Experiments Pdf
Practical Biology Question and Answer Pdf
Pre Mocks 2018
Preliminary Biology
Primary and Secondary Tillage Implements Ppt
Pte KNEC Past Papers
Questions About Cells Biology
Questions and Answers on Gaseous Exchange
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 1
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 2
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 3
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form 4
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Four
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form One
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Three
Questions and Answers Pdf Biology Form Two
Questions Based to Introduction to Biology
Questions on Cell Structure and Function
Questions on Gaseous Exchange in Humans
Questions on Introduction to Biology
Questions to Ask in Biology Class
Questions to Confuse Your Biology Teacher
Quizlet Biology Cells
Quizlet Biology Test
Quizlet Test Questions
Qustions in Biology and Answers
Radioactivity Form Four
Respiration and Gas Exchange Worksheet
Respiration Notes My Elim Form Two
Revision
Revision Biology Notes and Questions?
Revision Quiz for Biology for Form Three
S.1 Biology Questions
S.2 Biology Questions
S.3 Biology Questions
S.4 Biology Questions
Sample Essays on Betrayal in the City
School Biology Notes
Secondary Biology Notes
Secondary Biology Notes Pdf
Secondary BiologyNotes Pdf
Senior 1 Biology Notes
Senior 2 Biology Notes
Senior 3 Biology Notes
Senior 4 Biology Notes
Senior 5 Biology Notes
Senior 6 Biology Notes
Senior Five Biology Notes
Senior Four Biology Notes
Senior One Biology Notes
Senior Six Biology Notes
Senior Three Biology Notes
Senior Two Biology Notes
Simple Scientific Questions
Smart Questions to Ask a Biology Teacher
Snab Biology Revision Notes
Southwest Mock Paper 2 2016 Biology Only
Spm Biology Revision Notes
Spm Notes
Success Biology Spm Pdf
Success BiologySpm Pdf
Summary of Biology Form 3
Tahossa Past Papers
The Animal Cell Quiz Answers
The Excretory System Answer Key
The Excretory System Worksheet Answers
The Plant Cell Quiz Answer Key
To Motivate a Form 4 KCSE Student
To Motivate a Form 4 Student
Topical Revision Material
Tricky Biology Questions and Answers
Tricky Biology Questions for Adults
Tricky Biology Questions With Answers
Tricky Biology Quiz Questions
Two Biology Revision Questions
Types of Respiration
University Biology Volume 3 Openstax
University Biology Volume 3 Pdf
University Biology Volume 4 Pdf
Ur Revision Guide IGCSE Biology
What Are Gametes
What Are Gametes in Biology
What Are Gametes in Plants
What Are Gametes in Punnett Squares
What Are Gametes Quizlet
What Are the Types of Gametes
Working of Excretory System
Www.Biology Form One Notes.com
Www.Biology From One KLB.com
Www.form 1 Biology.com
Www.form 2 Biology.com
Www.form 3 Biology.com
Www.form 4 Biology.com
Www.form Four Biology.com
Www.form One Biology.com
Www.form Three Biology.com
Www.form Two Biology.com
Www.kusoma Notes
Www.kusoma Revision Materials
Www.kusoma.co.ke Biology Notes
Xtremepapers IGCSE Biology
Year 11 Biology
Z Notes Biology IGCSE
Znotes as Biology
15 Common Biology Questions From Form 1
15 Common Biology Questions From Form 2
15 Common Biology Questions From Form 3
15 Common Biology Questions From Form 4
15 Common Biology Questions From Form Four
15 Common Biology Questions From Form One
15 Common Biology Questions From Form Three
15 Common Biology Questions From Form Two
150 Common Biology Questions From Form 1
150 Common Biology Questions From Form 2
150 Common Biology Questions From Form 3
150 Common Biology Questions From Form 4
150 Common Biology Questions From Form Four
150 Common Biology Questions From Form One
150 Common Biology Questions From Form Three
150 Common Biology Questions From Form Two
2019 KCSE Exams Biology Papers
2019 KCSE Exams Papers
2020 KCSE Exams Biology Papers
2021 KCSE Exams Biology Papers
Best Biology Books for KCSE Knec
Biology
Biology 2 Topic Form Two
Biology Diagrams
Biology Form 1 and 2 Notes
Biology Form 1 Download
Biology Form 1 Notes Online
Biology Form 1 Notes Revision
Biology Form 1 Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 1 Revision Notes
Biology Form 1 Text Book
Biology Form 1 Text Book Notes
Biology Form 2 Download
Biology Form 2 Notes
Biology Form 2 Notes Online
Biology Form 2 Notes Revision
Biology Form 2 Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form 2 Pdf
Biology Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 2 Revision Notes
Biology Form 2 Text Book
Biology Form 2 Text Book Notes
Biology Form 3 Download
Biology Form 3 Notes Online
Biology Form 3 Notes Revision
Biology Form 3 Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 3 Revision Notes
