Jobs
Physics Notes Form 3 – Free Download
Published
6 years agoon
[ad_1]
Physics Notes Form 3 – Free KCSE Past Papers – Physics – Free KCSE Mocks – KCSE Questions and Answers – Download Free KCSE Marking Schemes – KCSE Revision – KCSE Results
Physics Notes Form 3
Physics Form Three
Chapter One
Linear Motion
Introduction
Study of motion is divided into two;
1. Kinematics
2. Dynamics
In kinematics forces causing motion are disregarded while dynamics deals with motion of objects and the forces causing them.
I. Displacement
Distance moved by a body in a specified direction is called displacement. It is denoted by letter‘s’ and has both magnitude and direction. Distance is the movement from one point to another. The Si unit for displacement is the metre (m).
II. Speed
This is the distance covered per unit time.
Speed= distance covered/ time taken. Distance is a scalar quantity since it has magnitude only.
The SI unit for speed is metres per second(m/s or ms-1)
Average speed= total distance covered/total time taken
Other units for speed used are Km/h.
Examples
1. A body covers a distance of 10m in 4 seconds. It rests for 10 seconds and finally covers a distance of 90m in 60 seconds. Calculate the average speed.
Solution
Total distance covered =10+90= 100m
Total time taken =4+10+6= 20 seconds
Therefore average speed = 100/20= 5m/s
2. Calculate the distance in metres covered by a body moving with a uniform speed of 180 km/h in 30 seconds.
Solution
Distance covered=speed*time
=180*1000/60*60=50m/s
=50*30
=1,500m
3. Calculate the time in seconds taken a by body moving with a uniform speed of 360km/h to cover a distance of 3,000 km?
Solution
Speed:360km/h=360*1000/60*60=100m/s
Time=distance/speed
3000*1000/100
=30,000 seconds.
III. Velocity
This is the change of displacement per unit time. It is a vector quantity.
Velocity=change in displacement/total time taken
The SI units for velocity are m/s
Examples
1. A man runs 800m due North in 100 seconds, followed by 400m due South in 80 seconds. Calculate,
a. His average speed
b. His average velocity
c. His change in velocity for the whole journey
Solution
a. Average speed: total distance travelled/total time taken
=800+400/100+80
=1200/180
=6.67m/s
b. Average velocity: total displacement/total time
=800-400/180
=400/180
=2.22 m/s due North
c. Change in velocity=final-initial velocity
= (800/100)-(400-80)
=8-5
=3m/s due North
2. A tennis ball hits a vertical wall at a velocity of 10m/s and bounces off at the same velocity. Determine the change in velocity.
Solution
Initial velocity(u)=-10m/s
Final velocity (v) = 10m/s
Therefore change in velocity= v-u
=10- (-10)
=20m/s
IV. Acceleration
This is the change of velocity per unit time. It is a vector quantity symbolized by ‘a’.
Acceleration ‘a’=change in velocity/time taken= v-u/t
The SI units for acceleration are m/s2
Examples
1. The velocity of a body increases from 72 km/h to 144 km/h in 10 seconds.
Calculate its acceleration.
Solution
Initial velocity= 72 km/h=20m/s
Final velocity= 144 km/h=40m/s
Therefore ‘a’ =v-u/t
= 40-20/10
2m/s2
2. A car is brought to rest from 180km/h in 20 seconds. What is its retardation?
Solution
Initial velocity=180km/h=50m/s
Final velocity= 0 m/s
A = v-u/t=0-50/20
= -2.5 m/s2
Hence retardation is 2.5 m/s2
Motion graphs
Distance-time graphs
a)
b)
Area under velocity-time graph
Consider a body with uniform or constant acceleration for time‘t’ seconds;
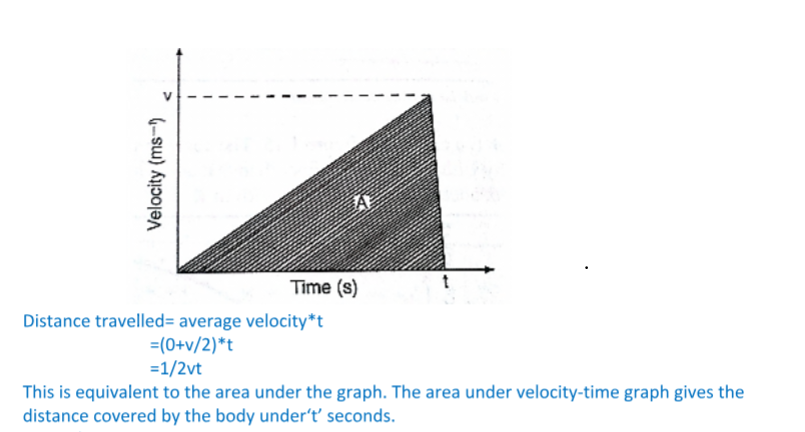
This is equivalent to the area under the graph. The area under velocity-time graph gives the distance covered by the body under‘t’ seconds.
Example
A car starts from rest and attains a velocity of 72km/h in 10 seconds.
It travels at this velocity for 5 seconds and then decelerates to stop after another 6 seconds.
Draw a velocity-time graph for this motion. From the graph;
i. Calculate the total distance moved by the car
ii. Find the acceleration of the car at each stage.
Solution
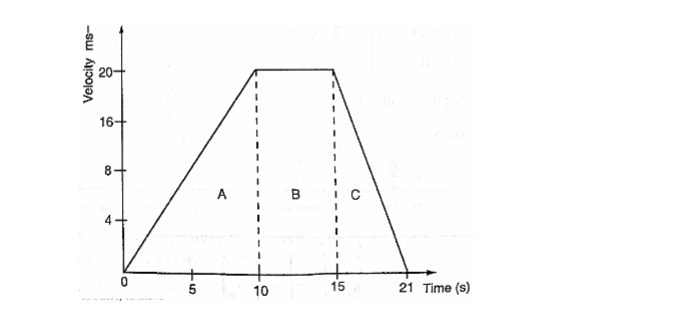
a. From the graph, total distance covered= area of (A+B+C)
=(1/2×10×20)+(1/2×6×20)+(5×20)
=100+60+100
=260m
Also the area of the trapezium gives the same result.
b. Acceleration= gradient of the graph
Stage A gradient= 20-0/ 10-0 = 2 m/s2
Stage b gradient= 20-20/15-10 =0 m/s2
Stage c gradient= 0-20/21-15 =-3.33 m/s2
Using a ticker-timer to measure speed, velocity and acceleration.
It will be noted that the dots pulled at different velocities will be as follows;
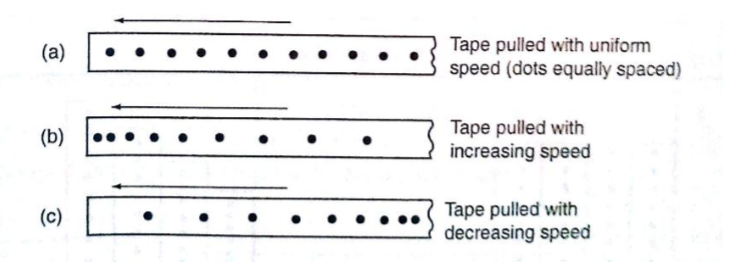
Most ticker-timers operate at a frequency of 50Hzi.e. 50 cycles per second hence they make 50 dots per second. Time interval between two consecutive dots is given as,
1/50 seconds= 0.02 seconds. This time is called a tick.
The distance is measured in ten-tick intervals hence time becomes 10×0.02= 0.2 seconds.
Examples
a. A tape is pulled steadily through a ticker-timer of frequency 50 Hz.
Given the outcome below, calculate the velocity with which the tape is pulled.
Solution
Distance between two consecutive dots= 5cm
Frequency of the ticker-timer=50Hz
Time taken between two consecutive dots=1/50=0.02 seconds
Therefore, velocity of tape=5/0.02= 250 cm/s
b. The tape below was produced by a ticker-timer with a frequency of 100Hz. Find the acceleration of the object which was pulling the tape.

Solution
Time between successive dots=1/100=0.01 seconds
Initial velocity (u) 0.5/0.01 50 cm/s
Final velocity (v) 2.5/0.01= 250 cm/s
Time taken= 4 ×0.01 = 0.04 seconds
Therefore, acceleration= v-u/t= 250-50/0.04=5,000 cm/s2
Equations of linear motion
The following equations are applied for uniformly accelerated motion;
v = u + at
s = ut + ½ at2
v2= u2 +2as
Examples
1. A body moving with uniform acceleration of 10 m/s2 covers a distance of 320 m. if its initial velocity was 60 m/s. Calculate its final velocity.
Solution
V2 = u2 +2as
= (60) +2×10×320
=3600+6400
= 10,000
Therefore v= (10,000)1/2
v= 100m/s
2. A body whose initial velocity is 30 m/s moves with a constant retardation of 3m/s. Calculate the time taken for the body to come to rest.
Solution
v = u+at
0= 30-3t
30=3t
t= 30 seconds.
3. A body is uniformly accelerated from rest to a final velocityof 100m/s in 10 seconds. Calculate the distance covered.
Solution
s=ut+ ½ at2
=0×10+ ½ ×10×102
= 1000/2=500m
Motion under gravity.
1. Free fall
The equations used for constant acceleration can be used to become,
v =u+gt
s =ut + ½ gt2
v2= u+2gs
2. Vertical projection
Since the body goes against force of gravity then the following equations hold
v =u-gt ……………1
s =ut- ½ gt2 ……2
v2= u-2gs …………3
N.B time taken to reach maximum height is given by the following
t=u/g since v=0 (using equation 1)
Time of flight
The time taken by the projectile is the timetaken to fall back to its point ofprojection. Using eq. 2 then, displacement =0
0= ut- ½ gt2
0=2ut-gt2
t(2u-gt)=0
Hence, t=0 or t= 2u/g
t=o corresponds to the start of projection
t=2u/gcorresponds to the time of flight
The time of flight is twice the time taken to attain maximum height.
Maximum height reached.
Using equation 3 maximum height, Hmax is attained when v=0 (final velocity).
Hence
v2= u2-2gs;- 0=u2-2gHmax, therefore
2gHmax=u2
Hmax=u2/2g
Velocity to return to point of projection.
At the instance of returning to the original point, total displacement equals to zero.
v2 =u2-2gs hence v2= u2
Thereforev=u or v=±u
Example
A stone is projected vertically upwards with a velocity of 30m/s from the ground.
Calculate,
a. The time it takes to attain maximum height
b. The time of flight
c. The maximum height reached
d. The velocity with which it lands on the ground. (take g=10m/s)
Solution
a. Time taken to attain maximum height
T=u/g=30/10=3 seconds
b. The time of flight
T=2t= 2×3=6 seconds
Or T=2u/g=2×30/10=6 seconds.
c. Maximum height reached
Hmax= u2/2g= 30×30/2×10= 45m
d. Velocity of landing (return)
v2= u2-2gs, but s=0,
Hence v2=u2
Thereforev=(30×30)1/2=30m/s
3. Horizontal projection
The path followed by a body (projectile) is called trajectory.
The maximum horizontal distance covered by the projectile is called range.
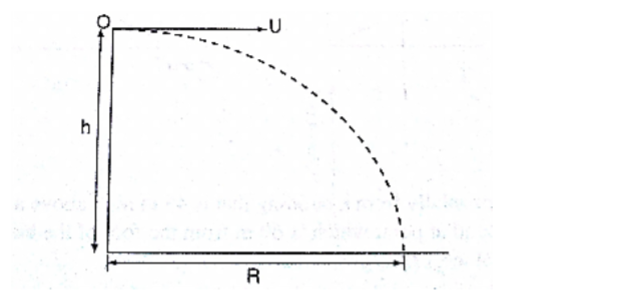
The horizontal displacement ‘R’ at a time‘t’ is given by s=ut+1/2at2
Taking u=u and a=0 hence R=ut, is the horizontal displacement and h=1/2gt2 is the vertical displacement.
NOTE
The time of flight is the same as the time of free fall.
Example
A ball is thrown from the top of a cliff 20m high with a horizontal velocity of 10m/s.
Calculate,
a. The time taken by the ball to strike the ground
b. The distance from the foot of the cliff to where the ball strikes the ground.
c. The vertical velocity at the time it strikes the ground. (take g=10m/s)
Solution
a. h= ½ gt2
20= ½ ×10×t2
40=10t2
t2=40/10=4
t=2 seconds
b. R=ut
=10×2
=20m
c. v=u+at=gt
= 2×10=20m/s
Chapter Two
Refraction of Light
Introduction
Refraction is the change of direction of light rays as they pass at an angle from one medium to another of different optical densities.
Exp. To investigate the path of light through rectangular glass block.
Apparatus: – soft-board, white sheet of paper, drawing pins (optical), rectangular glass block.
Procedure
1. Fix the white plain paper on the soft board using pins.
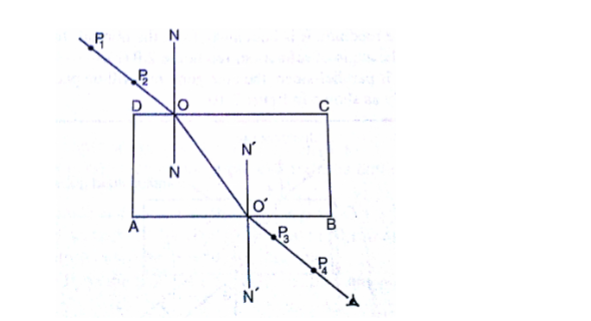
2. Place the glass block on the paper and trace its outline, label it ABCD as shown below.
3. Draw a normal NON at point O.
4. Replace the glass block to its original position.
5. Stick two pins P1 and P2 on the line such that they are at least 6cm apart and upright.
6. Viewing pins P1 and P2 from opposite side, fixpins P3 and P4 such that they’re in a straight line.
7. Remove the pins and the glass block.
8. Draw a line joining P3 and P4 and produce it to meet the outline face AB at point O
Explanation of refraction.
Light travels at a velocity of 3.0×108in a vacuum. Light travels with different velocities in different media. When a ray of light travels from an optically less dense media to more dense media, it is refracted towards the normal.
The glass block experiment gives rise to a very important law known as the law of reversibility which states that “if a ray of light is reversed, it always travels along its original path”.
If the glass block is parallel-sided, the emergent ray will be parallel to the incident ray but displaced laterally as shown
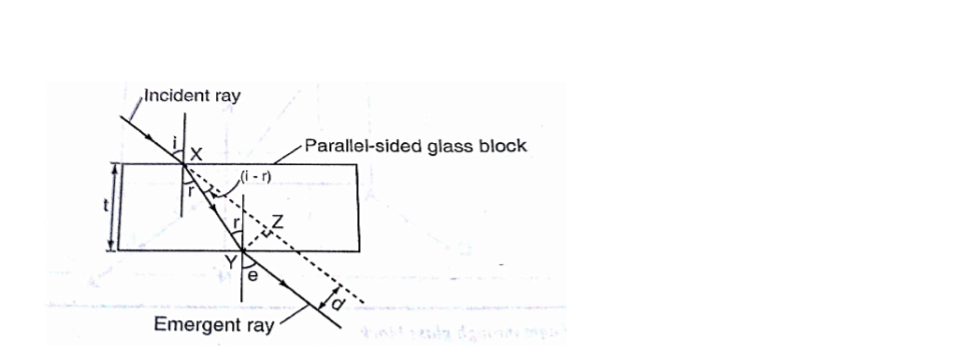
‘e’ is called the angle of emergence. The direction of the light is not altered but displaced sideways. This displacement is called lateral displacement and is denoted by‘d’.
Therefore
XY= t/Cos r YZ= Sin (i-r) ×xy
So, lateral displacement, d = t Sin (i-r)/Cos r
Laws of refraction
1. The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal at the point of incidence all lie on the same plane.
2. The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant for a given pair of media.
Sin i/sin r = constant (k)
Refractive index
Refractive index (n) is the constant of proportionality in Snell’s law; hence
Sin i/ sin r = n
Therefore sin i/sin r=n=1/sin r/sin i
Examples
1. Calculate the refractive index for light travelling from glass to air given thatang= 1.5
Solution
gna= 1/ang = 1/1.5=0.67
2. Calculate the angle of refraction for a ray of light from air striking an air-glass interface, making an angle of 600 with the interface. (ang= 1.5)
Solution
Angle of incidence (i) = 900-600=300
1.5=sin 30o/sin r, sin r =sin 300/ 1.5=0.5/1.5
Sin r=0.3333, sin-10.3333= 19.50
R= 19.50
Refractive index in terms of velocity.
Refractive index can be given in terms of velocity by the use of the following equation;
1n2 = velocity of light in medium 1/velocity of light in medium 2
When a ray of light is travelling from vacuum to a medium the refractive index is referred to as absolute refractive index of the medium denoted by ‘n’
Refractive index of a material ‘n’=velocity of light in a vacuum/velocity of light in material ‘n’
The absolute refractive indices of some common materials is given below
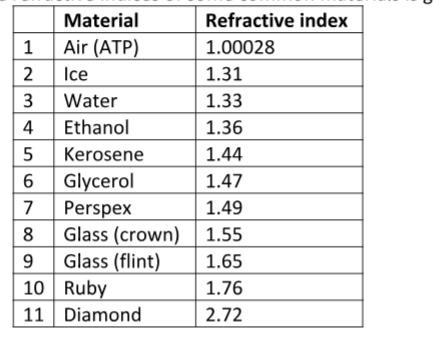
Examples
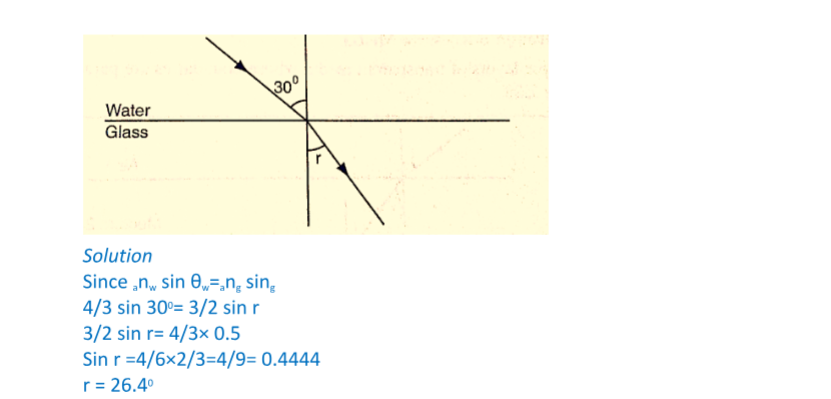
1. A ray of light is incident on a water-glass interface as shown. Calculate ‘r’. (Take the refractive index of glass and water as 3/2 and 4/3 respectively)
2. The refractive index of water is 4/3 and that of glass is 3/2. Calculate the refractive index of glass with respect to water.
Solution
wng= gna×ang, but wna = 1/ anw=3/4
wng=3/4×3/2=9/8= 1.13
Real and apparent depth
Consider the following diagram
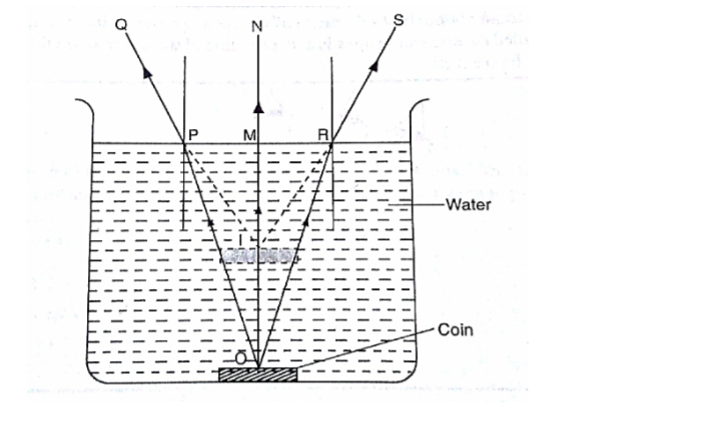
The depth of the water OM is the real depth, and the distance IM is known as the apparent depth. OI is the distance through which the coin has been displaced and is known as the vertical displacement.
The relationship between refractive index and the apparent depth is given by;
Refractive index of a material=real depth/apparent depth
NB
This is true only if the object is viewed normally.
Example
A glass block of thickness 12 cm is placed on a mark drawn on a plain paper.
The mark is viewed normally through the glass. Calculate the apparent depth of the mark and hence the vertical displacement. (Refractive index of glass =3/2)
Solution
ang= real depth/apparent depth
apparent depth= real depth/ ang=(12×2)/3= 8 cm
vertical displacement= 12-8=4 cm
Applications of refractive index
Total internal reflection
This occurs when light travels from a denser optical medium to a less dense medium. The refracted ray moves away from the normal until a critical angle is reached usually 900 where the refracted ray is parallel to the boundary between the two media.
If this critical angle is exceeded total internal reflection occurs and at this point no refraction occurs but the ray is reflected internally within the denser medium.
Relationship between the critical angle and refractive index.
