The full-scale invasion of the Russian Federation into Ukraine that happened in 2022 became the next step of the conflict that started in 2014 and caused the most acute international security and humanitarian crisis since World War II.
The consequences of the war go way beyond the battlefield, and the geopolitical alliances and the global economy have been redefined.
This article presents an in-depth discussion of the historical background of the conflict, the military events, the humanitarian cost, and the international implications of the war.
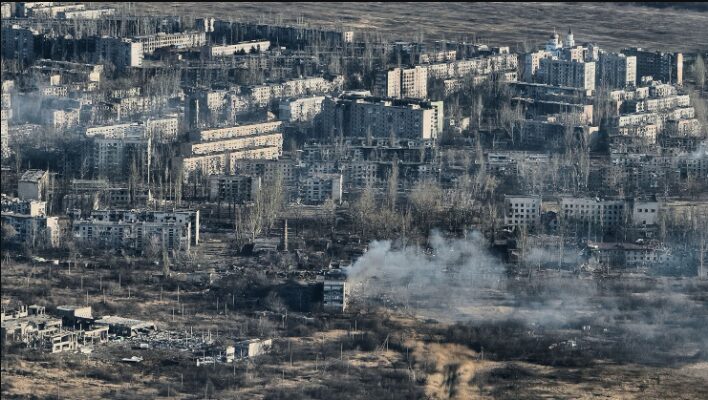

The 2022 Russian invasion marked the largest conflict in Europe since World War II. (Source: Getty images)
Historical Context of the Conflict
The origins of the existing war are also multifaceted and date back to the invasion of 2022.
After Ukraine gained its independence in the year 1991, the relations with Russia were strained, especially when it came to the geopolitical orientation of Ukraine.
Another crucial event occurred in 2014 with the Revolution of Dignity that toppled the pro-Russian president of Ukraine.
To counter this, the Russian Federation annexed the Crimean Peninsula and sparked a separatist war in Ukraine in the eastern Donbas.
The decade-long period of low-intensity warfare that preceded it preconditioned the full-scale invasion, which Russia framed as a special military operation.
Among the main proclaimed goals was the so-called demilitarization and denazification of Ukraine and the elimination of the risk of its possible entry into the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), which is perceived by Russia as an open threat to its security interests.
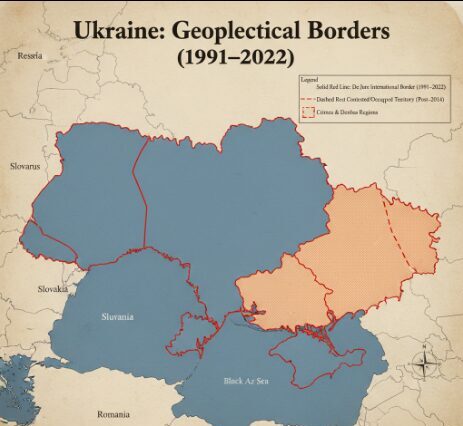
The conflict’s roots trace back to the 2014 annexation of Crimea and the ongoing Donbas unrest.(Source: Kenyan Digest)
Military Developments and the State of the War
The war has taken a number of different forms. First Russian efforts to take Kyiv were unsuccessful, as Ukrainian troops managed to repel the invasion and change the direction of the actions.
The war thereafter began to be concentrated in the east and south of Ukraine, becoming a violent war of attrition, with excessive artillery battles, trench warfare, and heavy usage of drones.
The two sides have fought to control critical territories in major cities such as Mariupol, Bakhmut, and Avdiivka.
The balance on the frontline keeps on changing with the constant stream of Western military assistance to Ukraine and the capacity of Russia to keep its war going despite global sanctions.

The war evolved into a grinding conflict of attrition marked by drone and artillery warfare. (Source: Getty images)
The Humanitarian Crisis
The human cost of the conflict has been staggering. The war has resulted in tens of thousands of civilian casualties and triggered the largest refugee crisis in Europe since the 1940s.
According to the United Nations, millions of Ukrainians have been forced to flee their homes, becoming either internally displaced persons or refugees in neighboring countries and beyond.
Furthermore, systematic attacks on civilian infrastructure, including hospitals, schools, and energy facilities, have created dire living conditions for millions who remain in Ukraine, severely limiting access to electricity, water, and essential services.