Biology Form 3 Text Book
Biology Form 3 Text Book Notes
Biology Form 4 Download
Biology Form 4 Notes Online
Biology Form 4 Notes Revision
Biology Form 4 Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form 4 Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form 4 Revision Notes
Biology Form 4 Text Book
Biology Form 4 Text Book Notes
Biology Form Four Download
Biology Form Four Notes Online
Biology Form Four Notes Revision
Biology Form Four Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form Four Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Four Revision Notes
Biology Form Four Text Book
Biology Form Four Text Book Notes
Biology Form One Download
Biology Form One Notes Online
Biology Form One Notes Revision
Biology Form One Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form One Questions and Answers
Biology Form One Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form One Revision Notes
Biology Form One Text Book
Biology Form One Text Book Notes
Biology Form Three Download
Biology Form Three Notes Online
Biology Form Three Notes Revision
Biology Form Three Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form Three Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Three Revision Notes
Biology Form Three Text Book
Biology Form Three Text Book Notes
Biology Form Two Download
Biology Form Two Notes Online
Biology Form Two Notes Revision
Biology Form Two Pastpapers and Marking Scheme
Biology Form Two Questions and Answers Pdf
Biology Form Two Revision Notes
Biology Form Two Text Book
Biology Form Two Text Book Notes
Biology Full Exam Papers
Biology K.C.S.E Revision Papers
Biology KCSE Revision
Biology Notes Book Four
Biology Notes Book One
Biology Notes Book Three
Biology Notes Book Two
Biology Notes Form 2
Biology Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf
Biology Questions and Answers Form 1
Biology Questions and Answers Form 2
Biology Questions and Answers Form 3
Biology Short Note for Revising Form 1
Biology Short Note for Revising Form 2
Biology Short Note for Revising Form 3
Biology Short Note for Revising Form 4
Biology Short Note for Revising Form Four
Biology Short Note for Revising Form One
Biology Short Note for Revising Form Three
Biology Short Note for Revising Form Two
Biology Short Notes Form 1
Biology Short Notes Form 2
Biology Short Notes Form 3
Biology Short Notes Form 4
Biology Short Notes Form Four
Biology Short Notes Form One
Biology Short Notes Form Three
Biology Short Notes Form Two
Biologyy Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf
Brief Notes Biology Form 1
Brief Notes Biology Form 2
Brief Notes Biology Form 3
Brief Notes Biology Form 4
Brief Notes Biology Form Four
Brief Notes Biology Form One
Brief Notes Biology Form Three
Brief Notes Biology Form Two
Brief Notes Biology Form3 Chapter1
Download Book 1 Biology Notes
Download Book 2 Biology Notes
Download Book 3 Biology Notes
Download Book 4 Biology Notes
Download Book Four Biology Notes
Download Book One Biology Notes
Download Book Three Biology Notes
Download Book Two Biology Notes
Download Book1 Biology Notes
Download Book2 Biology Notes
Download Book3 Biology Notes
Download Book4 Biology Notes
Download KCSE Biology Study Notes
Download Secondary Subjects
Download Secondary Subjects in Kenya
Download Secondary Subjects KCSE
Exams Revision Kenya
Exams Revision Kenya KCSE
Expected Questions and Answers in Biology Form One
Form 2 Biology Notes
Form 2 Biology Notes Pdf
Form 2 Biology Topics
Form 3 Biology Book Pdf
Form Iii Topics of Biology Revisios
How to Answer Biology Paper 1 Questions?
How to Answer Biology Paper 2 Questions?
How to Answer Biology Paper 3 Questions?
How to Answer KCSE Biology Paper 1 Questions?
How to Answer KCSE Biology Paper 2 Questions?
How to Answer KCSE Biology Paper 3 Questions?
How to Answer Paper 1 Biology Questions?
How to Answer Paper 2 Biology Questions?
How to Answer Paper 3 Biology Questions?
K.C.S.E Revision Papers
K.C.S.E Revision Papers Biology
KCSE Biology Essay Questions and Answers Pdf
KCSE Biology Revisions
KCSE Biology Study Notes
KCSE Free Biology Qussions
KCSE Free Qussions
KCSE Revision Kenya
KCSE Revisions
Biology Form Two Questions
Revision Kenya
Revision Kenya Kcsse
Sammary Note for Biology Form 1
Sammary Note for Biology Form 2
Sammary Note for Biology Form 3
Sammary Note for Biology Form 4
Sammary Note for Biology Form Four
Sammary Note for Biology Form One
Sammary Note for Biology Form Three
Sammary Note for Biology Form Two
Www.last Year KCSE Exams.com
Biology Past Papers and Marking Scheme
Igcse Biology Past Papers
Igcse Biology Past Papers 2015
Igcse Biology Past Papers by Topic
Edexcel Igcse Biology Past Papers
[ad_2]
Source link
Comments
The Kenyan Digest Team