Consider the following diagram
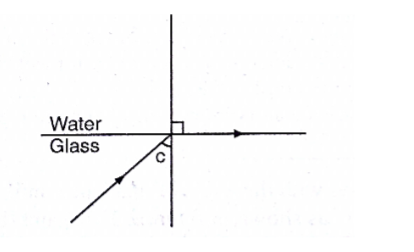
From Snell’s law
gnw = sin C/sin 900,but ang = 1/gna since sin 900 = 1
Thereforeang= 1/sin C, hence sin C=1/n or n=1/sin C
Example
Calculate the critical angle of diamond given that its refractive index is 2.42
Solution
Sin C= 1/n=1/ 2.42= 0.4132= 24.40
Effects of total internal reflection
1. Mirage: These are ‘pools of water’ seen on a tarmac road during a hot day.
They are also observed in very cold regions but the light curves in opposite direction such that a polar bear seems to be upside down in the sky.
2. Atmospheric refraction: the earths’ atmosphere refracts light rays so that the sun can be seen even when it has set. Similarly the sun is seen before it actually rises.
Applications of total internal reflection
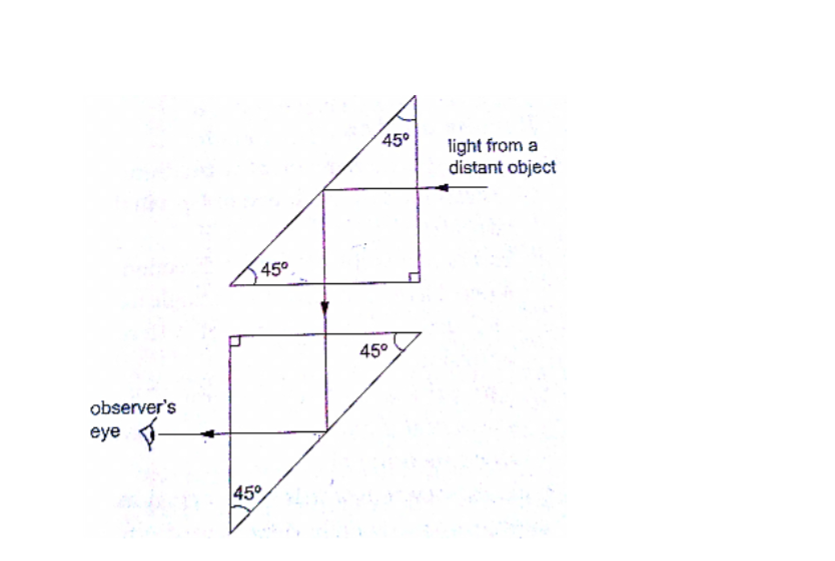
1. Periscope: a prism periscope consists of two right angled glass prisms of angles 450,900 and 450 arranged as shown below. They are used to observe distant objects.
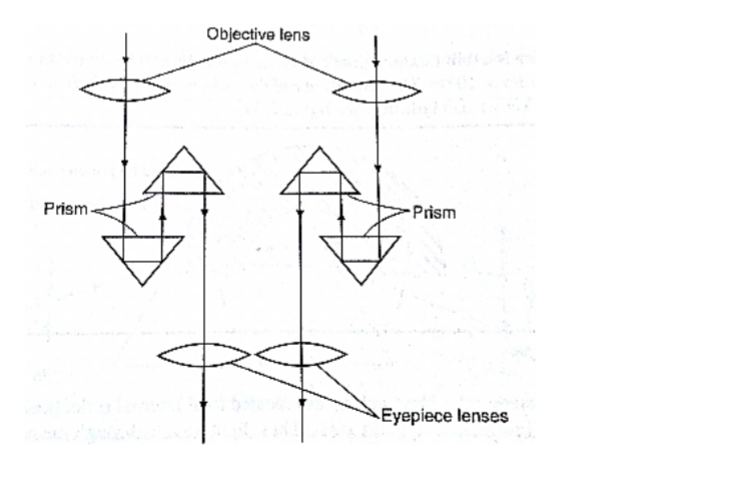
2. Prism binoculars: the arrangement of lenses and prisms is as shown below. Binoculars reduce the distance of objects such that they seem to be nearer.
3. Pentaprism: used in cameras to change the inverted images formed into erect and actual image in front of the photographer.
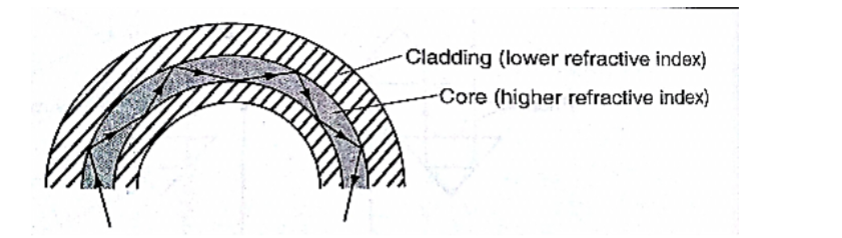
4. Optical fibre: this is a flexible glass rod of small diameter. A light entering through them undergoes repeated internal reflections.
They are used in medicine to observe or view internal organs of the body
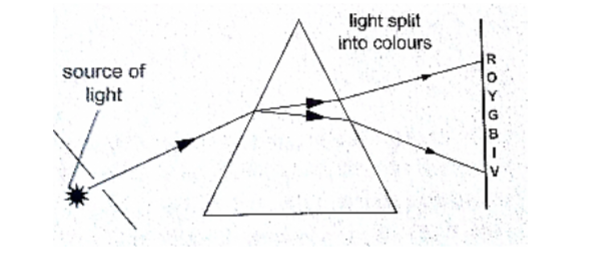
5. Dispersion of white light:
the splitting of light into its constituent colours is known as dispersion. Each colour represents a different wavelength as they strike the prism and therefore refracted differently as shown.
Chapter Three
Newton’s Laws of Motion
Newton’s first law (law of inertia)
This law states that “A body continues in its state of rest or uniform motion unless an unbalanced force acts on it”.
The mass of a body is a measure of its inertia. Inertia is the property that keeps an object in its state of motion and resists any efforts to change it.
Newton’s second law (law of momentum)
Momentum of a body is defined as the product of its mass and its velocity.
Momentum ‘p’=mv. The SI unit for momentum is kgm/s or Ns.
The Newton’s second law states that “The rate of change of momentum of a body is proportional to the applied force and takes place in the direction in which the force acts”
Change in momentum= mv-mu
Rate of change of momentum= mv-mu/∆t
Generally the second law gives rise to the equation of force F=ma
Hence F=mv-mu/∆t and F∆t=mv-mu
The quantity F∆t is called impulse and is equal to the change of momentum of the body. The SI unit for impulse is Ns.
Examples
1. A van of mass 3 metric tons is travelling at a velocity of 72 km/h. Calculate the momentum of the vehicle.
Solution
Momentum=mv=72km/h=(20m/s)×3×103 kg
=6.0×104kgm/s
2. A truck weighs 1.0×105 N and is free to move. What force willgiveit an acceleration of 1.5 m/s2? (take g=10N/kg)
Solution
Mass of the truck = (1.0×105)/10=6.0×104
Using F=ma
=1.5×10×104
=1.5×104 N
3. A car of mass 1,200 kg travelling at 45 m/s is brought to rest in 9 seconds.
Calculate the average retardation of the car and the average force applied by the brakes.
Solution
Since the car comes to rest, v=0, a=(v-u)/t =(0-45)/9=-5m/s (retardation)
F=ma =(1200×-5) N =-6,000 N (braking force)
4. A truck of mass 2,000 kg starts from rest on horizontal rails. Find the speed 3 seconds after starting if the tractive force by the engine is 1,000 N.
Solution
Impulse = Ft=1,000×3= 3,000 Ns
Let v be the velocity after 3 seconds.
Since the truck was initially at rest then u=0.
Change in momentum=mv-mu
= (2,000×v) – (2,000×0)
=2,000 v
But impulse=change in momentum
2,000 v = 3,000
v = 3/2=1.5 m/s.
Weight of a body in a lift or elevator
When a body is in a lift at rest then the weight
W=mg
When the lift moves upwards with acceleration ‘a’ then the weight becomes
W = m (a+g)
If the lift moves downwards with acceleration ‘a’ then the weight becomes
W = m (g-a)
Example
A girl of mass stands inside a lift which is accelerated upwards at a rate of 2 m/s2. Determine the reaction of the lift at the girls’ feet.
Solution
Let the reaction at the girls’ feet be ‘R’ and the weight ‘W’
The resultant force F= R-W
= (R-500) N
Using F = ma, then R-500= 50×2, R= 100+500 = 600 N.
Newton’s third law (law of interaction)
This law states that “For every action or force there is an equal and opposite force or reaction”
Example
A girl of mass 50 Kg stands on roller skates near a wall. She pushes herself against the wall with a force of 30N.
If the ground is horizontal and the friction on the roller skates is negligible, determine her acceleration from the wall.
Solution
Action = reaction = 30 N
Force of acceleration from the wall = 30 N
F = ma
a = F/m = 30/50 = 0.6 m/s2
Linear collisions
Linear collision occurs when two bodies collide head-on and move along the same straight line.
There are two types of collisions;
a) Inelastic collision: – this occurs when two bodies collide and stick together i.e. hitting putty on a wall. Momentum is conserved.
b) Elastic collision: – occurs when bodies collide and bounce off each other after collision. Both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved.
Collisions bring about a law derived from both Newton’s third law and conservation of momentum.
This law is known as the law of conservation of linear momentum which states that “when no outside forces act on a system of moving objects, the total momentum of the system stays constant”.
Examples
1. A bullet of mass 0.005 kg is fired from a gun of mass 0.5 kg.
If the muzzle velocity of the bullet is 300 m/s, determine the recoil velocity of the gun.
Solution
Initial momentum of the bullet and the gun is zero since they are at rest.
Momentum of the bullet after firing = (0.005×350) = 1.75 kgm/s
But momentum before firing = momentum after firing hence
0 = 1.75 + 0.5 v where ‘v’ = recoil velocity
0.5 v = -1.75
v =-1.75/0.5 = – 3.5 m/s (recoil velocity)
2. A resultant force of 12 N acts on a body of mass 2 kg for 10 seconds.
What is the change in momentum of the body?
Solution
Change in momentum = ∆P = mv – mu= Ft
= 12×10 = 12 Ns
3. A minibus of mass 1,500 kg travelling at a constant velocity of 72 km/h collides head-on with a stationary car of mass 900 kg.
The impact takes 2 seconds before the two move together at a constant velocity for 20 seconds.
Calculate
a) The common velocity
b) The distance moved after the impact
c) The impulsive force
d) The change in kinetic energy
Solution
a) Let the common velocity be ‘v’
Momentum before collision = momentum after collision
(1500×20) + (900×0) = (1500 +900)v
30,000 = 2,400v
v = 30,000/2,400 = 12.5 m/s (common velocity)
b) After impact, the two bodies move together as one with a velocity of 12.5 m/s
Distance = velocity × time
= 12.5×20
= 250m
c) Impulse = change in momentum
= 1500 (20-12.5) for minibus or
=900 (12.5 – 0) for the car
= 11,250 Ns
Impulse force F = impulse/time = 11,250/2 = 5,625 N
d) K.E before collision = ½ × 1,500 × 202 = 3 × 105 J
K.E after collision = ½ × 2400 × 12.52 = 1.875×105 J
Therefore, change in K.E =(3.00 – 1.875) × 105 = 1.25× 105 J
Some of the applications of the law of conservation of momentum
1. Rocket and jet propulsion: – rocket propels itself forward by forcing out its exhaust gases.
The hot gases are pushed through exhaust nozzle at high velocity therefore gaining momentum to move forward.
2. The garden sprinkler: – as water passes through the nozzle at high pressure it forces the sprinkler to rotate.
Solid friction
Friction is a force which opposes or tends to oppose the relative motion of two surfaces in contact with each other.
Measuring frictional forces
We can relate weight of bodies in contact and the force between them.
This relationship is called coefficient of friction.
Coefficient of friction is defined as the ratio of the force needed to overcome friction Ff to the perpendicular force between the surfaces Fn.
Hence
µ = Ff/ Fn
Examples
1. A box of mass 50 kg is dragged on a horizontal floor by means of a rope tied to its front.
If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the floor and the box is 0.30, what is the force required to move the box at uniform speed?
Solution
Ff = µFn
Fn= weight = 50×10 = 500 N
Ff = 0.30 × 500 = 150 N
2. A block of metal with a mass of 20 kg requires a horizontal force of 50 N to pull it with uniform velocity along a horizontal surface.
Calculate the coefficient of friction between the surface and the block. (take g = 10 m/s)
Solution
Since motion is uniform, the applied force is equal to the frictional force
Fn = normal reaction = weight = 20 ×10 = 200 N
Therefore, µ =Ff/ Fn = 50/ 200 = 0.25.
Laws of friction
1. Friction is always parallel to the contact surface and in the opposite direction to the force tending to produce or producing motion.
2. Friction depends on the nature of the surfaces and materials in contact with each other.
3. Sliding (kinetic) friction is less than static friction (friction before the body starts to slide).
4. Kinetic friction is independent of speed.
5. Friction is independent of the area of contact.
6. Friction is proportional to the force pressing the two surfaces together.
Applications of friction
1. Match stick
2. Chewing food
3. Brakes
4. Motion of motor vehicles
5. Walking
Methods of reducing friction
1. Rollers
2. Ball bearings in vehicles and machines
3. Lubrication / oiling
4. Air cushioning in hovercrafts
Example
A wooden box of mass 30 kg rests on a rough floor. The coefficient of friction between the floor and the box is 0.6. Calculate
a) The force required to just move the box
b) If a force of 200 N is applied the box with what acceleration will it move?
Solution
a) Frictional force Ff= µFn = µ(mg)
= 0.6×30×10 = 180 N
b) The resultant force = 200 – 180 = 20 N
From F =ma, then 20 = 30 a
a = 20 / 30 = 0.67 m/s2
Viscosity
This is the internal friction of a fluid. Viscosity of a liquid decreases as temperature increases.
When a body is released in a viscous fluid it accelerates at first then soon attains a steady velocity called terminal velocity.
Terminal velocity is attained when F + U = mg where F is viscous force, U is upthrust and mg is weight.
Chapter Four
Energy, Work, Power and Machines
Energy
This is the ability to do work.
Forms of energy.
1. Chemical energy: – this is found in foods, oils charcoal firewood etc.
2. Mechanical energy: – there are two types;
i. Potential energy – a body possesses potential energy due to its relative position or state
ii. Kinetic energy – energy possessed by a body due to its motion i.e. wind, water
iii. Wave energy – wave energy may be produced by vibrating objects or particles i.e. light, sound or tidal waves.
iv. Electrical energy – this is energy formed by conversion of other forms of energy i.e. generators.
Transformation and conservation of energy
Any device that facilitates energy transformations is called transducer. Energy can be transformed from one form to another i.e. mechanical – electrical – heat energy.
The law of conservation of energy states that “energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be transformed from one form to another”.
Work
Work is done when a force acts on a body and the body moves in the direction of the force.
Work done = force × distance moved by object
W = F × d
Work is measured in Nm. 1 Nm = 1 Joule (J)
Examples
1. Calculate the work done by a stone mason lifting a stone of mass 15 kg through a height of 2.0 m. (take g=10N/kg)
Solution
Work done = force × distance
= (15× 10) × 2 = 300 Nm or 300 J
2. A girl of mass 50 kg walks up a flight of 12 steps. If each step is 30 cm high, calculate the work done by the girl climbing the stairs.
Solution
Work done = force × distance
= (50× 10) × (12 ×30) ÷ 100 = 500 × 3.6 = 1,800 J
3. A force of 7.5 N stretches a certain spring by 5 cm. How much work is done in stretching this spring by 8.0 cm?
Solution
A force of 7.5 produces an extension of 5.0 cm.
Hence 8.0 cm = (7.5 ×8)/ 5 = 12.0 N
Work done = ½ × force × extension
= ½ × 12.0 × 0.08 = 0.48 J
4. A car travelling at a speed of 72 km/h is uniformly retarded by an applicationof brakes and comes to rest after 8 seconds. If the car with its occupants has a mass of 1,250 kg. Calculate;
a) The breaking force
b) The work done in bringing it to rest
Solution
a) F = ma and a = v – u/t
But 72 km/h = 20m/s
a = 0 -20/8 = – 2.5 m/s
Retardation = 2.5 m/s
Braking force F = 1,250 × 2.5
= 3,125 N
b) Work done = kinetic energy lost by the car
= ½ mv2 – ½ mu2
= ½ × 1250 × 02 – ½ × 1250 × 202
= – 2.5 × 105 J
5. A spring constant k = 100 Nm is stretched to a distance of 20 cm. calculate the work done by the spring.
Solution
Work = ½ ks2
= ½ × 100 × 0.22
= 2 J
Power
Poweris the time rate of doing work or the rate of energy conversion.
Power (P)
= work done / time
P = W / t
The SI unit for power is the watt (W) or joules per second (J/s).
Examples
1. A person weighing 500 N takes 4 seconds to climb upstairs to a height of 3.0 m. what is the average power in climbing up the height?
Solution
Power = work done / time = (force × distance) / time
= (500 ×3) / 4 = 375 W
2. A box of mass 500 kg is dragged along a level ground at a speed of 12 m/s. If the force of friction between the box and floor is 1200 N. Calculate the power developed.
Solution
Power = F v
= 2,000 × 12
= 24,000 W = 24 kW.
Machines
A machine is any device that uses a force applied at one point to overcome a force at another point. Force applied is called the effort while the resisting force overcome is called load. Machines makes work easier or convenient to be done.
Three quantities dealing with machines are;-
a) Mechanical advantage (M.A.) – this is defined as the ratio of the load (L) to the effort (E). It has no units.
M.A = load (L) / effort (E)
b) Velocity ratio – this is the ratio of the distance moved by the effort to the distance moved by the load
V.R = distance moved by effort/ distance moved by the load
c) Efficiency – is obtained by dividing the work output by the work input and the getting percentage
Efficiency = (work output/work input) × 100
= (M.A / V.R) × 100
= (work done on load / work done on effort) × 100
Examples
1. A machine; the load moves 2 m when the effort moves 8 m. If an effort of 20 N is used to raise a load of 60 N, what is the efficiency of the machine?
Solution
Efficiency = (M.A / V.R) × 100 M.A = load/effort =60/20 = 3
V.R =DE/ DL = 8/2 = 4
Efficiency = ¾ × 100 = 75%
Some simple machines
a) Levers – this is a simple machine whose operation relies on the principle of moments
b) Pulleys – this is a wheel with a grooved rim used for lifting heavy loads to high levels. The can be used as a single fixed pulley, or as a block-and-tackle system.
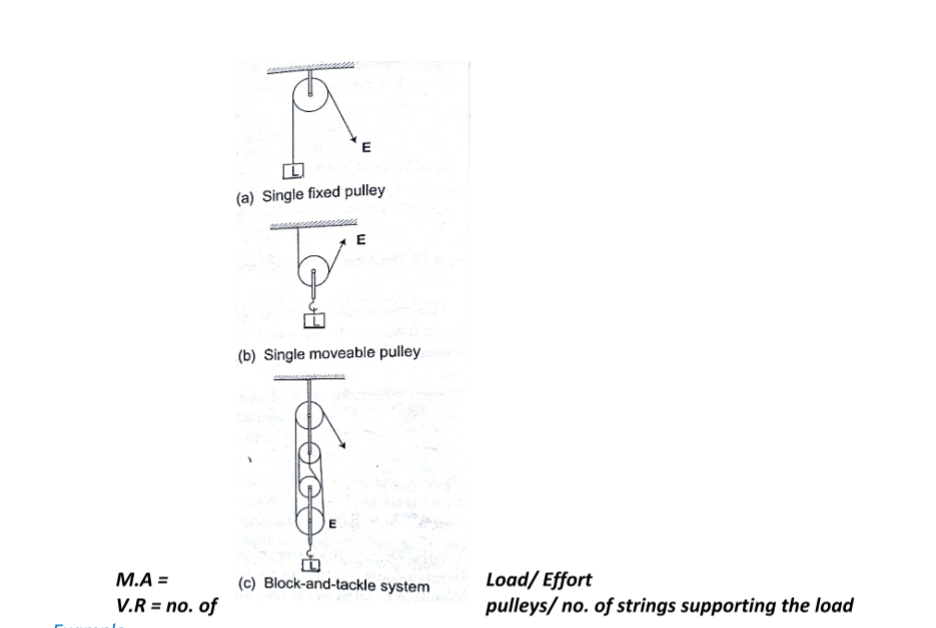
Example
A block and tackle system has 3 pulleys in the upper fixed block and two in the lower moveable block. What load can be lifted by an effort of 200 N if the efficiency of the machine is 60%?
Solution
V.R = total number of pulleys = 5
Efficiency = (M.A /V.R) × 100 = 60%
0.6 = M.A/ 5 =3, but M.A = Load/Effort
Therefore, load = 3 ×200 = 600 N
c) Wheel and axle– consists of a large wheel of big radius attached to an axle of smaller radius.