Millions of Ukrainians fled their homes, creating Europe’s largest refugee crisis since the 1940s (Source: Kenyan Digest)
Global Economic Consequences
This global economy has been experiencing a great shockwave as a result of the war.
To react to the invasion, the Western countries sanctioned Russia as never before, including financial, energy, and defense resources to paralyze its capacity to fund the war.
All of these steps, along with the interference with trade, have had ripple effects.
Energy prices skyrocketed in the world owing to the fact that Russia is one of the biggest exporters of oil and gas.
The war also disturbed agricultural exports in Ukraine, the so-called breadbasket of Europe, which worsened the issue of world food security and led to inflation in the global market.
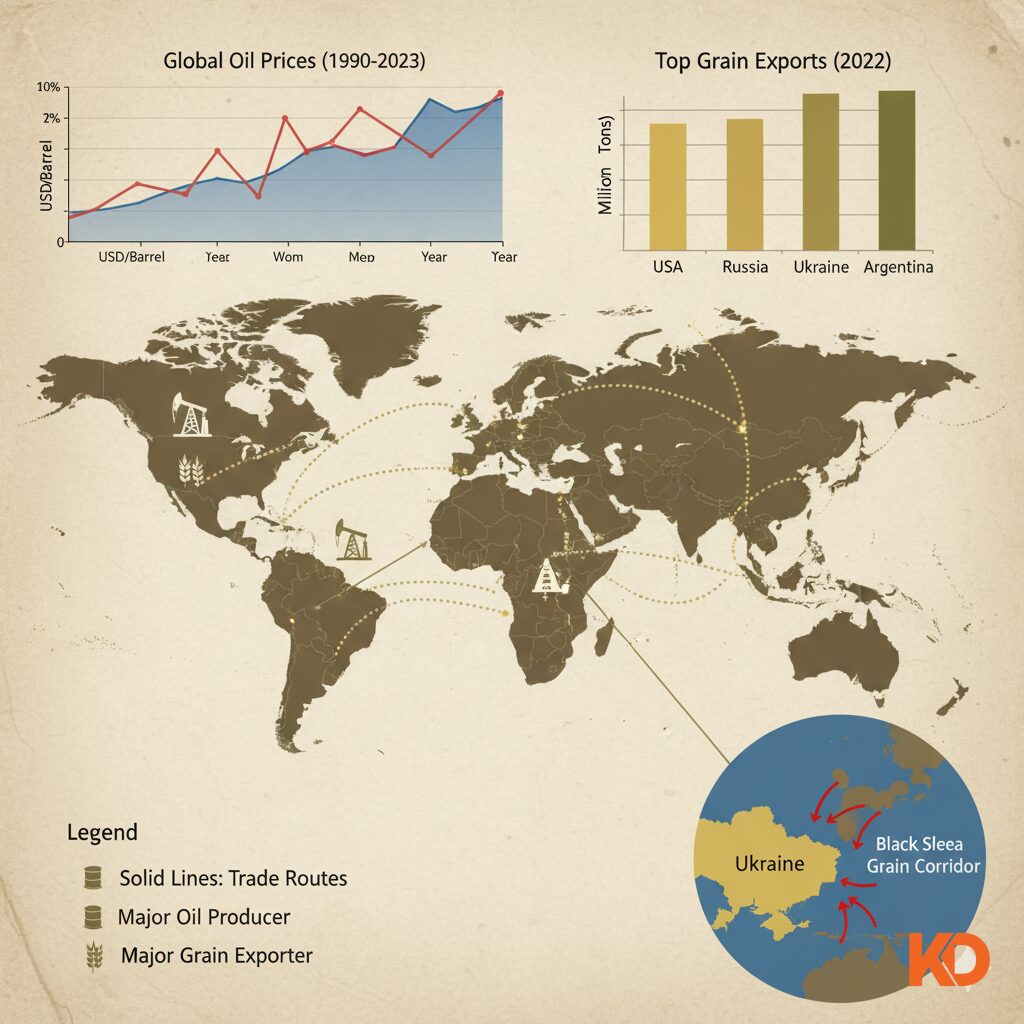
The war disrupted energy and food supplies worldwide, fueling inflation and market instability. (Source: Kenyan Digest)
The International Response and Geopolitical Shifts
The invasion brought together Western countries in their support of Ukraine.
NATO and the European Union have been exceptionally cohesive by offering tremendous financial, humanitarian, and military aid to Kyiv.
It is also due to the conflict that historically neutral states such as Finland and Sweden decided to apply for NATO membership, which has significantly changed the security structure in Europe.
The war has diplomatically alienated Russia in the international arena, which has seen it being suspended from several international organizations.
The reaction of other world powers has been more diverse, though, and it has reflected complicated geopolitical affiliations and divergent national interests.

The war unified Western allies and prompted historic security realignments in Europe. (Source: Getty images)
Prospects for Resolution
The way to a peaceful resolution of the conflict is yet to be obvious, as the conflict persists.
The diplomatic talks have been stalemated, with Ukraine and Russia insisting on what the other considers unacceptable.
Ukraine wants to have its territorial integrity restored in the 1991 boundaries, and Russia wants to be recognized as the possessor of its annexed regions.
There are still ongoing diplomatic talks by the international community to achieve peace, which will be long-lasting and fair, but it will require immense shifts in the strategic calculations of both sides of the war.
Read More: Global South Rising: Africa, Asia, and Latin America Demand a Louder Voice in World Governance

 General News7 days ago
General News7 days ago
 General News3 days ago
General News3 days ago
 Politics3 days ago
Politics3 days ago
 General News1 day ago
General News1 day ago