You may like

EXPOSED: How Kenya’s Student Leaders Have Been Silenced as Lecturers’ Strike Enters Another Week
Paul Biya’s Re-Election: What Cameroon’s Political Longevity Reveals About Leadership and Governance in Africa

Influencers for Sale: Inside the Government’s Attempt to Control Public Opinion Through the Cyber Crimes Bill 2025

How Powerful Politicians Are Using Proxies to Privatize Kenya’s Public Assets

President Ruto Congratulates Harambee Starlets, Pledges Sh1 Million Each After Historic WAFCON Qualification

15 Proven Ways to Make Money Online in Kenya; No Scams!

15 Proven Ways to Make Money Online in Kenya; No Scams!

President Ruto Congratulates Harambee Starlets, Pledges Sh1 Million Each After Historic WAFCON Qualification

How Powerful Politicians Are Using Proxies to Privatize Kenya’s Public Assets

Influencers for Sale: Inside the Government’s Attempt to Control Public Opinion Through the Cyber Crimes Bill 2025

EXPOSED: How Kenya’s Student Leaders Have Been Silenced as Lecturers’ Strike Enters Another Week
Paul Biya’s Re-Election: What Cameroon’s Political Longevity Reveals About Leadership and Governance in Africa

Why Mutahi Kahiga’s Remarks Might Be Part of President Ruto’s Larger Political Game
From Power to Prison: The Fall of France’s Former President Nicolas Sarkozy

8 Laws, One Moment: How Ruto Quietly Changed Kenya While the Nation Grieved Raila Odinga

The War in Ukraine: A Comprehensive Analysis of the Conflict
Trending
-

 General News1 week ago
General News1 week agoEXPOSED: How Kenya’s Student Leaders Have Been Silenced as Lecturers’ Strike Enters Another Week
-
Politics1 week ago
Paul Biya’s Re-Election: What Cameroon’s Political Longevity Reveals About Leadership and Governance in Africa
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoInfluencers for Sale: Inside the Government’s Attempt to Control Public Opinion Through the Cyber Crimes Bill 2025
-

 Business News1 week ago
Business News1 week agoHow Powerful Politicians Are Using Proxies to Privatize Kenya’s Public Assets
-
 General News7 days ago
General News7 days agoPresident Ruto Congratulates Harambee Starlets, Pledges Sh1 Million Each After Historic WAFCON Qualification
-

 Business News23 hours ago
Business News23 hours ago15 Proven Ways to Make Money Online in Kenya; No Scams!