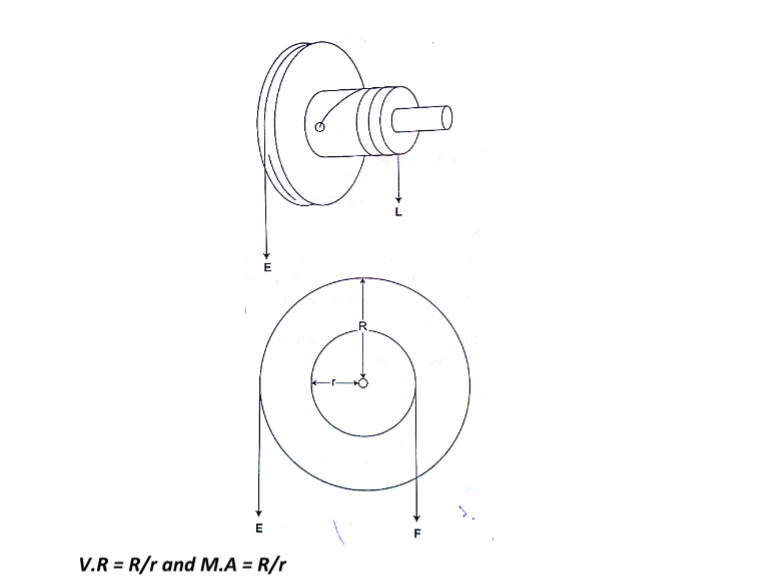
Example
A wheel and axle is used to raise a load of 280 N by a force of 40 N applied to the rim of the wheel. If the radii of the wheel and axle are 70 cm and 5 cm respectively. Calculate the M.A, V.Rand efficiency.
Solution
M.A = 280 / 40 = 7
V.R = R/r = 70/5 = 14
Efficiency = (M.A/ V.R) × 100 = 7/14 × 100 = 50 %
d) Inclined plane:
V.R = 1/ sin θ M.A = Load/ Effort
Example
A man uses an inclined plane to lift a 50 kg load through a vertical height of 4.0 m.
the inclined plane makes an angle of 300 with the horizontal.
If the efficiency of the inclined plane is 72%, calculate;
a) The effort needed to move the load up the inclined plane at a constant velocity.
b) The work done against friction in raising the load through the height of 4.0 m. (take g= 10 N/kg)
Solution
a) V.R = 1 / sin C = 1/ sin 300 = 2 M.A = efficiency × V.R = (72/100)× 2 = 1.44
Effort = load (mg) / effort (50×10)/ 1.44 = 347.2 N
b) Work done against friction = work input – work output
Work output = mgh = 50×10×4 = 2,000 J
Work input = effort × distance moved by effort
347.2 × (4× sin 300) = 2,777.6 J
Therefore work done against friction = 2,777.6 – 2,000 = 777.6 J
e) The screw: – the distance between two successive threads is called the pitch
V.R of screw = circumference of screw head / pitch P
= 2πr / P
Example
A car weighing 1,600 kg is lifted with a jack-screw of 11 mm pitch. If the handleis 28 cm from the screw, find the force applied.
Solution
Neglecting friction M.A = V.R
V.R = 2πr /P = M.A = L / E
1,600 / E = (2π× 0.28) / 0.011
E = (1,600 × 0.011 × 7) / 22×2×0.28 =10 N
f) Gears: – the wheel in which effort is applied is called the driver while the load wheel is the driven wheel.
V.R = revolutions of driver wheel / revolutions of driven wheel
Or
V.R = no.of teeth in the driven wheel/ no. of teeth in the driving wheel
Example
g) Pulley belts: -these are used in bicycles and other industrial machines
V.R = radius of the driven pulley / radius of the driving pulley
h) Hydraulic machines
V.R = R2 / r2 where R- radius of the load piston and r- radius of the effort piston
Example
The radius of the effort piston of a hydraulic lift is 1.4 cm while that of the load piston is 7.0 cm.
This machine is used to raise a load of 120 kg at a constant velocity through a height of 2.5 cm. given that the machine is 80% efficient, calculate;
a) The effort needed
b) The energy wasted using the machine
Solution
a) V.R = R2 / r2 = (7×7) / 1.4 × 1.4 = 25
Efficiency = M.A / V.R = (80 /100) × 25 = 20
But M.A = Load / Effort = (120×10) / 20 = 60 N
b) Efficiency = work output / work input = work done on load (m g h) /80
= (120 × 10× 2.5) / work input
80 / 100 = 3,000 / work input
Work input = (3,000 × 100) /80 = 3,750 J
Energy wasted = work input – work output
= 3,750 – 3,000 = 750 J
Chapter Five
Current Electricity
Electric potential difference and electric current
Electric current
Electric potential difference (p. d) is defined as the work done per unit charge in moving charge from one point to another. It is measured in volts.
Electric current is the rate of flow of charge. P. d is measured using a voltmeter while current is measured using an ammeter. The SI units for charge is amperes (A).
Ammeters and voltmeters
In a circuit an ammeter is always connected in series with the battery while a voltmeter is always connected parallel to the device whose voltage is being measured.
Ohm’s law
This law gives the relationship between the voltage across a conductor and the current flowing through it.
Ohm’s law states that “the current flowing through a metal conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across the ends of the wire provided that temperature and other physical conditions remain constant”
Mathematically V α I
So V /I = constant, this constant of proportionality is called resistance
V / I = Resistance (R)
Resistance is measured in ohms and given the symbol Ω
Examples
1. A current of 2m A flows through a conductor of resistance 2 kΩ. Calculate the voltage across the conductor.
Solution
V = IR = (2 × 10-3) × (2 × 103) = 4 V.
2. A wire of resistance 20Ω is connected across a battery of 5 V. What current is flowing in the circuit?
Solution
I = V/R = 5 / 20 = 0.25 A
Ohmic and non-ohmic conductors
Ohmic conductors are those that obey Ohms law(V α I) and a good example is nichrome wire i.e. the nichrome wire is not affected by temperature.
Non-ohmic conductors do not obey Ohms law i.e. bulb filament (tungsten), thermistor couple, semi-conductor diode etc. They are affected by temperature hence non-linear.
Factors affecting the resistance of a metallic conductor
1. Temperature – resistance increases with increase in temperature
2. Length of the conductor– increase in length increases resistance
3. Cross-sectional area– resistance is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of a conductor of the same material.
Resistivity of a material is numerically equal to the resistance of a material of unit length and unit cross-sectional area. It is symbolized by ρ and the units are ohmmeter (Ωm).
It is given by the following formula;
ρ = AR /lwhere A – cross-sectional area, R – resistance, l – length
Example
Given that the resistivity of nichrome is 1.1× 10-6Ωm, what length of nichrome wire of diameter 0.42 mm is needed to make a resistance of 20 Ω?
Solution
ρ = AR /l, hence l = RA/ ρ = 20 × 3.142 × (2.1×10-4) / 1.1 × 10-6 = 2.52 m
Resistors
Resistors are used to regulate or control the magnitude of current and voltage in a circuit according to Ohms law.
Types of resistors
i) Fixed resistors – they are wire-wound or carbon resistors and are designed togive a fixed resistance.
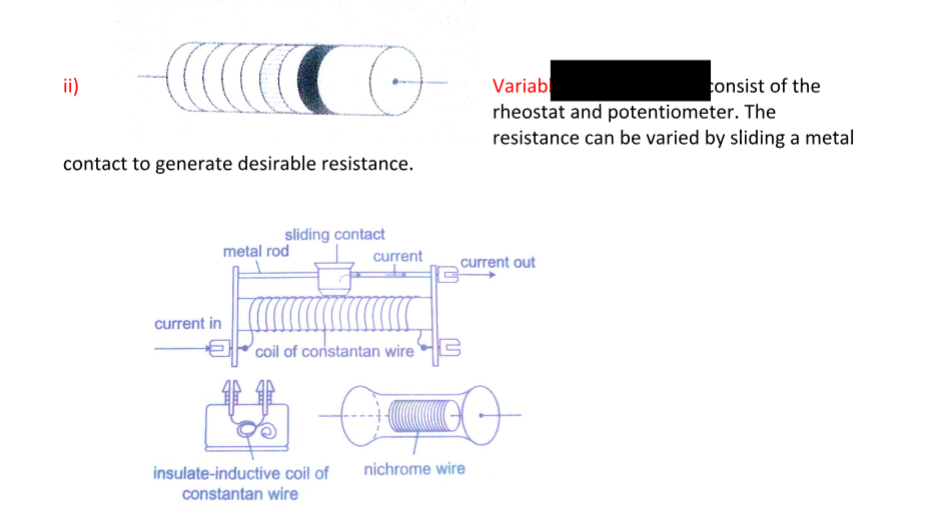
ii) Variable resistors – they consist of the rheostat and potentiometer. The resistance can be varied by sliding a metal contact to generate desirable resistance.
Resistor combination
a) Series combination
Consider the following loop
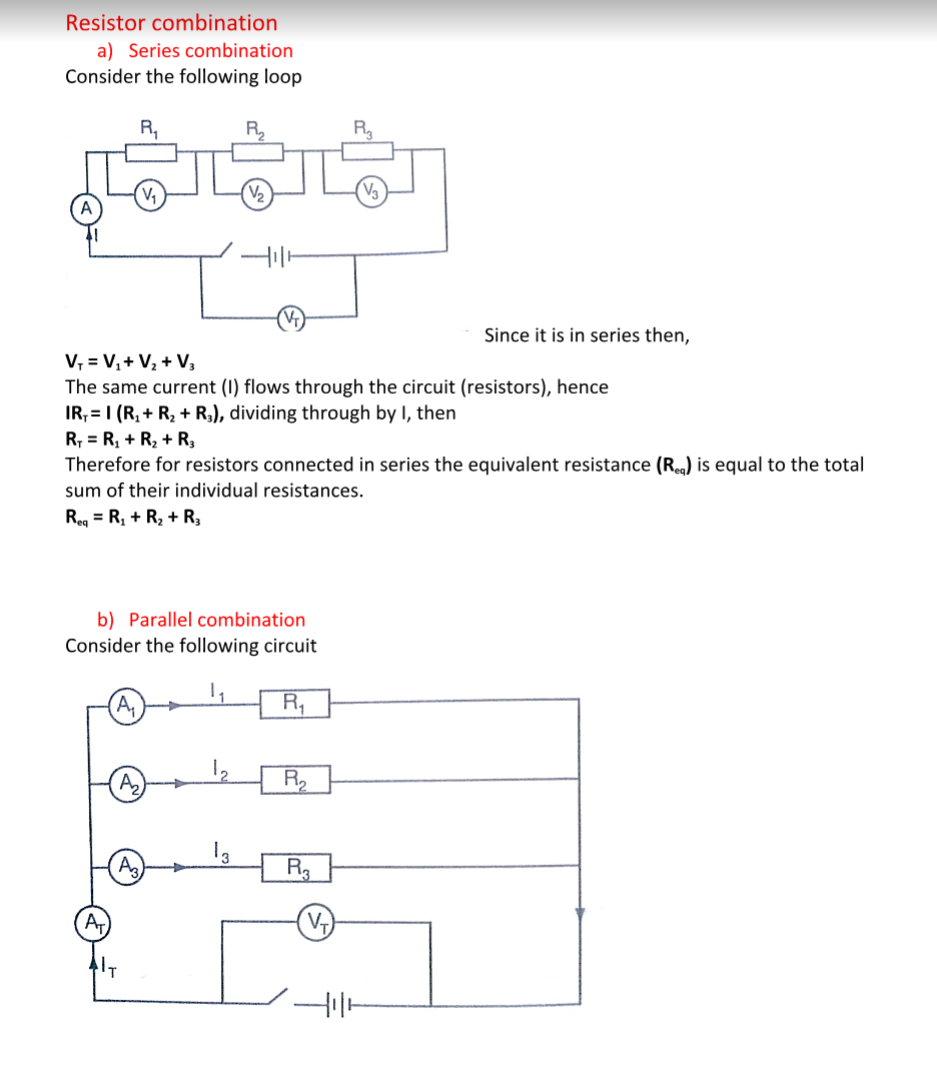
Combining those in series then this can be replaced by two resistors of 60 Ω and 40 Ω.
Current through 10 Ω = (p.d. between P and R)/ (30 + 10) Ω
p.d between P and R = 0.8 × Req. Req = (40 × 60)/ 40 + 60 = 2400/ 100 = 24 Ω
p.d across R and P = 0.8 × 24 (V=IR)
therefore, current through 10 Ω = 19.2 / 10 + 30 = 0.48 A
Electromotive force and internal resistance
Electromotive force (e.m.f.) is the p.d across a cell when no current is being drawn from the cell.
The p.d across the cell when the circuit is closed is referred to as the terminal voltage of the cell.
Internal resistance of a cell is therefore the resistance of flow of current that they generate. Consider the following diagram;

The current flowing through the circuit is given by the equation,
Current = e.m.f / total resistance
I = E / R + rwhere E – e.m.f of the cell
Therefore E = I (R + r) = IR + I r = V + I r
Examples
1. A cell drives a current of 0.6 A through a resistance of 2 Ω. if the value of resistance is increased to 7 Ω the current becomes 0.2 A.
calculate the value of e.m.f of the cell and its internal resistance.
Solution
Let the internal resistance be ‘r’ and e.m.f be ‘E’.
Using E = V + I r = IR + I r
Substitute for the two sets of values for I and R
E = 0.6 × (2 + 0.6 r) = 1.2 + 0.36 r
E = 0.6 × (7 × 0.2 r) = 1.4 + 0.12 r
Solving the two simultaneously, we have,
E = 1.5 v and R = 0.5 Ω
2. A battery consists of two identical cells, each of e.m.f 1.5 v and internal resistance of 0.6 Ω, connected in parallel. Calculate the current the battery drives through a 0.7 Ω resistor.
Solution
When two identical cells are connected in series, the equivalent e.m.f is equal to that of only one cell.
The equivalent internal resistance is equal to that of two such resistance connected in parallel.
Hence Req = R1 R2 / R1 + R2 = (0.6 × 0.6) / 0.6 + 0.6 = 0.36 / 1.2 = 0.3 Ω
Equivalent e.m.f =1.5 / (0.7 + 0.3) = 1.5 A
Hence current flowing through 0.7 Ω resistor is 1.5 A
Chapter Six
Waves II
Properties of waves
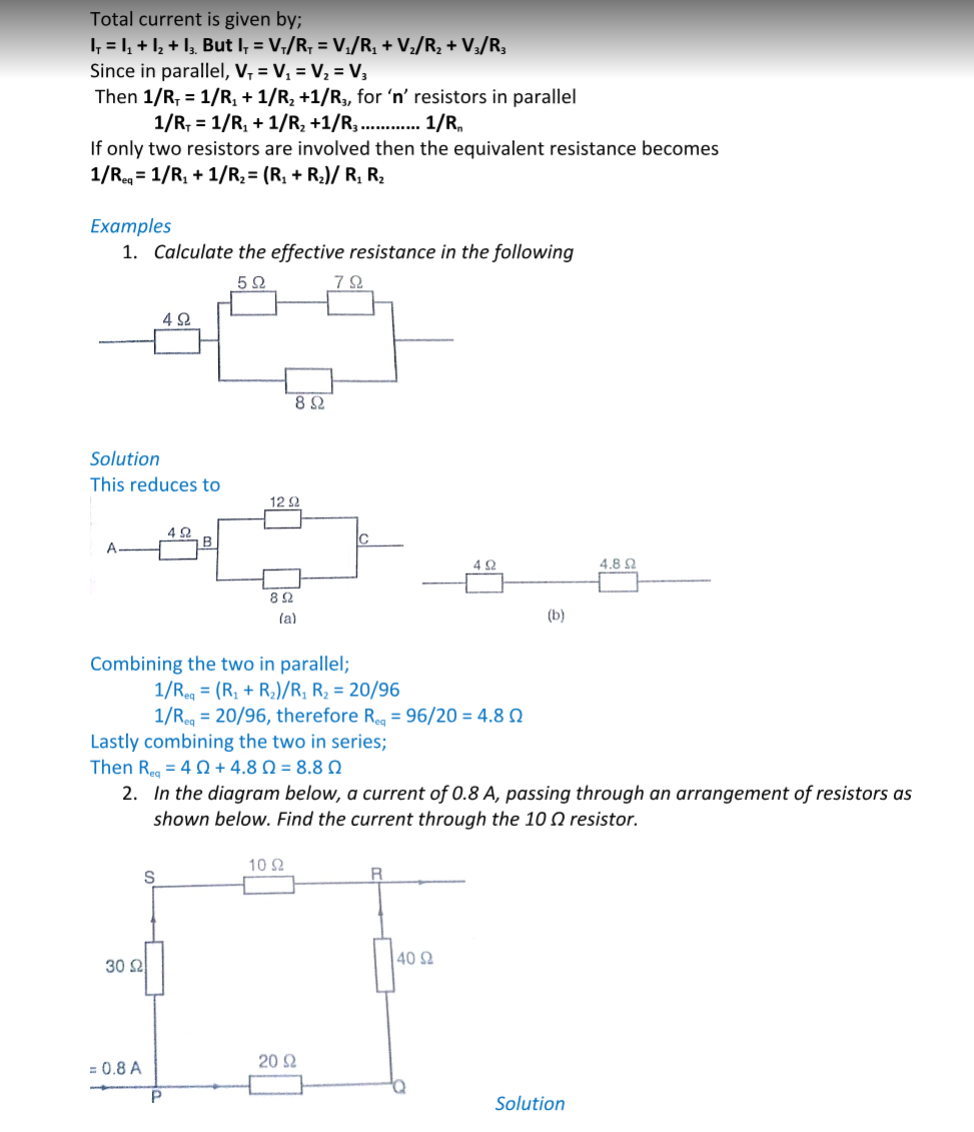
Waves exhibit various properties which can be conveniently demonstrated using the ripple tank.
It consists of a transparent tray filled with water and a white screen as the bottom. On top we have a source of light.
A small electric motor (vibrator) is connected to cause the disturbance which produces waves.
The wave fronts represent wave patterns as they move along.
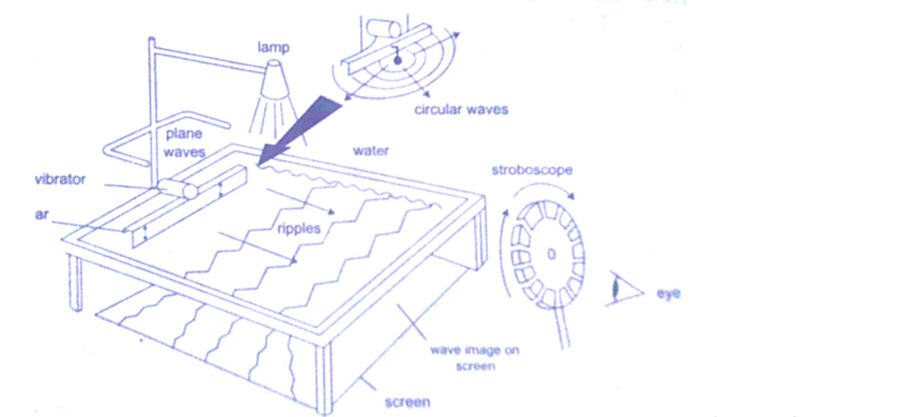
Rectilinear propagation
This is the property of the waves travelling in straight lines and perpendicular to the wave front.
The following diagrams represent rectilinear propagation of water waves.
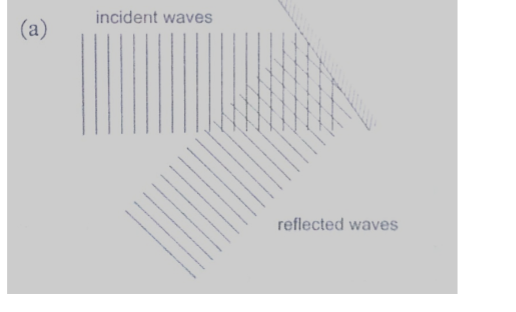
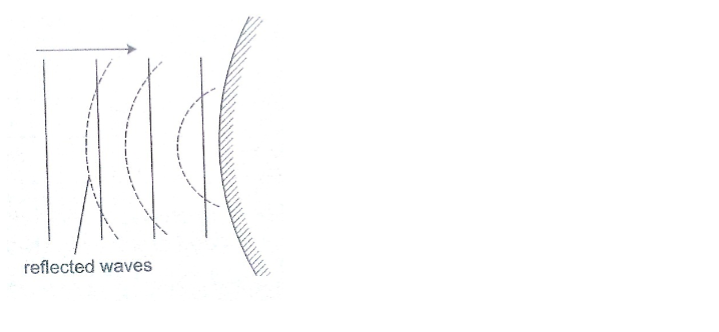
Refraction
This is the change of direction of waves at a boundary when they move from one medium to another.
This occurs when an obstacle is placed in the path of the waves. The change of direction occurs at the boundary between deep and shallow waters and only when the waves hit the boundary at an angle.
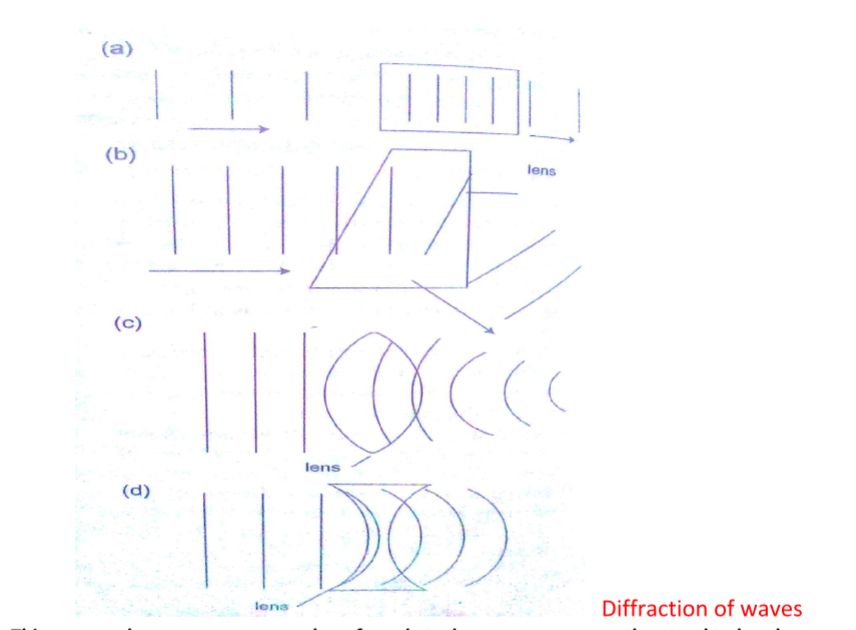
Diffraction of waves
This occurs when waves pass an edge of an obstacle or a narrow gap, they tend to bend around the corner and spread out beyond the obstacle or gap.

Interference of waves
This occurs when two waves merge and the result can be a much larger wave, smaller wave or no wave at all.
When the waves are in phase they add up and reinforce each other. This is called a constructive interference and when out of phase they cancel each other out and this is known as destructive interference.
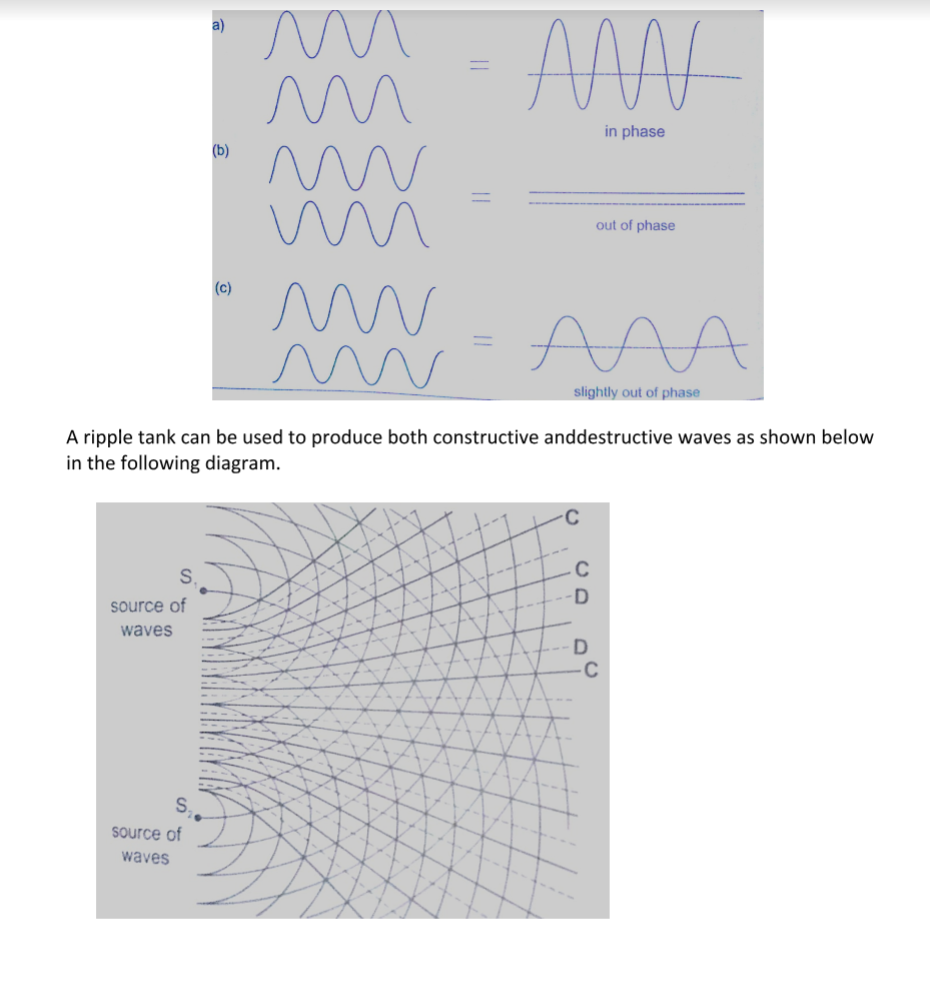
Interference in sound
Two loud speakers L1 and L2 are connected to the same signal generator so that sound waves from each of them are in phase.
The two speakers are separated by a distance of the order of wavelengths i.e. 0.5 m apart for sound frequency of 1,000 Hz.
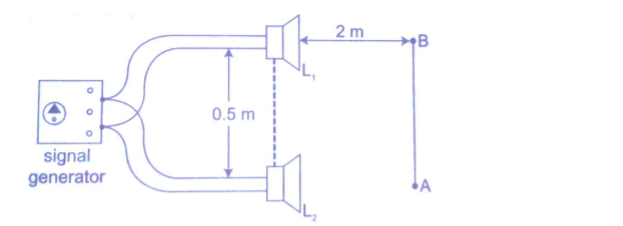
If you walk along line AB about 2m away from the speakers, the intensity of sound rises and falls alternately hence both destructive and constructive interference will be experienced.
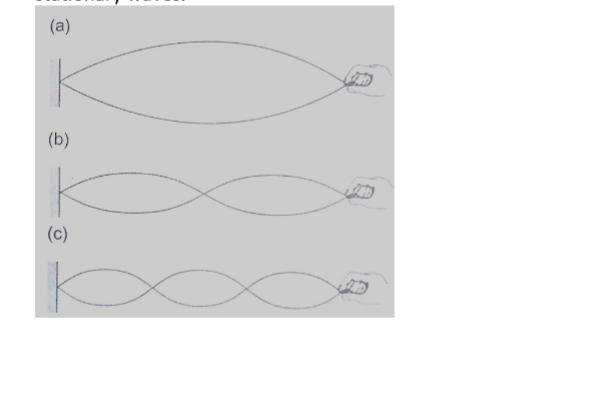
Stationary waves
They are also known as standing waves and are formed when two equal progressive waves travelling in opposite direction are superposed on each other.
When the two speakers are placed facing each other they produce standing waves.
A rope tied at one end will still produce stationary waves.
Chapter Seven
Electrostatics II
Electric fields
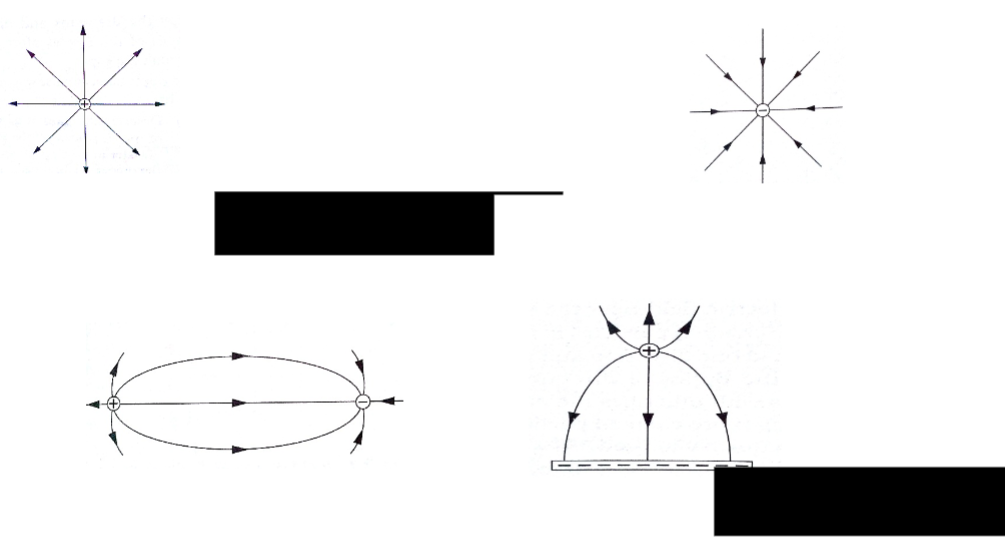
An electric field is the space around a charged body where another charged body would be acted on by a force. These fields are represented by lines of force.
This line of force also called an electric flux line points in the direction of the force.
Electric field patterns
Just like in magnetic fields, the closeness of the electric field-lines of force is the measure of the field strength.
Their direction is always from the north or positive to the south or negative.
Charge distribution on conductors’ surface
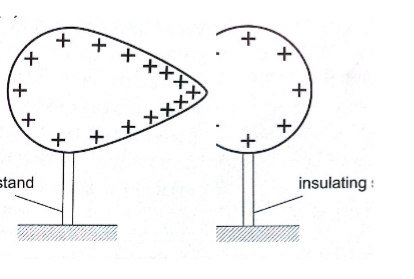
A proof plane is used to determine charge distribution on spherical or pear-shaped conductors.
For an isolated sphere it is found that the effect is the same for all points on the surface meaning that the charge is evenly distributed on all points on the spherical surface.
For appear-shaped conductor the charge is found to be denser in the regions of large curvature (small radius).
The density of charge is greatest where curvature is greatest.
Charges on or action at sharp points
A moving mass of air forms a body with sharp points.
The loss of electrons by molecules (ionization) makes the molecules positively charged ions.
These ions tend to move in different directions and collide producing more charged particles and this makes the air highly ionized.
When two positively charged bodies are placed close to each other, the air around them may cause a spark discharge which is a rush of electrons across the ionized gap, producing heat, light and sound in the process which lasts for a short time.
Ionization at sharp projections of isolated charged bodies may sometimes be sufficient to cause a discharge.
This discharge produces a glow called corona discharge observed at night on masts of ships moving on oceans.
The same glow is observed on the trailing edges of aircrafts.
This glow in aircrafts and ships is called St. Elmo’s fire. Aircrafts are fitted with ‘pig tails’ on the wings to discharge easily.
The lightning arrestors
Lightning is a huge discharge where a large amount of charge rushes to meet the opposite charge.
It can occur between clouds or the cloud and the earth. Lightning may not be prevented but protection from its destruction may be done through arrestors.
An arrestor consists of a thick copper strip fixed to the outside wall of a building with sharp spikes.
Capacitors and capacitance
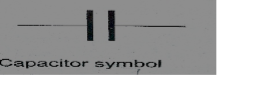
A capacitor is a device used for storing charge.
It consists of two or more plates separated by either a vacuum or air.
The insulating material is called ‘dielectric’. They are symbolized as shown below,
Capacitance C = Q / V where Q- charge and V – voltage.
The units for capacitance are coulombs per volt (Coul /volt) and are called farads.
1 Coul/ volt = 1 farad (F)
1 µF = 10-6 F and 1pF = 10-12
Types of capacitors are;
a) Paper capacitors
b) Electrolyte capacitors
c) Variable capacitors
d) Plastic capacitors
e) Ceramic capacitors
f) Mica capacitors
Factors affecting the capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor
1. Distance between the plates: – reducing separation increases capacitance but the plates should not be very close to avoid ionization which may lead to discharge.
2. Area of plate: – reduction of the effective area leads to reduction in capacitance.
3. Dielectric material between plates: – different materials will produce different capacitance effects.
Charging and discharging a capacitor
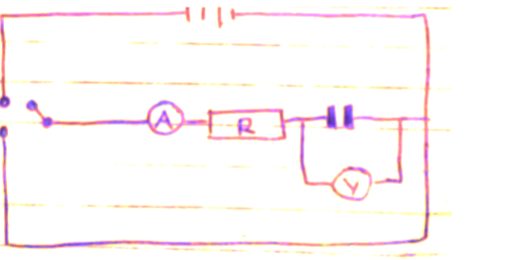
When the switch S1 is closed the capacitor charges through resistor R and discharges through the same resistor when switch S2 is closed.
Applications of capacitors
1. Variable capacitor: – used in tuning radios to enable it transmit in different frequencies.
2. Paper capacitors: – used in mains supply and high voltage installations.
3. Electrolytic capacitors: – used in transistor circuits where large capacitance values are required.
Other capacitors are used in reducing sparking as a car is ignited, smoothing rectified current and increasing efficiency in a. c. power transmission.
Example
A capacitor of two parallel plates separated by air has a capacitance of 15pF.
A potential difference of 24 volts is applied across the plates,
a) Determine the charge on the capacitors.
b) When the space is filled with mica, the capacitance increases to 250pF.
How much more charge can be put on the capacitor using a 24 V supply?
Solution
:
a) C= Q / V then Q = VC, hence Q = (1.5 × 10-12) × 24 = 3.6 × 10-10 Coul.
b) Mica C = 250pF, Q = (250 × 10-12) × 24 = 6 × 10-9 Coul.
Additional charge = (6 × 10-9) – (3.6 × 10-10) = 5.64 × 10-9 Coul.
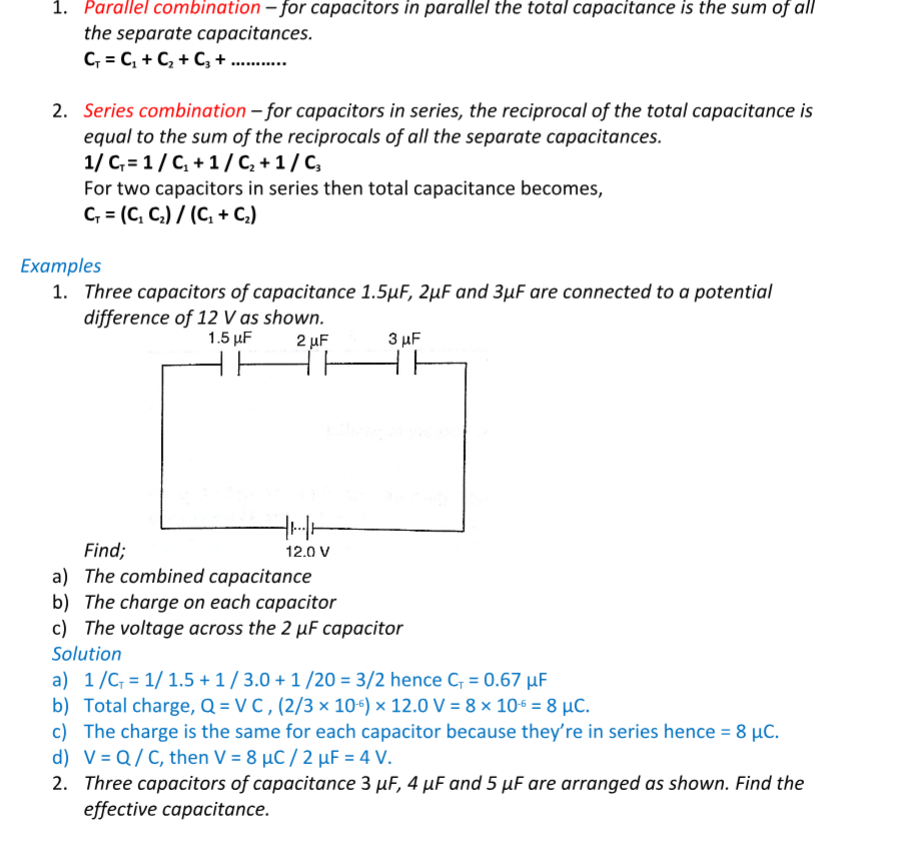
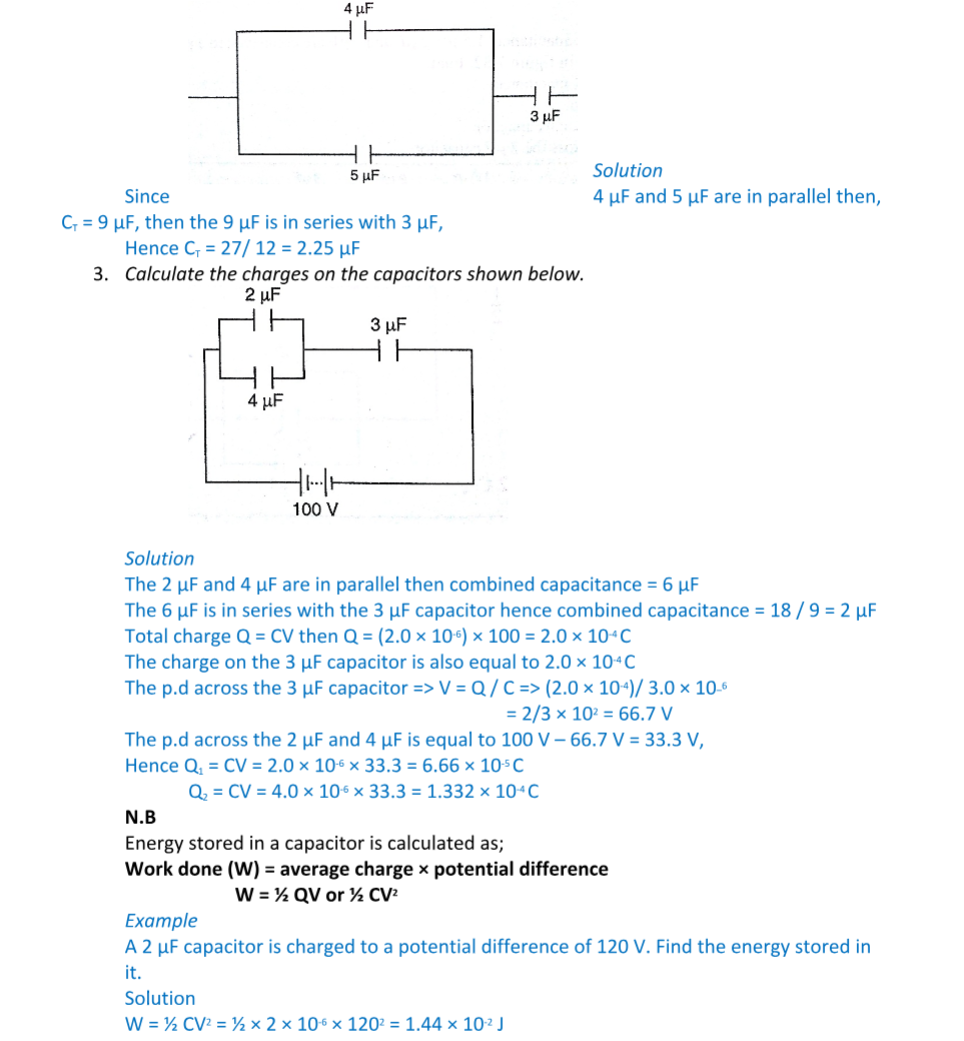
Capacitor combination
Chapter Eight
Heating Effect of an Electric Current
When current flows, electrical energy is transformed into other forms of energy i.e. light, mechanical and chemical changes.
Factors affecting electrical heating
Energy dissipated by current or work done as current flows depends on,
a) Current
b) Resistance
c) Time
This formula summarizes these factors as, E = I2 R t, E = I V t or E = V2 t / R
Examples
1. An iron box has a resistance coil of 30 Ω and takes a current of 10 A. Calculate the heat in kJ developed in 1 minute.
Solution
E = I2 R t = 102 × 30 × 60 = 18 × 104 = 180 kJ
2. A heating coil providing 3,600 J/min is required when the p.d across it is 24 V. Calculate the length of the wire making the coil given that its cross-sectional area is 1 × 10-7 m2 and resistivity 1 × 10-6 Ω m.
Solution
E = P t hence P = E / t = 3,600 / 60 = 60 W
P = V2 / R therefore R = (24 × 24)/ 60 = 9.6 Ω
R = ρ l/ A, l = (RA) / ρ = (9.6 × 1 × 10-7) / 1 × 10-6 = 0.96 m
Electrical energy and power
In summary, electrical power consumed by an electrical appliance is given by;
P = V I
P = I2 R
P = V2 / R
The SI unit for power is the watt (W)
1 W = 1 J/s and 1kW = 1,000 W.
Examples
1. What is the maximum number of 100 W bulbs which can be safely run from a 240 V source supplying a current of 5 A?
Solution
Let the maximum number of bulbs be ‘n’. Then 240 × 5 = 100 n
So ‘n’ = (240 × 5)/ 100 = 12 bulbs.
2. An electric light bulb has a filament of resistance 470 Ω.
The leads connecting the bulb to the 240 V mains have a total resistance of 10 Ω. Find the power dissipated in the bulb and in the leads.
Solution
Req = 470 + 10 = 480 Ω, therefore I = 240 / 480 = 0.5 A.
Hence power dissipated = I2 R = (0.5)2 × 470 = 117.5 W (bulb alone)
For the leads alone, R = 10 Ω and I = 0.5 A
Therefore power dissipated = (0.5)2 × 10 = 2.5 W.
Applications of heating of electrical current
1. Filament lamp – the filament is made up of tungsten, a metal with high melting point (3.400 0C). It is enclosed in aglass bulb with air removed and argon or nitrogen injected to avoid oxidation. This extends the life of the filament.
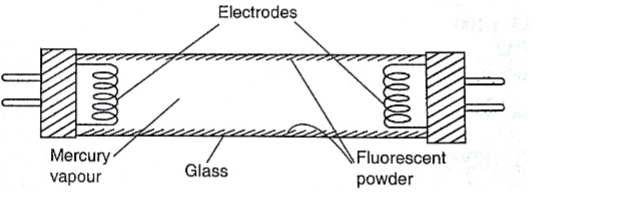
2. Fluorescent lamps – when the lamp is switched on, the mercury vapour emits ultra violet radiation making the powder in the tube fluoresce i.e. emit light. Different powders emit different colours.
3. Electrical heating – electrical fires, cookers e.tc. their elements are made up nichrome ( alloy of nickel and chromium) which is not oxidized easily when it turns red hot.
4. Fuse – this is a short length of wire of a material with low melting point (often thinned copper) which melts when current through it exceeds a certain value. They are used to avoid overloading.
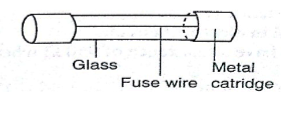
Chapter Nine
Quantity of Heat
Heat is a form of energy that flows from one body to another due to temperature differences between them.
Heat capacity
Heat capacity is defined as the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of a given mass of a substance by one degree Celsius or one Kelvin. It is denoted by ‘C’.
Heat capacity, C = heat absorbed, Q / temperature change θ.
The units of heat capacity are J / 0C or J / K.
Specific heat capacity.
S.H.C of a substance is the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1 0C or 1 K. It is denoted by ‘c’, hence,
c = Q / m θ where Q – quantity of heat, m – mass andθ – change in temperature.
The units for ‘c’ are J kg-1 K-1. Also Q = m c θ.
Examples
1. A block of metal of mass 1.5 kg which is suitably insulated is heated from 30 0C to 50 0C in 8 minutes and 20 seconds by an electric heater coil rated 54 watts.
Find;
a) The quantity of heat supplied by the heater
b) The heat capacity of the block
c) Its specific heat capacity
Solution
a) Quantity of heat = power × time = P t
= 54 × 500 = 27,000 J
b) Heat capacity, C = Q / θ = 27,000 / (50 – 30) = 1,350 J Kg-1 K-1
c) Specific heat capacity, c = C / m = 1,350 / 1.5 = 900 J Kg-1
2. If 300 g of paraffin is heated with an immersion heater rated 40 W, what is the temperature after 3 minutes if the initial temperature was 20 0C? (S.H.C for paraffin = 2,200 JK -1 K-1).
Solution
Energy = P t = m c θ = Q = quantity of heat.
P t = 40 × 180 = 7,200 J
m = 0.30 kg c = 2,200, θ = ..?
Q = m c θ, θ = Q / m c = 7,200 / (0.3 × 2,200) = 10.9 0C
3. A piece of copper of mass 60 g and specific heat capacity 390 J Kg-1 K-1 cools from 90 0C to 40 0C. Find the quantity of heat given out.
Solution
Q = m c θ, = 60 × 10-3 × 390 × 50 = 1,170 J.
Determination of specific heat capacity
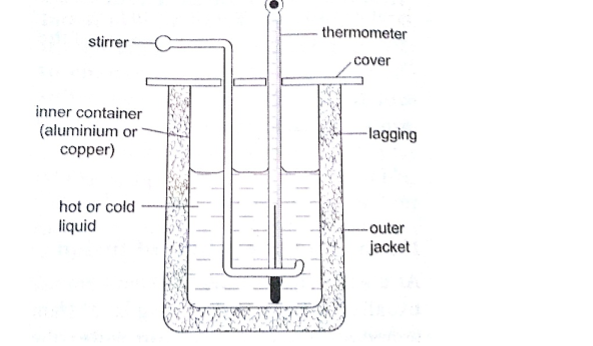
:
A calorimeter is used to determine the specific heat capacity of a substance.
This uses the principle of heat gained by a substance is equal to the heat lost by another substance in contact with each other until equilibrium is achieved.
Heat losses in calorimeter are controlled such that no losses occur or they are very minimal.
Examples
1. A 50 W heating coil is immersed in a liquid contained in an insulated flask of negligible heat capacity.
If the mass of the liquid is 10 g and its temperature increases by 10 0C in 2 minutes, find the specific heat capacity of the liquid.
Solution
Heat delivered (P t) = 50 × 2 × 60 = 2,400 J
Heat gained = 0.1 × c × 10 J
Therefore ‘c’ = 2,400 / 0.1 × 10 = 2,400 J Kg-1 K-1
2. A metal cylinder mass 0.5 kg is heated electrically.
If the voltmeter reads 15V, the ammeter 0.3A and the temperatures of the block rises from 20 0C to 85 0C in ten minutes.
Calculate the specific heat capacity of the metal cylinder.
Solution
Heat gained = heat lost, V I t = m c θ
15 × 3 × 10 × 60 = 0.5 × c × 65
c = (15 × 3 × 600)/ 0.5 × 65 = 831 J Kg-1 K-1
Fusion and latent heat of fusion
Fusion is the change of state from solid to liquid.
Change of state from liquid to solid is called solidification.
Latent heat of fusion is the heat energy absorbed or given out during fusion. Specific latent heat of fusion of a substance is the quantity of heat energy required to change completely 1 kg of a substance at its melting point into liquid without change in temperature.
It is represented by the symbol (L), we use the following formula,
Q = m Lf
Different substances have different latent heat of fusion.
Factors affecting the melting point
a) Pressure
b) Dissolved substances
Specific latent heat of vaporization is the quantity of heat required to change completely 1 kg of a liquid at its normal boiling point to vapour without changing its temperature.
Hence
Q = m Lv
The SI unit for specific latent heat of vaporization is J / Kg.
Example
An immersion heater rated 600 W is placed in water. After the water starts to boil, the heater is left on for 6 minutes.
It is found that the mass of the water had reduced by 0.10 kg in that time.
Estimate the specific heat of vaporization of steam.
Solution
Heat given out by the heater = P t = 600 × 6 × 60
Heat absorbed by steam = 0.10 × L v
Heat gained = heat lost, therefore, 600 × 6 × 60 = 0.10 × L v = 2.16 × 106 J / Kg
Evaporation
Factors affecting the rate of evaporation
a) Temperature
b) Surface area
c) Draught (hot and dry surrounding)
d) Humidity
Comparison between boiling and evaporation
Evaporation Boiling
1. Takes place at all temperature – takes place at a specific temperature
2. Takes place on the surface (no bubbles formed)- takes place throughout the liquid ( bubbles formed)
3. Decrease in atmospheric pressure increases the rate –decreases as atmospheric pressure lowers
Applications of cooling by evaporation
a) Sweating
b) Cooling of water in a porous pot
c) The refrigerator
Chapter Ten
The Gas Laws
Pressure law
This law states that “the pressure of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature if the volume is kept constant”. The comparison between Kelvin scale and degrees Celsius is given by; θ0 = (273 + θ) K, and T (K) = (T – 273) 0C.
Examples
1. A gas in a fixed volume container has a pressure of 1.6 × 105 Pa at a temperature of 27 0C.
What will be the pressure of the gas if the container is heated to a temperature of 2770C?
Solution
Since law applies for Kelvin scale, convert the temperature to kelvin
T1 = 270C = (273 + 27) K = 300 K
T2 = 2270C = (273 + 277) = 550 K
P1 / T1 = P2 / T2, therefore P2 = (1.6 × 105) × 550 / 300 = 2.93 × 105 Pa.
2. At 200C, the pressure of a gas is 50 cm of mercury. At what temperature would the pressure of the gas fall to 10 cm of mercury?
Solution
P / T = constant, P1 / T1 = P2 / T2, therefore T2= (293 × 10) / 50 = 58.6 K or (– 214.4 0C)
Charles law
Charles law states that “the volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (Kelvin) provided the pressure is kept constant”. Mathematically expressed as follows,
V1 / T1 = V2 / T2
Examples
1. A gas has a volume of 20 cm3 at 270C and normal atmospheric pressure.
Calculate the new volume of the gas if it is heated to 540C at the same pressure.
Solution
Using, V1 / T1 = V2 / T2, then V2 =(20 × 327) / 300 = 21.8 cm3.
2. 0.02m3 of a gas is at 27 0C is heated at a constant pressure until the volume is 0.03 m3. Calculate the final temperature of the gas in 0C.
Solution
Since V1 / T1 = V2 / T2, T2 = (300 × 0.03) / 0.02 = 450 K 0r 1770C
Boyle’s law
Boyle’s law states that “the pressure of a fixed mass of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume provided the temperature of the gas is kept constant”.
Mathematically expressed as,
P1 V1 = P2 V2
Examples
1. A gas in a cylinder occupies a volume of 465 ml when at a pressure equivalent to 725 mm of mercury. If the temperature is held constant, what will be the volume of the gas when the pressure on it is raised to 825 mm of mercury?
Solution
Using, P2 V1 = P2 V2, then V2 = (725 × 465) / 825 = 409 ml.
2. The volume of air 26 cm long is trapped by a mercury thread 5 cm long as shown below. When the tube is inverted, the air column becomes 30 cm long. What is the value of atmospheric pressure?
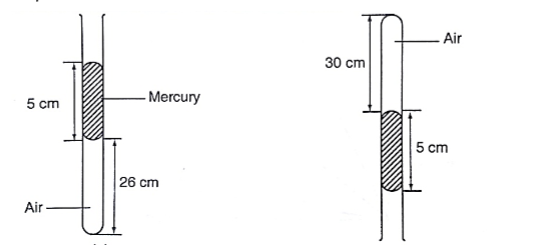
Solution
Before inversion, gas pressure = atm. Pressure + h p g
After inversion, gas pressure = atm. Pressure – h p g
From Boyle’s law, P1 V1 = P2 V2, then let the atm. Pressure be ‘x’,
So (x + 5) 0.26 = (x – 5) 0.30
0.26x + 1.30 = 0.3x – 1.5, x = 2.8/ 0.04 = 70 cm.
A general gas law
Any two of the three gas laws can be used derive a general gas law as follows,
P1 V1 / T1 = P2 V2 / T2 or
P V / T = constant – equation of state for an ideal gas.
Examples
1. A fixed mass of gas occupies 1.0 × 10-3 m3 at a pressure of 75 cmHg. What volume does the gas occupy at 17.0 0C if its pressure is 72 cm of mercury?
Solution
P V / T = constant so V1 = (76 × 1.0 × 10-3 × 290) / 273 ×72 = 1.12 × 10-3 m3
2. A mass of 1,200 cm3 of oxygen at 270C and a pressure 1.2 atmosphere is compressed until its volume is 600 cm3 and its pressure is 3.0 atmosphere. What is the Celsius temperature of the gas after compression?
Solution
Since P1 V1 / T1 = P2 V2 / T2, then T2 = (3 × 600 × 300) / 1.2 × 1,200 = 375 K or 102 0C.
KCSE Revision Notes Form 1 – Form 4 All Subjects
KCPE Results » List of National Schools in Kenya (Classified According to Clusters) » National Secondary Schools in Kenya » List of All Secondary Schools in Kenya Per County » Form 1 Intake – Selection Criteria, Selection List » KCSE Results » Secondary Schools in Kenya » KNEC – Kenya National Examinations Council
KCPE Results Performance » KNEC – Kenya National Examinations Council » KCSE Results
Secondary School Scholarships in Kenya » Kenya Postgraduate Scholarships » Undergraduate Scholarships for Kenyan Students » Kenya Scholarships for Kenyan Students Studying in Kenya » Kenya Undergraduate Scholarships » The Kenya Youth Education Scholarship Fund – Scholarships Kenya – Scholarships
KCSE Results » KCSE Results Top 100 Schools – Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education – KCSE » KCSE Top 100 Candidates » Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education – KCSE » KNEC – Kenya National Examinations Council » Secondary Schools in Kenya » KNEC – Kenya National Examinations Council » Free KNEC KCSE Past Papers
Kenya Scholarships for Undergraduate Students » Kenya Scholarships for Postgraduate Students » Undergraduate Scholarships for Kenyan Students » Kenya Undergraduate Scholarships » Full Undergraduate Scholarships for Kenyans » Kenya Postgraduate Scholarships » Scholarships & Grants » Undergraduate Scholarships » Universities in Kenya » Kenya Universities and Colleges Central Placement Service (KUCCPS) » Colleges in Kenya » KASNEB Registration & Results » Secondary Schools Scholarships in Kenya » Undergraduate & Graduate Scholarships for Kenyans
Powerful Motivational Quotes for Students » Success Quotes for Students » KCSE Motivational Quotes for KCSE Candidates » KCSE Success Quotes for KCSE Candidates
a a a physics notes!
chapter 1 introduction to physics
college physics notes
download klb physics book 4
download physics notes form 3
electronics form four notes
form 1 past papers
form 1 past papers with answers
form 1 physics notes
form 1 physics questions and answers
form 1 physics revision notes
form 1 physics syllabus
form 1 physics test paper pdf
form 2 physics exam paper
form 2 physics exam paper 2016
form 2 physics exam paper free download
form 2 physics exam paper with answer
form 2 physics final year exam paper 2
form 2 physics past papers
form 2 physics revision notes
form 2 physics short notes
form 2 physics syllabus
form 3 past papers
form 3 physics exam paper
form 3 physics notes
form 3 physics past papers
form 3 physics questions
form 3 physics questions and answers pdf
form 3 physics revision notes
form 3 physics syllabus
form 4 exam papers
form 4 physics notes
form 4 physics revision notes
form 4 physics syllabus
form 4 physics topics
form 5 physics topics
form five physics notes
form four physics notes
form four physics questions and answers
form four physics questions and answers pdf
form four physics topics
form four revision papers
form one exams
form one past papers
form one physics examination
form one physics past papers pdf
form one physics questions and answers
form one physics questions and answers pdf
form one physics topics
form one term one physics exam
form three physics notes
form three physics notes pdf
form three physics questions and answers
form three physics questions and answers pdf
form three physics topics
form two notes
form two physics notes
form two physics notes pdf
form two physics questions and answers
form two physics questions and answers pdf
form two physics syllabus
form two physics topics
high school physics notes
high school physics study guide
introduction of physics form one
introduction to physics notes
k.l.b physics notes
kcse physics notes
kcse physics syllabus
kenya secondary school physics syllabus pdf
klb physics book 1 pdf
klb physics book 2 pdf
klb physics book 3 pdf
klb physics book 3 pdf download
klb physics book 4 notes
klb physics book 4 pdf
klb physics book 4 pdf download
klb physics book 4 topics
klb physics form 1
klb physics form 1 pdf
klb physics form 2
klb physics form 2 notes
klb physics form 2 pdf
klb physics form 2 pdf download
klb physics form 3
klb physics form 3 pdf
klb physics form 3 pdf download
klb physics form 4
klb physics form 4 pdf
klb physics form four notes
klb physics form one notes
klb physics form three notes
klb physics form two notes
klb physics notes
klb physics notes form 4
klb physics pdf
maktaba tetea notes
necta form four past papers
necta past papers form 4 2016
necta past papers form six
necta past papers form two
necta physics past papers
necta physics practicals
necta questions and answers
necta review questions
notes za physics form one
notes za physics form three
past papers 2014
physic form 4 chapter 1 mind map
physic notes
physics book 4 pdf
physics exam form three
physics form 1 exams
physics form 1 mid year exam
physics form 1 past papers
physics form 1 pressure
physics form 1 questions and answers
physics form 1 questions and answers pdf
physics form 2 exam paper 2014
physics form 2 exams
physics form 2 notes
physics form 2 past papers
physics form 2 pdf
physics form 2 questions and answers
physics form 2 questions and answers pdf
physics form 3 exams
physics form 3 notes pdf
physics form 3 past papers
physics form 3 questions and answers
physics form 3 syllabus
physics form 4 chapter 1 conversion of units
physics form 4 chapter 1 exercise
physics form 4 chapter 1 exercise and answers
physics form 4 chapter 1 exercise pdf
physics form 4 chapter 1 mind map
physics form 4 chapter 2
physics form 4 chapter 2 exercise and answers
physics form 4 chapter 2 exercise pdf
physics form 4 chapter 2 experiment
physics form 4 chapter 2 formula
physics form 4 chapter 2 mind map
physics form 4 chapter 2 momentum
physics form 4 chapter 2 notes pdf
physics form 4 chapter 2 objective questions and answers
physics form 4 chapter 2 paper 2
physics form 4 chapter 2 slideshare
physics form 4 chapter 3
physics form 4 chapter 3 questions and answers
physics form 4 chapter 4 notes pdf
physics form 4 chapter 5 light questions and answers
physics form 4 chapter 5 notes pdf
physics form 4 exam paper 1
physics form 4 exams
physics form 4 exercise
physics form 4 exercise pdf
physics form 4 module with answer
physics form 4 notes chapter 1
physics form 4 notes free download
physics form 4 notes pdf
physics form 4 paper 2 questions and answers
physics form 4 past papers
physics form 4 questions and answers
physics form 4 revision notes
physics form 5 chapter 1 exercise and answers
physics form 5 chapter 1 notes pdf
physics form 5 chapter 2 notes pdf
physics form 5 chapter 2 slideshare
physics form 5 chapter 3 notes pdf
physics form 5 notes pdf
physics form four book
physics form four notes pdf
physics form four questions
physics form four study notes
physics form four topics
physics form one
physics form one book
physics form one notes
physics form one notes pdf
physics form one study notes
physics form three book
physics form three notes
physics form three study notes
physics form two book
physics form two notes
physics form two notes pdf
physics form two questions
physics form two study notes
physics form two topics
physics module form 5
physics notes
physics notes for class 11 pdf
physics notes for class 12 pdf
physics notes form 1 free download
physics notes igcse
physics notes pdf
physics simple notes
physics spm notes download
physics spm notes pdf
physics spm questions
physics study guide answers
physics study guide pdf
physics study guides
radioactivity form four
secondary physics notes pdf
spm notes
success physics spm pdf
tahossa past papers
1 a a kcse past papers
2014 kcse marking schemes
2016 kcse papers
2016 kcse prediction questions
2018 kcse exam
2018 kcse questions
a a kcse past papers
advance-africa.com kcse rev quiz
agriculture mock papers
agriculture paper 2 questions and answers pdf
alliance mocks 2017
ap biology essay questions and answers
arabic exam 2016
arabic oral exam questions
betrayal in the city essay questions and answers pdf
betrayal in the city essay questions with answers
betrayal in the city, ,,revision questions
biology book 3 klb
biology essay questions and answers form 4
biology essay questions and answers form 4 pdf
biology essays pdf
biology exam questions and answers pdf
biology form 2 questions and answers pdf
biology form 3 notes pdf
biology form 3 questions and answers pdf
biology form 3 syllabus
biology form three reproduction
biology form three-questions and answers
biology kcse – kcse biology questions and answers – kcse biology essay questions and answers – kcse biology paper 1 2015 – kcse biology notes – kcse 2015 biology paper 2 – kcse biology practical 2015 – kcse biology practicals – kcse biology 2011
biology kcse 2017
biology kcse questions
biology paper 1 questions and answers
biology paper 2 questions and answers
biology paper 3 questions and answers
biology questions and answers for high schools
biology questions and answers for high schools pdf
biology questions and answers form 2
biology questions and answers multiple choice
biology questions and answers on cells
biology questions and answers online
biology questions and answers pdf
biology revision notes form 3
business past kcse past papers
c.r.e form one notes pdf
cambridge igcse computer science
cambridge igcse computer science answers
cambridge igcse computer science coursebook pdf download
cambridge igcse computer science revision guide pdf
cambridge igcse computer science study and revision guide pdf
cambridge igcse computer science workbook – free download
cambridge igcse computer science workbook pdf
caucasian chalk circle essay questions
chemistry paper 1 questions and answers
chemistry paper 2 questions and answers
chemistry paper 3 question and answer
chemistry past papers form 1
chemistry past papers form 2
cie past papers
computer science 0478
computer science igcse past papers xtremepapers
computer science paper 2 2017
computer science past papers a level
computer science past papers o level
computer studies form 1 questions
computer studies form 3 past papers
computer studies past papers
computer studies questions and answers pdf
county mocks 2017
cre form 2 notes pdf
cre form 3 notes
cre form 3 notes pdf
cre form 4 notes
cre form 4 notes pdf
cre form one notes
cre kcse 2016
cre notes
cre notes form 2
cre notes pdf
cre paper 1 with answers
cre paper 2
cre paper 2 topics
cre preparation notes
cre questions form one
cre revision notes
cre revision questions and answers
download kcse past papers with answers
dvance kcse past papers
edexcel igcse computer science past papers
english paper 3 question paper – 2014 kcse
english paper 3 question paper – 2015 kcse
english paper 3 question paper – 2016 kcse
english paper 3 question paper – 2017 kcse
english paper 3 question paper – 2018 kcse
essay questions and answers on betrayal in the city
essay questions based on betrayal in the city
find download kcse past papers with answers – kcse past papers pdf download – kcse 2013 marking scheme – kcse mathematics past papers pdf – free kcse past papers and marking schemes – kcse mock papers pdf – kcse past papers 2014 pdf – kcse past papers 2015 – kcse past papers 2010
find kcse biology essay questions and answers – kcse biology practicals – kcse biology paper 1 2015 – biology essay questions and answers form 4 – kcse biology questions and answers – ap biology essay questions and answers – kcse biology notes – kcse biology paper 2 2012 – kcse biology paper 2 2015
form 2 biology questions and answers
free kcse mocks 2015
free kcse past papers – kcse past papers – knec kcse online past papers – knec kcse results past papers
free kcse past papers 2014
free kcse past papers kenya, free marking schemes, download …
free kcse past papers with answers
free kcse questions and answers on chemistry
free revision papers
general biology test questions and answers
general science questions and answers pdf
history and government paper one topics
history form one questions and answers pdf
history paper 1 questions and answers
history paper 2 questions and answers
home science past papers
igcse computer science book
igcse computer science book pdf download
igcse computer science notes
igcse computer science paper 2 notes
igcse computer science past papers
igcse computer science past papers 2014
igcse computer science past papers 2017
igcse computer science pdf
igcse computer science pre release material 2018
igcse computer science resources
igcse computer science revision notes pdf
igcse computer science workbook pdf
igcse computer studies past papers
interesting biology questions
ire kcse past papers
k.c.s.e cre paper 1 2017
k.c.s.e geography 2017
k.c.s.e mathematics paper 1 2017
k.c.s.e mocks 2018
k.c.s.e past papers 2014
kcpe 2018 predictions
kcpe prediction questions
kcse 2010 marking scheme
kcse 2010 past papers
kcse 2011 cre paper 1
kcse 2011 marking scheme
kcse 2012 history paper 2 marking scheme
kcse 2012 marking schemes
kcse 2013 cre paper 1
kcse 2013 marking scheme
kcse 2013 marking scheme pdf
kcse 2014
kcse 2015 biology paper 2
kcse 2015 biology paper 3
kcse 2015 marking scheme
kcse 2015 past papers
kcse 2016 agriculture paper 2
kcse 2016 biology paper 1
kcse 2016 biology paper 2
kcse 2016 computer paper 1
kcse 2017 marking scheme
kcse 2017 maths paper 1
kcse 2017 papers
kcse 2017 papers and marking scheme
kcse 2017 past papers
kcse 2017 prediction pdf
kcse 2018 cre prediction
kcse 2018 leakage
kcse 2018 marking scheme
kcse 2018 papers
kcse 2018 predictions
kcse 2019 marking scheme
kcse agriculture past papers
kcse answers
kcse arabic paper 1
kcse arabic paper 2
kcse arabic paper 3
kcse arabic paper 3 2016
kcse arabic past papers
kcse biology 2011
kcse biology essay questions and answers
kcse biology essay questions and answers – kcse revision questions and answers – kcse chemistry questions and answers – kcse revision papers with answers – kcse past papers with answers – download kcse past papers with answers – kcse questions on the river and the source – kcse revision notes
kcse biology essay questions and answers – kcse revision questions and answers – kcse chemistry questions and answers – kcse revision papers with answers – kcse past papers with answers – download kcse past papers with answers – kcse questions on the river and the source – kcse revision notes
kcse biology essay questions and answers pdf
kcse biology essays
kcse biology essays pdf
kcse biology notes
kcse biology paper 1
kcse biology paper 1 2017
kcse biology paper 1 2017 pdf
kcse biology paper 2 2012
kcse biology paper 2 2015
kcse biology paper 2 2017
kcse biology paper 3 2016
kcse biology paper 3 past papers
kcse biology past papers
kcse biology past papers and answers
kcse biology practical 2016
kcse biology practical past papers
kcse biology practicals
kcse biology questions and answers
kcse biology questions and answers – kcse past papers biology – kcse biology essay questions and answers – kcse chemistry past papers – download kcse past papers with answers – k.c.s.e papers 2015 – k.c.s.e papers 2016 – kcse biology paper 1 2015 – kcse past papers 2015 – kcse past papers 2011 – kcse past papers 2016 – kcse past papers 2017 – 2017 kcse prediction questions – 2018 kcse prediction questions
kcse business paper 1 2016
kcse business past papers
kcse business studies past papers
kcse chemistry paper 1 2016
kcse chemistry paper 1 2017
kcse chemistry paper 3 2012
kcse chemistry past papers
kcse chemistry past papers and answers
kcse chemistry practical
kcse computer studies paper 1
kcse computer studies paper 2
kcse computer studies paper 2 pdf
kcse cre 2016
kcse cre paper 1 2013
kcse cre paper 1 2015
kcse cre paper 1 2016
kcse cre paper 1 2017
kcse cre paper 2
kcse cre paper 2 2016
kcse cre past papers
kcse cre past papers and answers
kcse english paper 3 2016
kcse english paper 3 2017
kcse essay questions in betrayal in the city
kcse exam papers 2018
kcse exam papers answers
kcse french paper 1
kcse french paper 2
kcse french past papers
kcse general science syllabus
kcse geography paper 2 2016
kcse history paper 1 2012
kcse history paper 2 2016
kcse history paper 2 2017
kcse kiswahili paper 1 2017
kcse marking scheme 2016
kcse marking schemes
kcse marking schemes 2017
kcse marking schemes pdf
kcse mathematics marking schemes
kcse mathematics paper 1 2015
kcse mathematics paper 1 2016
kcse mathematics paper 2 2016
kcse mathematics past papers
kcse mathematics past papers pdf
kcse mock exams
kcse mock papers 2015
kcse mock papers 2017
kcse mock papers 2018
kcse mock papers pdf
kcse mock papers pdf 2018
kcse mocks 2017
kcse mocks 2018
kcse music past papers
kcse online past papers
kcse papers 2015
kcse past papers
kcse past papers – kcpe and answers – free mocks online – kcse answers past exams question papers – downloads | kcse papers and marking schemes | exams – kcse mathematics paper 1 questions and answers – kcse cre paper 1 questions and answers – knec past papers free downloads – kcse online registration – kcpe – kcse past papers – knec – knec portal – knec past papers for colleges – kasneb – past papers – kasneb past papers for colleges – cpa past papers – https://www.knec.ac.ke/ – www.knec-portal.ac.ke/ – knec portal: kcse results, online registration, kcse result slip. knec portal confirmation – knec portal kcse results – knec examiners portal – knec website
kcse past papers – kcpe and answers – free mocks online – kcse answers past exams question papers – downloads | kcse papers and marking schemes | exams – kcse mathematics paper 1 questions and answers – kcse cre paper 1 questions and answers
kcse past papers 2007
kcse past papers 2009
kcse past papers 2010
kcse past papers 2011
kcse past papers 2011 pdf
kcse past papers 2012
kcse past papers 2013
kcse past papers 2013 -knec
kcse past papers 2014
kcse past papers 2014 pdf
kcse past papers 2015
kcse past papers 2015 marking schemes
kcse past papers 2015 pdf
kcse past papers 2016
kcse past papers 2016 pdf
kcse past papers 2017
kcse past papers 2017 pdf
kcse past papers agriculture and answers
kcse past papers arabic and answers
kcse past papers art and design and answers
kcse past papers biology
kcse past papers building and construction and answers
kcse past papers business studies and answers
kcse past papers chemistry
kcse past papers chemistry and answers
kcse past papers chemistry pdf
kcse past papers computer studies and answers
kcse past papers cre and answers
kcse past papers electricity and answers
kcse past papers english and answers
kcse past papers french and answers
kcse past papers general science and answers
kcse past papers geography and answers
kcse past papers german and answers
kcse past papers history and government and answers
kcse past papers home science and answers
kcse past papers hre and answers
kcse past papers ire and answers
kcse past papers kenya sign language and answers
kcse past papers kiswahili and answers
kcse past papers marking scheme
kcse past papers maths
kcse past papers metal work and answers
kcse past papers music and answers
kcse past papers pdf download
kcse past papers physics and answers
kcse past papers physics with answers
kcse past papers power mechanics and answers
kcse past papers with answers
kcse past papers woodwork and answers
kcse physics past papers
kcse prediction 2017
kcse prediction 2018
kcse prediction 2018 pdf
kcse prediction papers 2018
kcse prediction questions 2018
kcse prediction questions and answers
kcse questions and answers
kcse questions and answers. download free kcse past papers from knec. all marking schemes – questions and answers are sourced from knec.
kcse revision
kcse revision papers 2014
kcse revision | secondary school | text books | text book centre
kcse trial 2017
kcse trial exams 2017
kenyaplex kcse past papers
kenyaplex past papers for secondary
kiswahili paper 3 questions and answers
klb biology form 3 pdf
klb cre form 1
klb cre form 3
knec ict past papers
knec past papers for colleges
knec past papers free download
knec past papers pdf
knec revision papers
knec technical exams past papers
kusoma.com past papers
maths kcse 2017
mock past papers 2017
mock past papers with answers
mokasa mock 2017
page navigation
papacambridge computer science igcse
past kcse papers
past papers in kenya
pre mocks 2018
pte knec past papers
revision
sample essays on betrayal in the city
school biology notes
school geography notes
school physics notes
school river and the source
themes used in betrayal in the city
xtremepapers igcse computer science
z notes computer science igcse
Physics Notes Form 3
“Pdf” Revision Questions Physics Form 1
“Pdf” Revision Questions Physics Form 2
“Pdf” Revision Questions Physics Form 3
“Pdf” Revision Questions Physics Form 4
“Pdf” Revision Questions Physics Form Four
“Pdf” Revision Questions Physics Form One
“Pdf” Revision Questions Physics Form Three
“Pdf” Revision Questions Physics Form Two
1 a a KCSE Past Papers
10th Grade Physics Questions and Answers
10th Grade Physics Test
11th Ncert Physics
12th Class Physics Book Free Download
2014 KCSE Marking Schemes
2014 Pdf KCSE Past Papers 2015
2015 Physics Essay Questions and Answers Form 4
2016 KCSE Papers
2016 KCSE Prediction Questions
2017 Physics Hsc Answers
2017 KCSE Prediction Questions
2018 Physics KCSE Leakage
2018 Physics KCSE Questions
2018 KCSE Busineness Studies
2018 KCSE Exam
2018 KCSE Leakage
2018 KCSE Prediction Questions
2018 KCSE Questions
2019 Physics KCSE Leakage
2019 Physics KCSE Questions
2019 KCSE Leakage
2019 KCSE Questions
9th Grade Physics Study Guide
A a a Physics Notes
a a a Physics Notes!
a a a PhysicsNotes!
A a KCSE Past Papers
A Biblical View of Social Justice
A Level Physics Biological Molecules Questions
A Level Physics Exam Questions by Topic
A Level Physics Notes Edexcel
A Level Physics Notes Xtremepapers
A Level Physics Past Papers
A Level Physics Questions and Answers
a Level Physics Questions and Answers
A Level Physics Questions and Answers (Pdf)
A Level Physics Questions and Answers Pdf
A Level Physics Questions by Topic Kidney Questions With Markschemes
A Level Physics Revision
A Level Physics Revision Edexcel
A Level Physics Revision Guide
A Level Physics Revision Notes
A Level Physics Revision Notes Pdf
A Level Physics Textbook Pdf
A Level Physics Year 1 / as Aqa Exam Questions by Topic
A Level Edexcel Notes a* Physics
aa Physics Form 3 Questions and Answers
Advance KCSE Past Papers
Advance-africa.com KCSE Rev Quiz
Advantages and Disadvantages.
All Physics Essays
All Physics Notes for Senior Two
All KCSE Past Papers Physics With Making Schemes
All Marking Schemes Questions and Answers
All Past K.c.s.e Questions With Answers
Alliance Mocks 2017
Ap Bio Quizzes
Ap Physics 1 Textbook Pdf
Ap Physics Essay Questions and Answers
Are Sourced From KNEC.
As Level Physics Notes
Atika Physics Notes
Atika School Physics Notes
B/s Book 2 Notes
Basic Physics Books Pdf
basic Physics Interview Questions and Answers Pdf
Basic Physics Interview Questions and Answers Pdf
Basic Physics Pdf
Basic Physics Questions and Answers
Basic Physics Questions and Answers Pdf
Bbc Bitesize Physics Ks3
Bihar Board Physics Objective Answer 2017
Bihar Board Physics Objective Answer 2018
Bio Answers
Bio Quesions
Physics 0478
Physics 101
Physics 12th
Physics 12th Class Notes Pdf
Physics 2019 Syllabus
Physics All KCSE Short Notes
Physics Answers
Physics Answers Online Free
Physics Answers Quizlet
Physics Bk 2 Notes
Physics Book 1
Physics Book 1 Notes
Physics Book 2
Physics Book 2 Notes
Physics Book 3
Physics Book 3 KLB
Physics Book 3 Notes
Physics Book 4
Physics Book 4 Notes
Physics Book 4 Pdf
Physics Book for Class 11
Physics Book Four
Physics Book Four Notes
Physics Book One
Physics Book One Notes
Physics Book Pdf Free Download
Physics Book Three
Physics Book Three Notes
Physics Book Three Pdf
Physics Book Two
Physics Book Two Notes
Physics Books Form Three
Physics Bowl Physics Study Guide
Physics Bowl Questions Physics
Physics Bowl Questions Earth Physics
Physics Bowl Questions Math
Physics Bowl Questions Middle School
Physics Brekthrough Form Two Notes
Physics Class 12 Ncert Solutions
Physics Class 12 Pdf
Physics Communication Syllabus
Physics Diagram Software
Physics Diagrams for Class 11
Physics Diagrams for Class 12
Physics Diagrams for Class 9
Physics Diagrams for Class-10
Physics Diagrams in Form 1
Physics Diagrams in Form 2
Physics Diagrams in Form 3
Physics Diagrams in Form 4
Physics Diagrams Pdf
Physics Diagrams to Label
Physics Essay Questions and Answers
Physics Essay Questions and Answers 2018
Physics Essay Questions and Answers Form 1
Physics Essay Questions and Answers Form 2
Physics Essay Questions and Answers Form 3
Physics Essay Questions and Answers Form 4
Physics Essay Questions and Answers Form 4 Pdf
Physics Essay Questions and Answers Pdf
Physics Essay Revision Q
Physics Essays and Answers
Physics Essays Form One to Form Four
Physics Essays Form One to Form Three
Physics Essays KCSE
Physics Essays Pdf
Physics Exam 1 Multiple Choice
Physics Exam 2 Advance
Physics Exam 2 Test
Physics Exam 2016
Physics Exam Form Four
Physics Exam Form One
Physics Exam Form Three
Physics Exam Form Two
Physics Exam Practice Test
Physics Exam Questions
Physics Exam Questions and Answers
Physics Exam Questions and Answers Pdf
Physics Exam Study Guide
Physics Exams
Physics Excretion Notes
Physics Exercise Form 4 With Answers
Physics Final Exam Answer Key
Physics Final Exam Answer Key 2016
Physics Final Exam Answer Key 2017
Physics Final Exam Answers 2018
Physics Final Exam Answers 2019
Physics Final Exam Questions and Answers
Physics Fom 1 Notes
Physics Fom 2 Notes
Physics Fom 3 Notes
Physics Fom 4 Notes
Physics Form 1
Physics Form 1 & 2 and Answers
Physics Form 1 and 2 Essays
Physics Form 1 and 2 Essays Questions and Answers
Physics Form 1 Chapter 1
Physics Form 1 Diagrams
Physics Form 1 Exams
Physics Form 1 Mid Year Exam
Physics Form 1 Notes
Physics Form 1 Notes and Questions
Physics Form 1 Notes Download
Physics Form 1 Notes Free Download
Physics Form 1 Notes GCSE
Physics Form 1 Notes KCSE-kcse
Physics Form 1 Notes Pdf
Physics Form 1 Notes Pdf Download
Physics Form 1 Past Papers
Physics Form 1 Pdf
Physics Form 1 Pressure
Physics Form 1 Question Papers
Physics Form 1 Questions
Physics Form 1 Questions and Answers
Physics Form 1 Questions and Answers Pdf
Physics Form 1 Quiz
Physics Form 1 Revision Questions
Physics Form 1 Summary Notes
Physics Form 1 Syllabus
Physics Form 1 Work
Physics Form 1-4 Notes
Physics Form 2
Physics Form 2 Chapter 1
Physics Form 2 Chapter 2
Physics Form 2 Diagrams
Physics Form 2 Exam Paper 2014
Physics Form 2 Exams
Physics Form 2 Notes
Physics Form 2 Notes and Questions
Physics Form 2 Notes GCSE
Physics Form 2 Notes KCSE-kcse
Physics Form 2 Notes Pdf
Physics Form 2 Notes Pdf Download
Physics Form 2 Past Papers
Physics Form 2 Pdf
Physics Form 2 Question Papers
Physics Form 2 Questions
Physics Form 2 Questions and Answers
Physics Form 2 Questions and Answers Pdf
Physics Form 2 Quiz
Physics Form 2 Revision Notes
Physics Form 2 Salts
Physics Form 2 Structure and Bonding
Physics Form 2 Summary Notes
Physics Form 2 Syllabus
Physics Form 2 Work
Physics Form 3
Physics Form 3 and 4 Essays
Physics Form 3 and 4 Essays Questions and Answers
Physics Form 3 Chapter 3
Physics Form 3 Classification
Physics Form 3 Diagrams
Physics Form 3 Ecology
Physics Form 3 Exams
Physics Form 3 Notes
Physics Form 3 Notes and Questions
Physics Form 3 Notes GCSE
Physics Form 3 Notes KCSE-kcse
Physics Form 3 Notes Pdf
Physics Form 3 Notes Pdf Download
Physics Form 3 Notes Topic 1
Physics Form 3 Past Papers
Physics Form 3 Pdf
Physics Form 3 Question Papers
Physics Form 3 Questions
Physics Form 3 Questions and Answers
Physics Form 3 Questions and Answers Pdf
Physics Form 3 Questions and Answers Term 3
Physics Form 3 Questions and Answers+pdf
Physics Form 3 Quiz
Physics Form 3 Revision Notes
Physics Form 3 Revision Questions
Physics Form 3 Summary Notes
Physics Form 3 Syllabus
Physics Form 3 Syllabus Pdf
Physics Form 3 Topics
Physics Form 3 Work
Physics Form 4
Physics Form 4 All Chapter
Physics Form 4 Chapter 1 Conversion of Units
Physics Form 4 Chapter 1 Exercise
Physics Form 4 Chapter 1 Exercise and Answers
Physics Form 4 Chapter 1 Exercise Pdf
Physics Form 4 Chapter 1 Mind Map
Physics Form 4 Chapter 2
Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 Exercise and Answers
Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 Exercise Pdf
Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 Experiment
Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 Formula
Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 Mind Map
Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 Momentum
Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 Notes Pdf
Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 Objective Questions and Answers
Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 Paper 2
Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 Slideshare
Physics Form 4 Chapter 3
Physics Form 4 Chapter 3 Questions and Answers
Physics Form 4 Chapter 4
Physics Form 4 Chapter 4 Notes Pdf
Physics Form 4 Chapter 5 Light Questions and Answers
Physics Form 4 Chapter 5 Notes Pdf
Physics Form 4 Diagrams
Physics Form 4 Exam Paper 1
Physics Form 4 Exams
Physics Form 4 Exercise
Physics Form 4 Exercise Pdf
Physics Form 4 Module With Answer
Physics Form 4 Note
Physics Form 4 Notes
Physics Form 4 Notes (Pdf)
Physics Form 4 Notes All Chapter Pdf
Physics Form 4 Notes and Questions
Physics Form 4 Notes Chapter 1
Physics Form 4 Notes Chapter 2
Physics Form 4 Notes Chapter 3
Physics Form 4 Notes Download
Physics Form 4 Notes Free Download
Physics Form 4 Notes GCSE
Physics Form 4 Notes KCSE-kcse
Physics Form 4 Notes Pdf
Physics Form 4 Notes Pdf Download
Physics Form 4 Paper 2 Questions and Answers
Physics Form 4 Past Papers
Physics Form 4 Question Papers
Physics Form 4 Questions
Physics Form 4 Questions and Answers
Physics Form 4 Questions and Answers Pdf
Physics Form 4 Quiz
Physics Form 4 Revision Notes
Physics Form 4 Schemes of Work
Physics Form 4 Summary Notes
Physics Form 4 Syllabus
Physics Form 4 Textbook Pdf
Physics Form 4 Work
Physics Form 5 Chapter 1 Exercise and Answers
Physics Form 5 Chapter 1 Notes Pdf
Physics Form 5 Chapter 2 Notes Pdf
Physics Form 5 Chapter 2 Slideshare
Physics Form 5 Chapter 3 Notes Pdf
Physics Form 5 Notes Pdf
Physics Form Four Book
Physics Form Four Notes
Physics Form Four Notes and Questions
Physics Form Four Notes GCSE
Physics Form Four Notes Pdf
Physics Form Four Past Papers
Physics Form Four Questions
Physics Form Four Questions and Answers
Physics Form Four Questions and Answers Pdf
Physics Form Four Quiz
Physics Form Four Study Notes
Physics Form Four Syllabus
Physics Form Four Topic 2
Physics Form Four Topic 4
Physics Form Four Topics
Physics Form Four Work
Physics Form One
Physics Form One Book
Physics Form One Book Pdf
Physics Form One Download Topic 1 Upto 3
Physics Form One Exam
Physics Form One Notes
Physics Form One Notes and Questions
Physics Form One Notes GCSE
Physics Form One Notes Pdf
Physics Form One Pdf
Physics Form One Questions
Physics Form One Questions and Answers
Physics Form One Questions and Answers Pdf
Physics Form One Questions and Their Answers
Physics Form One Quiz
Physics Form One Revision Question
Physics Form One Schemes of Work
Physics Form One Study Notes
Physics Form One Syllabus
Physics Form One Term Three Test
Physics Form One to Three Notes
Physics Form One Work
Physics Form Three
Physics Form Three Book
Physics Form Three Notes
Physics Form Three Notes and Questions
Physics Form Three Notes GCSE
Physics Form Three Questions and Answers
Physics Form Three Questions and Answers Pdf
Physics Form Three Quiz
Physics Form Three Reproduction
Physics Form Three Reproduction.
Physics Form Three Study Notes
Physics Form Three Work
Physics Form Three-questions and Answers
Physics Form Two
Physics Form Two Book
Physics Form Two Diagrams
Physics Form Two Notes
Physics Form Two Notes and Questions
Physics Form Two Notes GCSE
Physics Form Two Notes Pdf
Physics Form Two Notes-pdf
Physics Form Two Pdf
Physics Form Two Questions
Physics Form Two Questions and Answers
Physics Form Two Questions and Answers Pdf
Physics Form Two Quiz
Physics Form Two Study Notes
Physics Form Two Topics
Physics Form Two Work
Physics Form Two,schemes of Work
Physics Form2
Physics Form2 Textbook
Physics Game Form Four Question End Answers
Physics Grade 10 Exam Papers
Physics Hsc Pdf
Physics Human Reproduction Video
Physics IGCSE Past Papers Xtremepapers
Physics K.c.s.e 2017
Physics KCSE
Physics KCSE 2016
Physics KCSE 2017
Physics KCSE 2017 Paper 1
Physics KCSE Past Papers
Physics KCSE Questions
Physics KCSE Questions and Answer
Physics KCSE Quizzes & Answers
Physics KCSE Revision
Physics KCSE Revision Notes
Physics KCSE Setting Questions Form One and Two
Physics Ksce 2015
Physics Last Year K.c.s.e Questions
Physics Lesson Plan Form Two
Physics Made Familiar
Physics Mcq for Class 11
Physics Mcq for Class 12
Physics Mcq for Competitive Exams
Physics Mcq for Competitive Exams Pdf
Physics Mcq for Neet Pdf
Physics Mcq for Ssc
Physics Mcq Questions With Answers
Physics Mcq With Answers Pdf
Physics Mcqs for Class 12 Pdf
Physics Mcqs With Answers Pdf
Physics Mid Familia Form One
Physics Mock Papers
Physics Module Form 5
Physics Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Cxc
Physics Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Pdf
Physics Multiple Choice Questions With Answers Pdf
Physics Note
Physics Note Form Two All Chapters
Physics Notes
Physics Notes and Guestion and Answear
Physics Notes and Syllabus
Physics Notes Class 10
Physics Notes for Class 11 Pdf
Physics Notes for Class 12 Pdf
Physics Notes for High School Students
Physics Notes for IGCSE 2014
Physics Notes Form 1
Physics Notes Form 1 4
Physics Notes Form 1 Free Download
Physics Notes Form 1 KLB
Physics Notes Form 1 Pdf
Physics Notes Form 1-4
Physics Notes Form 1-4(1) Physics
Physics Notes Form 14
Physics Notes Form 2
Physics Notes Form 2 KLB
Physics Notes Form 2 Pdf
Physics Notes Form 2; Physics Notes
Physics Notes Form 3
Physics Notes Form 3 KLB
Physics Notes Form 3 Pdf
Physics Notes Form 4
Physics Notes Form 4 Chapter 2
Physics Notes Form 4 KLB
Physics Notes Form 4 Pdf
Physics Notes Form 4-pdf
Physics Notes Form Four
Physics Notes Form Four KLB
Physics Notes Form Four Pdf
Physics Notes Form One
Physics Notes Form One KLB
Physics Notes Form One Pdf
Physics Notes Form One to Form Four
Physics Notes Form Three
Physics Notes Form Three KLB
Physics Notes Form Three Pdf
Physics Notes Form Two
Physics Notes Form Two KLB
Physics Notes Form Two Pdf
Physics Notes Form2
Physics Notes IGCSE
Physics Notes Kenya
Physics Notes on Agroforestry
Physics Notes Pdf
Physics Notes:
Physics Objective Answer
Physics Objective Answer 2018
Physics Objective Questions for Competitive Exams
Physics Objective Questions for Competitive Exams Pdf
Physics Oral Exam Questions
Physics Paper 1
Physics Paper 1 2018 Marking Rules
Physics Paper 1 Notes
Physics Paper 1 Questions
Physics Paper 1 Questions and Answers
Physics Paper 1 Topics
Physics Paper 1 With Answers
Physics Paper 2
Physics Paper 2 2017
Physics Paper 2 2018 Marking Rules
Physics Paper 2 Questions and Answers
Physics Paper 2 Questions and Answers Pdf
Physics Paper 2 Revision
Physics Paper 2 Topics
Physics Paper 2018
Physics Paper 3 2018 Marking Rules
Physics Paper 3 Question and Answer
Physics Paper 3 Question Paper 2014 KCSE
Physics Paper 3 Question Paper 2015 KCSE
Physics Paper 3 Question Paper 2016 KCSE
Physics Paper 3 Question Paper 2017 KCSE
Physics Paper 3 Question Paper 2018 KCSE
Physics Paper 3 Questions and Answers
Physics Paper One Questions and Answers
Physics Paper One Topics
Physics Paper Two Qestions With Answers
Physics Paper1
Physics Paper2
Physics Paper3
Physics Paper4
Physics Past Papers
Physics Past Papers 2017
Physics Past Papers a Level
Physics Past Papers Form 1
Physics Past Papers Form 2
Physics Past Papers Form 3
Physics Past Papers O Level
Physics Pdf Download
Physics Pp1 KCSE 2016
Physics Practical Book Class 12 Pdf
Physics Practical Exam
Physics Practicals Form One
Physics Practicals Questions and Answers
Physics Practice Test 9th Grade
Physics Practice Test Answers
Physics Practice Test Questions and Answers
Physics Practice Test Quizlet
Physics Predicted Questions This Year KCSE
Physics Preparation Notes
Physics Pretest High School Pdf
Physics Question and Answer With Explanation
Physics Question and Answers 2019
Physics Question and Answers 2020
Physics Question and Answers 2021
Physics Question and Answers 2022
Physics Question and Answers Note
Physics Questions
Physics Questions and Answers
Physics Questions and Answers for High School
Physics Questions and Answers for High Schools
Physics Questions and Answers for High Schools Pdf
Physics Questions and Answers for Secondary Schools
Physics Questions and Answers Form 1
Physics Questions and Answers Form 2
Physics Questions and Answers Form 3
Physics Questions and Answers Form 4
Physics Questions and Answers Multiple Choice
Physics Questions and Answers Notes
Physics Questions and Answers O
Physics Questions and Answers Online
Physics Questions and Answers Pdf
Physics Questions and Answers Pdf for Class 12
Physics Questions and Answers Pdf for Competitive Exams
Physics Questions and Answers-form 2
Physics Questions for High School
Physics Questions for High School Students With Answers
Physics Questions for Senior 1
Physics Questions for Senior 2
Physics Questions for Senior 3
Physics Questions for Senior 4
Physics Questions for Senior 5
Physics Questions for Senior 6
Physics Questions for Senior Five
Physics Questions for Senior Four
Physics Questions for Senior One
Physics Questions for Senior Six
Physics Questions for Senior Three
Physics Questions for Senior Two
Physics Questions Form One
Physics Questions Multiple Choice
Physics Questions Quizlet
Physics Questions to Ask Your Teacher
Physics Quetion and Answer Form Four
Physics Quetion and Answer Form One
Physics Quetion and Answer Form Three
Physics Quetion and Answer Form Two
Physics Quiz for Class 9
Physics Quiz for Class 9 Physics
Physics Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10
Physics Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 10 Pdf
Physics Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 12
Physics Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 9
Physics Quiz Questions and Answers for Class 9 Pdf
Physics Quiz Questions and Answers for High School
Physics Quiz Questions and Answers Multiple Choice
Physics Quiz Questions and Answers Pdf
Physics Quiz Questions for Class 12
Physics Quiz Questions for College Students
Physics Quiz With Answers
Physics Quiz With Answers Pdf
Physics Quizlet
Physics Revision
Physics Revision a Level
Physics Revision Physics Notes Physics
Physics Revision Exam
Physics Revision Examination
Physics Revision Form One
Physics Revision Notes
Physics Revision Notes Physics
Physics Revision Notes Form 1
Physics Revision Notes Form 2
Physics Revision Notes Form 3
Physics Revision Notes Form 4
Physics Revision Notes IGCSE
Physics Revision Paper One
Physics Revision Questions
Physics Revision Questions and Answers
Physics Revision Questions and Answers Form 1
Physics Revision Questions and Answers Form 2
Physics Revision Questions and Answers Form 3
Physics Revision Questions and Answers Form 4
Physics Revision Questions and Answers Form Four
Physics Revision Questions and Answers Form One
Physics Revision Questions and Answers Form Three
Physics Revision Questions and Answers Form Two
Physics Revision Questions Form 1
Physics Revision Questions Form 2
Physics Revision Questions Form 3
Physics Revision Questions Form 4
Physics Revision Questions Form Four
Physics Revision Questions Form One
Physics Revision Questions Form Three
Physics Revision Questions Form Two
Physics Revision Quiz
Physics Revision Test
Physics Secondary School Revision
Physics Simple Notes
Physics Spm Notes Download
Physics Spm Notes Pdf
Physics Spm Questions
Physics Study Form 2
Physics Study Guide
Physics Study Guide Answer Key
Physics Study Guide Answers
Physics Study Guide Physics Questions and Answers
Physics Study Guide Ib
Physics Study Guide Pdf
Physics Study Guides
Physics Study Notes
Physics Study Notes Materials Form 1 Pdf
Physics Study Notes Materials Form 2 3 Pdf
Physics Study Notes Materials Form 2 Pdf
Physics Study Notes Materials Form 3 Pdf
Physics Study Notes Materials Form 4 Pdf
Physics Syllabus in Kenya
Physics Syllabus Pdf
Physics Test 1 Quizlet
Physics Test Questions
Physics Test Questions and Answers
Physics Test Questions and Answers Pdf
Physics Topic One Form Four
Physics Topics Form One
Physics Unit 1 Quiz
Physics Vol 3
Physics | Revision Physics
Physics,form 4
Physics.form Four.topic Three
PhysicsExam Form Three
PhysicsModule Form 5
PhysicsNotes
PhysicsNotes for Class 11 Pdf
PhysicsNotes for Class 12 Pdf
PhysicsNotes Form 1
PhysicsNotes Form 1 Free Download
PhysicsNotes Form 2
PhysicsNotes Form 3
PhysicsNotes Form 3 Pdf
PhysicsNotes IGCSE
PhysicsNotes Pdf
PhysicsPast Papers
PhysicsQuestions and Answers Pdf
PhysicsSimple Notes
PhysicsSpm Notes Download
PhysicsSpm Notes Pdf
PhysicsSpm Questions
PhysicsStudy Guide Answers
PhysicsStudy Guide Pdf
PhysicsStudy Guides
Blologytextpapers
Bridge Physics
Business Past KCSE Past Papers
Physics Form 3 Notes Pdf
Physics Form 4 Notes Pdf
C R E Form One KLB
C R E Form One Oli Topic
C.r.e Form 1 Notes Kenya
C.r.e Form 2 Notes Kenya
C.r.e Form 3 Notes
C.r.e Form 3 Notes Kenya
C.r.e Form 3 Pdf
C.r.e Form 4 Notes Kenya
C.r.e Form One Notes Pdf
C.r.e Notes Form 1
C.r.e Revision Notes
C.r.e Short Notes
Cambridge IGCSE Physics
Cambridge IGCSE Physics 3rd Edition
Cambridge IGCSE Physics 3rd Edition Plus Cd South Asia Edition
Cambridge IGCSE Physics Answers
Cambridge IGCSE Physics Coursebook Pdf Download
Cambridge IGCSE Physics Practical Workbook
Cambridge IGCSE Physics Revision Guide Pdf
Cambridge IGCSE Physics Study and Revision Guide 2nd Edition Pdf
Cambridge IGCSE Physics Study and Revision Guide Pdf
Cambridge IGCSE Physics Workbook Free Download
Cambridge IGCSE Physics Workbook Pdf
Cambridge IGCSE® Physics Coursebook
Caucasian Chalk Circle Essay Questions
Chapter 1 Introduction to Physics
Chapter 1 Introduction to Physics Studies
Cie a Level Physics Notes 2016
Cie a Level Physics Notes Pdf
Cie Past Papers
Class 10 Physics Chapter 1 Mcqs
Class 8 Physics Notes KCSE-kcse
College Physics Notes
College Physics Practice Test
College Physics Quiz
College Physics Quiz Chapter 1
College Physics Quizlet
College Physics Study Guide
College Physics Study Guide Pdf
College Physics Test Questions and Answers
College Physics Volume 3 Pdf
College PhysicsNotes
Complete Physics for Cambridge IGCSE
Complete Physics for Cambridge IGCSE Revision Guide Pdf
County Mocks 2017
Cse Past Papers Physics 2017
Dl Physics Form 3 Pdf Kusoma
Download Physics Form 1
Download Physics Form 2
Download Physics Form 2 Notes
Download Physics Form 3
Download Physics Form 3 Notes
Download Physics Form 4
Download Physics Form Four
Download Physics Form One
Download Physics Form Three
Download Physics Form Two
Download Physics Notes Form 3
Download Physics Notes Form One
Download PhysicsNotes Form 3
Download Form Three Physics Notes
Download Free KCSE Past Papers Physics
Download Free KCSE Past Papers From KNEC.
Download KCSE Past Papers With Answers
Download KCSE Revision Notes
Download KLB Physics Book 2
Download KLB Physics Book 3
Download KLB Physics Book 4
Download Notes of Physics
Downloads | Physics | Form Four Exams | Exams
Downloads | Physics | Form One Exams | Exams
Downloads | Physics | Form Three Exams | Exams
Downloads | Physics | Form Two Exams | Exams
Downloads | KCSE Papers and Marking Schemes |
Dvance KCSE Past Papers
Easy Physics Questions
Edexcel a Level Physics B
Edexcel a Level Physics Notes Pdf
Edexcel a Level Physics Salters Nuffield
Edexcel A2 Physics Notes
Edexcel as Physics Revision Guide Pdf
Edexcel Physics A2 Revision Notes Pdf
Edexcel Physics Unit 2 Revision Notes
Edexcel GCSE Physics Revision Guide Pdf
Edexcel IGCSE Physics Past Papers
Edexcel IGCSE Physics Revision Guide Free Pdf Download
Edexcel IGCSE Physics Revision Guide Pdf
Edexcel IGCSE Physics Revision Guide Pdf Download
Electronics Form Four Notes
Energy Questions Physics Bowl
Essay Questions and Answers KCSE Physics Notes
Essay Questions and Answers on Betrayal in the City
Essay Questions Based on Betrayal in the City
Evolving World Physics Book 1 Pdf
Evolving World Physics Book 4 Notes
Evolving World Physics Book Form 1
Evolving World-history Book 3
Exam Notes for Physics 101
Exams KCSE Physics Paper 1 Questions and Answers
F3 Physics Test Paper
Find Download KCSE Past Papers With Answers
Find KCSE Physics Essay Questions and Answers
Form 1 Physics Exam
Form 1 Physics Notes
Form 1 Physics Questions and Answers
Form 1 Physics Questions and Answers Pdf
Form 1 Physics Revision Notes
Form 1 Physics Summurized Revision Pdf
Form 1 Physics Syllabus
Form 1 Physics Test Paper Pdf
Form 1 Physics Topics
Form 1 PhysicsNotes
Form 1 PhysicsQuestions and Answers
Form 1 PhysicsRevision Notes
Form 1 PhysicsSyllabus
Form 1 PhysicsTest Paper Pdf
Form 1 Past Papers
Form 1 Past Papers With Answers
Form 1 Revision Papers
Form 1 Subjects in Kenya
Form 2 Physics Exam
Form 2 Physics Exam Paper
Form 2 Physics Exam Paper 2016
Form 2 Physics Exam Paper Free Download
Form 2 Physics Exam Paper With Answer
Form 2 Physics Final Year Exam Paper 2
Form 2 Physics Notes
Form 2 Physics Notes and Revision Questions
Form 2 Physics Notes Pdf
Form 2 Physics Past Papers
Form 2 Physics Questions
Form 2 Physics Questions and Answers
Form 2 Physics Questions and Answers >
Form 2 Physics Questions and Answers Pdf
Form 2 Physics Revision Notes
Form 2 Physics Short Notes
Form 2 Physics Syllabus
Form 2 PhysicsExam Paper
Form 2 PhysicsExam Paper Free Download
Form 2 PhysicsExam Paper With Answer
Form 2 PhysicsFinal Year Exam Paper 2
Form 2 PhysicsPast Papers
Form 2 PhysicsRevision Notes
Form 2 PhysicsShort Notes
Form 2 PhysicsSyllabus
Form 2 Revision Papers
Form 2 Subjects in Kenya
Form 3 Physics Book
Form 3 Physics Exam
Form 3 Physics Exam Paper
Form 3 Physics Notes
Form 3 Physics Past Papers
Form 3 Physics Questions
Form 3 Physics Questions and Answers
Form 3 Physics Questions and Answers Pdf
Form 3 Physics Revision Notes
Form 3 Physics Syllabus
Form 3 PhysicsExam Paper
Form 3 PhysicsNotes
Form 3 PhysicsPast Papers
Form 3 PhysicsQuestions
Form 3 PhysicsQuestions and Answers Pdf
Form 3 PhysicsRevision Notes
Form 3 PhysicsSyllabus
Form 3 C.r.e
Form 3 Notes of Physics Topic on Fish
Form 3 Past Papers
Form 3 Revision Papers
Form 3 Subjects in Kenya
Form 4 Physics Exam
Form 4 Physics Notes
Form 4 Physics Notes Pdf
Form 4 Physics Questions and Answers
Form 4 Physics Questions and Answers Pdf
Form 4 Physics Revision Notes
Form 4 Physics Syllabus
Form 4 Physics Topics
Form 4 PhysicsNotes
Form 4 PhysicsRevision Notes
Form 4 PhysicsSyllabus
Form 4 PhysicsTopics
Form 4 Exam Papers
Form 4 Revision Papers
Form 4 Subjects in Kenya
Form 5 Physics Topics
Form 5 PhysicsTopics
Form Five Physics Notes
Form Five PhysicsNotes
Form Four Physics Book
Form Four Physics Notes
Form Four Physics Notes Pdf
Form Four Physics Questions and Answers
Form Four Physics Questions and Answers Pdf
Form Four Physics Revision Questions
Form Four Physics Syllabus
Form Four Physics Topics
Form Four PhysicsNotes
Form Four PhysicsQuestions and Answers
Form Four PhysicsQuestions and Answers Pdf
Form Four PhysicsTopics
Form Four Notes
Form Four Revision Papers
Form Four Subjects in Kenya
Form One Physics Book
Form One Physics Examination
Form One Physics First Topic
Form One Physics Lesson Plan
Form One Physics Notes Pdf
Form One Physics Past Papers Pdf
Form One Physics Questions
Form One Physics Questions and Answers
Form One Physics Questions and Answers Pdf
Form One Physics Revision Questions
Form One Physics Short Notes
Form One Physics Syllabus
Form One Physics Topics
Form One PhysicsExamination
Form One PhysicsPast Papers Pdf
Form One PhysicsQuestions and Answers
Form One PhysicsQuestions and Answers Pdf
Form One PhysicsTopics
Form One Exams
Form One Notes of Physics
Form One Past Papers
Form One Subjects in Kenya
Form One Term One Physics Exam
Form One Term One PhysicsExam
Form Three Physics Book
Form Three Physics Book Pdf
Form Three Physics Notes
Form Three Physics Notes Pdf
Form Three Physics Questions and Answers
Form Three Physics Questions and Answers Pdf
Form Three Physics Revision Questions
Form Three Physics Syllabus
Form Three Physics Topics
Form Three PhysicsNotes
Form Three PhysicsNotes Pdf
Form Three PhysicsQuestions and Answers
Form Three PhysicsQuestions and Answers Pdf
Form Three PhysicsTopics
Form Three Subjects in Kenya
Form Two Physics Book
Form Two Physics Cat
Form Two Physics Examination
Form Two Physics Notes
Form Two Physics Notes Pdf
Form Two Physics Past Papers
Form Two Physics Questions and Answers
Form Two Physics Questions and Answers Pdf
Form Two Physics Revision Questions
Form Two Physics Syllabus
Form Two Physics Topics
Form Two PhysicsNotes
Form Two PhysicsNotes Pdf
Form Two PhysicsQuestions and Answers
Form Two PhysicsQuestions and Answers Pdf
Form Two PhysicsSyllabus
Form Two PhysicsTopics
Form Two Notes
Form Two Subjects in Kenya
Free a-level Physics Revision App | Pass Your Physics Exams
Free Physics Form 1 Notes
Free Physics Notes Form 1
Free Physics Notes Pdf
Free PhysicsNotes Pdf
Free College Physics Practice Test
Free Form1,form2,form3 Past Papers Free KCSE Past Papers
Free KCSE Mocks 2015
Free KCSE Past Papers 2014
Free KCSE Past Papers KCSE Past
Free KCSE Past Papers Kenya,
Free KCSE Past Papers With Answers
Free KCSE Questions and Answers on Physics
Free KCSE Revision Notes
Free Marking Schemes
Free Mocks Online KCSE Answers Past Exams Question Papers
Free Revision Papers
From Three Notes Topic One KLB
Fun Physics Questions
Funny Physics Questions
Funny Physics Questions and Answers
Funny Physics Questions to Ask
Funny Physics Quotes
GCSE Physics Exam Questions and Answers
GCSE Physics Past Papers
GCSE Physics Revision
GCSE Physics Revision Notes
GCSE Physics Revision Notes Pdf
GCSE Physics Revision Notes Pdf 9-1
GCSE Physics Revision Questions and Answers
GCSE Physics Textbook Pdf
GCSE Physics Topics Pass My Exams: Easy Exam Revision Notes
Home Physics Notes Pdf
Home Physics Practice Test With Answers
Home Physics Quiz
Home Physics Quiz Pdf
Home Physics Test Questions and Answers
Home Physics Test Questions and Answers Pdf
Home Knowledge in Physics Human Body
Good Physics Questions to Ask
GRE Physics Practice Test
GRE Physics Subject Test Pdf
Handbook of Physics Pdf Free Download
Hard Physics Questions
Hard Physics Questions and Answers
Hard Physics Questions to Ask Your Teacher
Hard Physics Quiz Questions
Hard Form 3 Physics Question
High School Physics Final Exam Doc
High School Physics Final Exam Pdf
High School Physics Final Exam Questions
High School Physics Final Exam Questions and Answers
High School Physics Notes
High School Physics Practice Test
High School Physics Pretest With Answers
High School Physics Questions and Answers Pdf
High School Physics Study Guide
High School Physics Test Questions and Answers Pdf
High School PhysicsNotes
High School PhysicsStudy Guide
How to Answer KCSE Physics Question
How to Motivate a Form 4 Student
How to Motivate a KCSE Candidate
How to Motivate a KCSE Student
How to Pass Physics Questions & Answers Form 1&2 | Text Book
How to Revise Physics
How to Revise Effectively for KCSE
How to Study Physics: 5 Study Techniques to Master Physics
Hsc Physics 2018
Hsc Physics 2019
Https://www.knec.ac.ke/ Www.knec-portal.ac.ke/ KNEC Portal:
Ial Physics Notes
Ib Physics Cold War Notes
Ib Physics Notes
Ib Physics Notes Pdf
Ib Physics of the Americas Notes
Ib Physics of the Americas Study Guide
Ib Physics Paper 2 Study Guide
Ib Physics Question Bank by Topic
Ib Physics Study Guide Pdf
Ict Notes Form 1
IGCSE Physics Alternative to Practical Revision
IGCSE Physics Alternative to Practical Revision Notes
IGCSE Physics Book
IGCSE Physics Book Pdf Download
IGCSE Physics Notes
IGCSE Physics Notes 2017 Pdf
IGCSE Physics Notes Edexcel
IGCSE Physics Paper 2 Notes
IGCSE Physics Paper 6 Notes
IGCSE Physics Past Papers
IGCSE Physics Past Papers 2014
IGCSE Physics Past Papers 2017
IGCSE Physics Pdf
IGCSE Physics Pre Release Material 2018
IGCSE Physics Resources
IGCSE Physics Revision Guide
IGCSE Physics Revision Guide Free Download
IGCSE Physics Revision Guide Pdf Download
IGCSE Physics Revision Notes Pdf
IGCSE Physics Revision Worksheets
IGCSE Physics Workbook Pdf
IGCSE Physics Znotes
IGCSE PhysicsPast Papers
IGCSE Notes Physics
Importance of Agroforestry
Inorganic Physics Multiple Choice Questions With Answers Pdf
Inorganic Physics Questions and Answers Pdf
Interesting Physics Questions
Interesting Physics Questions and Answers
Interesting Questions to Ask About Physics
Intro to Physics Quiz
Introduction of Physics Form One
Introduction to Physics
Introduction to Physics Notes
Introduction to Physics Pdf
Introduction to PhysicsNotes
Is Agroforestry Sustainable?
K.c.s.e Answers Physics Paper One 2018
K.c.s.e Physics 2017
K.c.s.e Physics 2018
K.c.s.e Physics Paper 1 2017
K.c.s.e Mocks 2018
K.c.s.e Papers 2015
K.c.s.e Papers 2016
K.c.s.e Past Papers 2014
K.c.s.e.Physics Paper 2 Year 2018
K.c.s.e.results 2018 for Busia County
K.l.b Physics Form 3
K.l.b Physics Notes
K.l.b PhysicsNotes
Kasneb Past Papers for Colleges Physics Past Papers
KCSE 2010 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2010 Past Papers
KCSE 2011 Physics Paper 1
KCSE 2011 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2012 Physics Paper 2 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2012 Marking Schemes
KCSE 2013 Physics Paper 1
KCSE 2013 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2013 Marking Scheme Pdf
KCSE 2014
KCSE 2015 Physics Paper 2
KCSE 2015 Physics Paper 3
KCSE 2015 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2015 Past Papers
KCSE 2016 Physics Paper 1
KCSE 2016 Physics Paper 2
KCSE 2017 Physics Paper 1
KCSE 2017 Physics Paper 2
KCSE 2017 Hostory Papers With Answers.com
KCSE 2017 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2017 Papers
KCSE 2017 Papers and Marking Scheme
KCSE 2017 Papers Pdf
KCSE 2017 Past Papers
KCSE 2017 Prediction Pdf
KCSE 2018 Physics and Answers
KCSE 2018 Physics Prediction
KCSE 2018 Leakage
KCSE 2018 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2018 Papers
KCSE 2018 Prediction Pdf
KCSE 2018 Predictions
KCSE 2018 Questions
KCSE 2018 Questions and Answers
KCSE 2019 Leakage Physics
KCSE 2019 Marking Scheme
KCSE 2019 Questions
KCSE 2019 Questions and Answers
KCSE 2020 Questions
KCSE 2020 Questions and Answers
KCSE Answers
KCSE Answers Past Exams Question Papers Downloads |
KCSE Physics 2011
KCSE Physics 2016
KCSE Physics Diagramsbiology Revision Tips
KCSE Physics Essay Questions and Answers
KCSE Physics Essay Questions and Answers Pdf
KCSE Physics Essays
KCSE Physics Essays Pdf
KCSE Physics Marking Schemes
KCSE Physics Notes
KCSE Physics Notes Pdf
KCSE Physics Notes, Syllabus, Questions, Answers
KCSE Physics Paper 1
KCSE Physics Paper 1 2011
KCSE Physics Paper 1 2012
KCSE Physics Paper 1 2013
KCSE Physics Paper 1 2015
KCSE Physics Paper 1 2016
KCSE Physics Paper 1 2017
KCSE Physics Paper 1 2017 Pdf
KCSE Physics Paper 1 Questions and Answers
KCSE Physics Paper 2
KCSE Physics Paper 2 2012
KCSE Physics Paper 2 2012 KCSE Physics Paper 2 2015
KCSE Physics Paper 2 2013
KCSE Physics Paper 2 2014
KCSE Physics Paper 2 2015
KCSE Physics Paper 2 2016
KCSE Physics Paper 2 2017
KCSE Physics Paper 3
KCSE Physics Paper 3 2012
KCSE Physics Paper 3 2016
KCSE Physics Paper 3 2017
KCSE Physics Paper 3 Past Papers
KCSE Physics Past Papers
KCSE Physics Past Papers and Answers
KCSE Physics Past Papers Pdf
KCSE Physics Practical
KCSE Physics Practical 2015
KCSE Physics Practical 2016
KCSE Physics Practical Past Papers
KCSE Physics Practicals
KCSE Physics Practicals KCSE Physics Paper 1
KCSE Physics Question and Answer
KCSE Physics Questions and Answers
KCSE Physics Questions and Answers Ap Physics
KCSE Physics Revision
KCSE Physics Revision Notes
KCSE Physics Revision Papers
KCSE Physics Revision Questions
KCSE Physics Revision Questions and Answers
KCSE Physics Syllabus
KCSE PhysicsNotes
KCSE PhysicsPaper 1
KCSE PhysicsPaper 2
KCSE PhysicsPaper 2 Pdf
KCSE PhysicsSyllabus
KCSE Business Paper 1 2016
KCSE Business Past Papers
KCSE Physics Past Papers
KCSE Essay Questions in Betrayal in the City
KCSE Essays
KCSE Exam Papers 2018
KCSE Exam Papers Answers
KCSE Form 1 Physics Revision
KCSE Form 2 Physics Revision
KCSE Form 3 Physics Revision
KCSE Form 4 Physics Revision
KCSE Form Four Physics Revision
KCSE Form One Physics Revision
KCSE Form Three Physics Revision
KCSE Form Two Physics Revision
KCSE KCSE Past Papers KNEC
KCSE Leakage
KCSE Leakage Physics
KCSE Made Familiar Physics
KCSE Made Familiar Physics Pdf
KCSE Marking Scheme 2016
KCSE Marking Schemes
KCSE Marking Schemes 2017
KCSE Marking Schemes Pdf
KCSE Mock Exams
KCSE Mock Papers 2015
KCSE Mock Papers 2017
KCSE Mock Papers 2018
KCSE Mock Papers Pdf
KCSE Mock Papers Pdf 2018
KCSE Mock Papers Pdf KCSE Past Papers
KCSE Mocks 2017
KCSE Mocks 2018
KCSE Notes
KCSE Online Notes
KCSE Online Past Papers
KCSE Online Registration
KCSE Papers 2015
KCSE Papers and Marking Schemes | Exams
KCSE Past Papers
KCSE Past Papers 2007
KCSE Past Papers 2009
KCSE Past Papers 2010
KCSE Past Papers 2011
KCSE Past Papers 2011 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2012
KCSE Past Papers 2013
KCSE Past Papers 2013knec
KCSE Past Papers 2014
KCSE Past Papers 2014 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2015
KCSE Past Papers 2015 Marking Schemes
KCSE Past Papers 2015 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2016
KCSE Past Papers 2016 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2017
KCSE Past Papers 2017 Pdf
KCSE Past Papers 2018
KCSE Past Papers Physics
KCSE Past Papers Physics and Answers
KCSE Past Papers Physics Pdf
KCSE Past Papers Physics With Answers
KCSE Past Papers Physicsand Answers
KCSE Past Papers Physics and Answers
KCSE Past Papers KCSE and Answers
KCSE Past Papers KCSE and Answers Free Mocks Online
KCSE Past Papers Marking Scheme
KCSE Past Papers Pdf Download
KCSE Past Papers Pdf Download KCSE 2013
KCSE Past Papers With Answers
KCSE Past Papers Woodwork and Answers
KCSE Prediction 2017
KCSE Prediction 2018
KCSE Prediction 2018 Pdf
KCSE Prediction Papers 2018
KCSE Prediction Questions
KCSE Prediction Questions 2018
KCSE Prediction Questions and Answers
KCSE Questions
KCSE Questions and Answers
KCSE Questions and Answers.
KCSE Questions on Physics
KCSE Results, Online Registration, KCSE Result Slip.
KCSE Revision
KCSE Revision Notes
KCSE Revision Notes Physics
KCSE Revision Notes Pdf
KCSE Revision Papers
KCSE Revision Papers 2014
KCSE Revision Papers With Answers
KCSE Revision Question for Physics
KCSE Revision Questions
KCSE Revision Questions and Answers
KCSE Revision | Secondary School | Text Books | Text Book Centre
KCSE Syllabus Pdf
KCSE Trial 2017
KCSE Trial Exams 2017
Kenya Secondary School Physics Syllabus
Kenya Secondary School Physics Syllabus Pdf
Kenya Secondary School PhysicsSyllabus Pdf
Kenya Secondary School Syllabus Pdf
Kenya-kcse-christian Religious Education Syllabus
Kenyaplex KCSE Past Papers
Kenyaplex Past Papers for Secondary
KLB Physics Book 1 Download
KLB Physics Book 1 Notes
KLB Physics Book 1 Pdf
KLB Physics Book 2
KLB Physics Book 2 Notes
KLB Physics Book 2 Notes Pdf
KLB Physics Book 2 Pdf
KLB Physics Book 3 Notes
KLB Physics Book 3 Pdf
KLB Physics Book 3 Pdf Download
KLB Physics Book 4 Notes
KLB Physics Book 4 Pdf
KLB Physics Book 4 Pdf Download
KLB Physics Book 4 Topics
KLB Physics Book One
KLB Physics Form 1
KLB Physics Form 1 Notes
KLB Physics Form 1 Pdf
KLB Physics Form 2
KLB Physics Form 2 Book
KLB Physics Form 2 Notes
KLB Physics Form 2 Pdf
KLB Physics Form 2 Pdf Download
KLB Physics Form 2 Schemes of Work
KLB Physics Form 3
KLB Physics Form 3 Notes
KLB Physics Form 3 Notes Pdf
KLB Physics Form 3 Pdf
KLB Physics Form 3 Pdf Download
KLB Physics Form 4
KLB Physics Form 4 Notes
KLB Physics Form 4 Pdf
KLB Physics Form Four
KLB Physics Form Four Notes
KLB Physics Form One
KLB Physics Form One Notes
KLB Physics Form Three
KLB Physics Form Three Notes
KLB Physics Form Two
KLB Physics Form Two Notes
KLB Physics Notes
KLB Physics Notes Form 4
KLB Physics Pdf
KLB PhysicsNotes
KLB PhysicsNotes Form 4
KLB PhysicsPdf
KNEC Physics Syllabus
KNEC Examiners Portal KNEC Website
KNEC Ict Past Papers
KNEC Past Papers for Colleges
KNEC Past Papers Free Download
KNEC Past Papers Free Downloads
KNEC Past Papers Pdf
KNEC Portal Confirmation
KNEC Portal KCSE Results
KNEC Portal KNEC Past Papers for Colleges Kasneb Past Papers
KNEC Revision Papers
KNEC Technical Exams Past Papers
Kusoma Physics Notes
Kusoma Physics Notes Pdf
Kusoma Notes Physics
Kusoma.co.ke
Kusoma.com Past Papers
Learner Guide for Cambridge IGCSE Physics
Longhorn Physics Book 3 Pdf
Made Familiar Physics
Made Familiar Physics Pdf
Made Familiar Physics Questions
Maktaba Tetea Notes
Marking Scheme KCSE Physics Past Papers
Math Form2 Note
Mcqs About Gaseous Exchange
Middle School Physics Bowl Physics Questions
Mock Past Papers 2017
Mock Past Papers With Answers
Mokasa Mock 2017
More Than 1800 Physics Questions and Answers to Help You Study
Multiple Choice Questions on Physics
Necta Physics Past Papers
Necta Physics Practicals
Necta PhysicsPast Papers
Necta PhysicsPracticals
Necta Form Four Past Papers
Necta Past Papers Form 4
Necta Past Papers Form 4 2016
Necta Past Papers Form Six
Necta Past Papers Form Two
Necta Questions and Answers
Necta Review Questions
Notes Physics Form 1
Notes Physics Form 2
Notes Physics Form 3
Notes Physics Form 3 Notes Pdf
Notes Physics Form 3 Syllabus
Notes Physics Form 4 Syllabus
Notes on Physics Studies
Notes Za Physics 4m 2
Notes Za Physics Form One
Notes Za Physics Form Three
O Level Physics Practical Experiments
O Level Physics Questions and Answers Pdf
Orm Three Physics Notes
Page Navigation
Papacambridge Physics IGCSE
Papers KNEC KCSE Online Past
Papers KNEC KCSE Results Past Papers
Past KCSE Papers
Past Paper Questions by Topic Physics
Past Papers 2014
Past Papers in Kenya
Pdf Physics Form 3
Pdf Physics Notes
Pdf Physics Notes Form 1
Pdf Physics Notes Form 2
Pdf Physics Notes Form 3
Pdf Physics Notes Form 4
Pdf Physics Notes Form Four
Pdf Physics Notes Form One
Pdf Physics Notes Form Three
Pdf Physics Notes Form Two
Pdf Form 1 Physics Questions and Answers
Pdf Form 2 Physics Questions and Answers
Pdf Form 3 Physics Questions and Answers
Pdf Form 4 Physics Questions and Answers
Pdf Form Four Physics Questions and Answers
Pdf Form One Physics Questions and Answers
Pdf Form Three Physics Questions and Answers
Pdf Form Two Physics Questions and Answers
Pdf Free KCSE Past Papers and Marking Schemes
Pdf” Revision Questions Physics Form 1
Practical Physics Experiments Pdf
Practical Physics Question and Answer Pdf
Pre Mocks 2018
Preliminary Physics
Primary and Secondary Tillage Implements Ppt
Pte KNEC Past Papers
Questions and Answers Pdf Physics Form 1
Questions and Answers Pdf Physics Form 2
Questions and Answers Pdf Physics Form 3
Questions and Answers Pdf Physics Form 4
Questions and Answers Pdf Physics Form Four
Questions and Answers Pdf Physics Form One
Questions and Answers Pdf Physics Form Three
Questions and Answers Pdf Physics Form Two
Questions Based to Introduction to Physics
Questions on Gaseous Exchange in Humans
Questions on Introduction to Physics
Questions to Ask in Physics Class
Questions to Confuse Your Physics Teacher
Quizlet Physics Test
Quizlet Test Questions
Qustions in Physics and Answers
Revision
Revision Physics Notes and Questions?
Revision Quiz for Physics for Form Three
S.1 Physics Questions
S.2 Physics Questions
S.3 Physics Questions
S.4 Physics Questions
Sample Essays on Betrayal in the City
School Physics Notes
Secondary Physics Notes
Secondary Physics Notes Pdf
Secondary PhysicsNotes Pdf
Senior 1 Physics Notes
Senior 2 Physics Notes
Senior 3 Physics Notes
Senior 4 Physics Notes
Senior 5 Physics Notes
Senior 6 Physics Notes
Senior Five Physics Notes
Senior Four Physics Notes
Senior One Physics Notes
Senior Six Physics Notes
Senior Three Physics Notes
Senior Two Physics Notes
Simple Scientific Questions
Smart Questions to Ask a Physics Teacher
Snab Physics Revision Notes
Southwest Mock Paper 2 2016 Physics Only
Spm Physics Revision Notes
Spm Notes
Success Physics Spm Pdf
Success PhysicsSpm Pdf
Summary of Physics Form 3
Tahossa Past Papers
To Motivate a Form 4 KCSE Student
To Motivate a Form 4 Student
Topical Revision Material
Tricky Physics Questions and Answers
Tricky Physics Questions for Adults
Tricky Physics Questions With Answers
Tricky Physics Quiz Questions
Two Physics Revision Questions
University Physics Volume 3 Openstax
University Physics Volume 3 Pdf
University Physics Volume 4 Pdf
Ur Revision Guide IGCSE Physics
What Are the Types of Gametes
Working of Excretory System
Www.Physics Form One Notes.com
Www.Physics From One KLB.com
Www.form 1 Physics.com
Www.form 2 Physics.com
Www.form 3 Physics.com
Www.form 4 Physics.com
Www.form Four Physics.com
Www.form One Physics.com
Www.form Three Physics.com
Www.form Two Physics.com
Www.kusoma Notes
Www.kusoma Revision Materials
Www.kusoma.co.ke Physics Notes
Xtremepapers IGCSE Physics
Year 11 Physics
Z Notes Physics IGCSE
Znotes as Physics
[ad_2]
Source link
Comments
The Kenyan Digest Team

You may like
Rayvanny officially leaves Diamond’s WCB Wasafi after 6 years
Raila Odinga is the most popular presidential candidate, a survey released by Infotrak
Newly-crowned Kenyan Wimbledon champion Angella Okutoyi would like to play against American star Serena Williams

The Mombasa High Court has ordered IEBC to clear Sonko to run for the Mombasa governorship.

A new born baby was pulled out of latrine in Mururi.

Kenyan Rapper Colonel Mustafa has leveled fresh accusations against his ex-girlfriend Katoto.

Okutoyi and Nijkamp qualify for Wimbledon Open final
Fans will have to brace themselves for a sober 90 minutes, the Gulf Arab state announces.
